Abstract
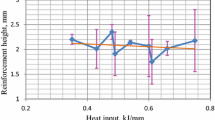
Weld bead geometry influences mechanical properties, microstructure of the weld joint or weld overlay. It is much biased by heat input of a particular welding technique. In current work, weld bead of 316 austenitic stainless steel is produced on E250 low alloy steel by gas metal arc welding process using 100% carbon dioxide as shielding gas. Nine sets of welding current and welding voltage combinations were chosen for producing nine weld beads, keeping travel speed constant throughout the experiment. Two identical set of experiments were repeated. Experimental results depicted that the width of weld bead, PSF, RFF extended with increment in heat input, while height of reinforcement and depth of penetration declined slightly for the identical condition. Quadratic equations are generated successfully between different bead geometry parameters and heat input by means of polynomial regression analysis which agree with the real data.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Saha, M.K., Das S.: A Review on different cladding techniques employed to resist corrosion. J. Assoc. Eng. India 56(1&2) (2016)
Saha, M.K., Das, S.: Gas metal arc welding and its anti-corrosive performance—a brief review. Athens J. Techno. Engg. 5(2), 154–174 (2018)
Nasir, N.S.M., Razab, M.K.A.A., Ahmad, M.I., Mamat, S.: Influence of heat input on carbon steel microstructure. ARPN J. Eng. Appl. Sci. 12(8), 2689–2697 (2017)
Shen, S., Oguocha, I.N.A., Yannacopoulos, S.: Effect of heat input on weld bead geometry of submerged arc welded ASTM A709 Grade 50 steel joints. J. Mater. Proc. Techno. 212(1), 286–294 (2012)
Frei, J., Alexandrov, B.T., Rethmeier, M.: Low heat input gas metal arc welding for dissimilar metal weld overlays part II: the transition zone. Weld. World 62(2), 317–324 (2018)
Frei, J., Alexandrov, B.T., Rethmeier, M.: Low heat input gas metal arc welding for dissimilar metal weld overlays part I: the heat-affected zone. Weld. World. 60(3), 459–473 (2016)
Kah, P., Mvola, B., Suoranta, R., Martikainen, J.: Modified GMAW processes: control of heat input. J. Comput. Theor. Nanosci. 19(3), 710–718 (2013)
Sreeraj, P., Kannan, T., Maji, S.: Simulation and parameter optimization of GMAW process using neural networks and particle swarm optimization algorithm. Int. J. Mech. Eng. Robot. Res. 2, 130–146 (2013)
Palani, P.K., Murugan, N.: Development of mathematical models for prediction of weld bead geometry in cladding by flux cored arc welding. Int J. Adv. Manu. Tech. 30, 669–676 (2006)
Campbell, S., Galloway, A., McPherson, N.: Artificial neural network prediction of weld geometry performed using GMAW with alternating shielding gases. Weld. J. 91(6), 174S–181S (2012)
Nagesh, D.S., Datta, G.L.: Genetic Algorithm for optimization of welding variables for height to width ratio and application of ANN for Prediction of bead geometry for TIG welding process. Appl. Soft Com. 10, 897–907 (2010)
Sreeraj, P., Kannan, T.: Modelling and prediction of stainless steel clad bead geometry deposited by GMAW using regression and artificial neural network models. Adv. Mech. Eng. 2012, 1–12 (2012)
Mondal, A., Saha, M.K., Hazra, R., Das, S.: Influence of heat input on weld bead geometry using duplex stainless steel wire electrode on low alloy steel specimens. Cogent. Eng. 3, 1143598 (2016)
Kannan, T., Yoganandh, J.: Effect of process parameters on clad bead geometry and its shape relationships of stainless steel claddings deposited by GMAW. Int. J. Adv. Manu. Tech. 47, 1083–1095 (2010)
Kolahan, F., Heidari, M.: Modeling and optimization of MAG welding for gas pipelines using regression analysis and simulated annealing algorithm. J. Sci. Ind. Res. 69(4), 177–183 (2010)
Saha, M.K., Dhara, L.N., Das, S.: Varıation of Bead Geometry of 316 Austenitic Stainless Steel Weld with Varying Heat Input Using Metal Active Gas Welding. In: National Conference on Leveraging Simulation & Optimisation Techniques for Productivity Enhancement and Manufacturing Excellence, at SNTI, Jamshedpur, Jharkhand, India (2018)
Saha, M.K., Hazra, R., Mondal, A., Das, S.: Effect of heat input on geometry of austenite stainless steel weld bead on low alloy steel. J. Inst. Eng. (India): Ser C. (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40032-018-0461-7
Sharma, A., Verma, D.K., Arora, N.: A scheme of comprehensive assessment of weld bead geometry. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Techno. 82(9–12), 1507–1515 (2016)
Senthilkumar, B., Kannan, T., Madesh, R.: Optimization of flux-cored arc welding process parameters by using genetic algorithm. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Tech. 93(1–4), 35–41 (2017)
Sreeraj, P., Kannan, T., Maji, S.: Optimization of process parameters of stainless steel clad bead geometry deposited by GMAW using integrated SA-GA. Int. J. Res. Aeronaut. Mech. Eng. 1(1), 26–52 (2013)
Rodrigues, L.O., Paiva, A.P., Costa, S.C.: Optimization of the FCAW process by weld bead geometry analysis. Weld. Int. 23(2), 261–269 (2009)
Gautam, U., Vipin.: Weld bead geometry prediction model by design of experiments for mild steel. Int. J. Mech. Eng. Rob. Res. 3(3), 517–527 (2014)
Soares, L.B., Weis, A.A., Rodrigues, R.N., Drews, P. Jr., Guterres, B., Botelho, S.S.C., Filho, N.D.: Seam Tracking and Welding Bead Geometry Analysis for Autonomous Welding Robot. In: Proceedings of Conference IEEE Latin American Robotics Symposium, at Curitiba, Brazil (2017)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2020 Springer Nature Singapore Pte Ltd.
About this paper
Cite this paper
Saha, M.K., Sadhu, S., Ghosh, P., Mondal, A., Hazra, R., Das, S. (2020). Dependency of Bead Geometry Formation During Weld Deposition of 316 Stainless Steel Over Constructional Steel Plate. In: Venkata Rao, R., Taler, J. (eds) Advanced Engineering Optimization Through Intelligent Techniques. Advances in Intelligent Systems and Computing, vol 949. Springer, Singapore. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-13-8196-6_37
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-13-8196-6_37
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Singapore
Print ISBN: 978-981-13-8195-9
Online ISBN: 978-981-13-8196-6
eBook Packages: Intelligent Technologies and RoboticsIntelligent Technologies and Robotics (R0)