Abstract
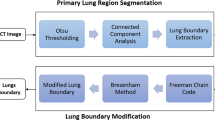
Advances in the fields of image processing and information technology have led to the use of computers for the diagnosis of diseases. This has led to the emergence of Computer-Aided Diagnosis (CAD) systems for disease diagnosis. This research work focuses on improving the performance of CAD systems that use Computed Tomography (CT) of the chest for diagnosis of lung disorders. This improvement has been achieved by developing techniques for determining the significance of image features for discrimination among different diseases of the lung and a technique for segmentation of lung parenchyma in chest CT irrespective of the presence or absence of peripherally placed Pathology Bearing Regions (PBRs). Another major challenge in CAD of lung disorders based on analysis of chest CTs is accurate segmentation of lungs especially in the presence of peripherally placed PBRs. In this research work, a segmentation algorithm has been developed to extract the complete lung parenchyma even in the presence of severe peripherally placed PBR in chest CT. The proposed system has been found to improve the diagnostic performance of CAD systems for diagnosis of lung disorders based on analysis of chest CT slices. This would aid the physicians to perform better diagnosis, which would result in choosing the appropriate treatment strategy, thereby reducing the mortality rate.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
https://www.emeraldinsight.com/doi/abs/10.1108/09504120710719671
Murin S, Bilello KS (2005) Respiratory tract infections. Clevel Clin J Med 72(10):916–920
Panda BN (2004) Fungal infections of lungs: the emerging scenario. Indian J Tuberculosis 51:63–69
Machado RD, Eickelberg O, Elliott CG, Geraci MW, Hanaoka M, Loyd JE, Newman JH, Phillips III JA, Soubrier F, Trembath RC, Chung WK (2009) Genetics and genomics of pulmonary arterial hypertension. J Am College Cardiol 54(1), Supplement:S32–S42
Kraft M (2011) Approach to the patient with respiratory disease. In: Goldman L, Schafer AI (eds) Cecil medicine, 24th edn, Chap 83. Saunders Elsevier, Philadelphia, PA
Stark P (2011) Imaging of the lungs, mediastinum, and chest wall. In: Goldman L, Schafer AI (eds) Cecil medicine, 24th edn, Chap 84. Saunders Elsevier, Philadelphia, PA
Welte T (2014) Imaging in the diagnosis of lung disease: more sophisticate methods require greater interdisciplinary collaboration. Deutsches Arzteblatt Int 111(11):170–180
Bunyaviroch T, Coleman RE (2006) PET evaluation of lung cancer. J Nuclear Med 47(3):451–469
Kaarteenaho R (2013) The current position of surgical lung biopsy in the diagnosis of idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Respir Res 14:43
Desikan P (2013) Sputum smear microscopy in tuberculosis: is it still relevant? Indian J Med Res 137(3):442–444
Shafiyabi S, Ravikumar R, Krishna Ramaprasad S (2013) Study of same day sputum smear examination in diagnosis of pulmonary tuberculosis under RNTCP. Sch Acad J Biosci 1(7):352–356
Fujita H, Uchiyama Y, Nakagawa T, Fukuoka D, Hatanaka Y, Hara T, Lee GN, Hayashi Y, Ikedo Y, Gao X, Zhou X (2008) Computer-aided diagnosis: the emerging of three CAD systems induced by Japanese health care needs. Comput Methods Programs Biomed 92:238–248
Way TW, Hadjiiski LM, Sahiner B, Chan HP, Cascade PN, Kazerooni EA, Bogot N, Zhou C (2006) Computer-aided diagnosis of pulmonary nodules on CT scans: segmentation and classification using 3D active contours. Med Phys 33(7):2237–2323
Balaji GN, Subashini TS, Chidambaram N (2016) Detection and diagnosis of dilated cardiomyopathy and hypertrophic cardiomyopathy using image processing techniques. Eng Sci Technol Int J 19(4):1871–1880
Depeursinge A, Iavindrasana J, Cohen G (2008) Lung tissue classification in HRCT data integrating the clinical context. In: Proceedings of the twenty-first IEEE international symposium on computer-based medical systems, pp 542–547
Hu S, Hoffman EA, Reinhardt JMM (2001) Automatic lung segmentation for accurate quantitation of volumetric x-ray CT images. IEEE Trans Med Imaging 20(6):490–498
Elizabeth DS, Kannan A, Nehemiah HK (2009) Computer aided diagnosis system for the detection of bronchiectasis in chest computed tomography images. Int J Imaging Syst Technol 19(4):290–298
Balaji GN, Subashini TS (2013) Detection of cardiac abnormality from measures calculated from segmented left ventricle in ultrasound videos. In: Mining intelligence and knowledge exploration. Springer, Cham, pp 251–259
Sluimer I, Prokop M, Ginneken BV (2005) Toward automated segmentation of the pathological lung in CT. IEEE Trans Med Imaging 24(8):1025–1038
Lai J, Ye M (2009) Active contour based lung field segmentation. In: Proceedings of the international conference on intelligent human machine systems and cybernetics, pp 288–291
Darmanayagam SE, Harichandran KN, Cyril SRR, Arputharaj K (2013) A novel supervised approach for segmentation of lung parenchyma from chest CT for computer-aided diagnosis. J Digit Imaging 26(3):496–509
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2019 Springer Nature Singapore Pte Ltd.
About this paper
Cite this paper
Balaji, G.N., Subramanian, P. (2019). Computer-Aided Lung Parenchyma Segmentation Using Supervised Learning. In: Saini, H., Sayal, R., Govardhan, A., Buyya, R. (eds) Innovations in Computer Science and Engineering. Lecture Notes in Networks and Systems, vol 74. Springer, Singapore. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-13-7082-3_46
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-13-7082-3_46
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Singapore
Print ISBN: 978-981-13-7081-6
Online ISBN: 978-981-13-7082-3
eBook Packages: EngineeringEngineering (R0)