Abstract
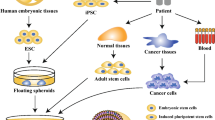
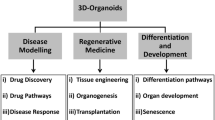
Historical developmental biology experiments demonstrated the remarkable capacity of reaggregated vertebrate cells for self-organization, now exploited to rebuild human tissues, reminiscent of native organs, from somatic or pluripotent stem cells, namely, an organoid. Organoid technology is thus rapidly evolving and becoming an independent research field due to its potential for modelling human development and disease. Coupled with patient-derived stem cells, diseased organoid recapitulates a pathological state in a dish, promoting personalized medicine and drug development. Ultimately, organoid transplantation paves a way for organ replacement strategies against end-stage diseases. This article summarizes the evolutionary organoid technology backed by developmental biology and outlines its phenomenal potential for future therapeutic applications.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Wilson HV. A new method by which sponges may be artificially reared. Science. 1907;25:912–5.
Martz E, Phillips HM, Steinberg MS. Contact inhibitions of overlapping and differential cell adhesion: a sufficient model for the control of certain cell culture morphologies. J Cell Sci. 1974;16:401–19.
Takeichi M. Self-organization of animal tissues: cadherin-mediated processes. Dev Cell. 2011;21:24–6.
Li ML, Aggeler J, Farson DA, Hatier C, Hassell J, Bissell MJ. Influence of a reconstituted basement membrane and its components on casein gene expression and secretion in mouse mammary epithelial cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987;84:136–40.
Shannon JM, Mason RJ, Jennings SD. Functional differentiation of alveolar type II epithelial cells in vitro: effects of cell shape, cell-matrix interactions and cell-cell interactions. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1987;931:143–56.
Montesano R, Schaller G, Orci L. Induction of epithelial tubular morphogenesis in vitro by fibroblast-derived soluble factors. Cell. 1991;66:697–711.
Gjorevski N, Sachs N, Manfrin A, Giger S, Bragina ME, Ordez-Morn P, Clevers H, Lutolf MP. Designer matrices for intestinal stem cell and organoid culture. Nature. 2016;539(7630):560–4.
Cruz-Acua R, Quirs M, Farkas AE, Dedhia PH, Huang S, Siuda D, Garca-Hernndez V, Miller AJ, Spence JR, Nusrat A, Garca AJ. Synthetic hydrogels for human intestinal organoid generation and colonic wound repair. Nat Cell Biol. 2017;19(11):1326–35.
Thomson JA, Itskovitz-Eldor J, Shapiro SS, Waknitz MA, Swiergiel JJ, Marshall VS, Jones JM. Embryonic stem cell lines derived from human blastocysts. Science. 1998;282:1145–7.
Takahashi K, Yamanaka S. Induction of pluripotent stem cells from mouse embryonic and adult fibroblast cultures by defined factors. Cell. 2006;126:663–76.
Eiraku M, Watanabe K, Matsuo-Takasaki M, Kawada M, Yonemura S, Matsumura M, Wataya T, Nishiyama A, Muguruma K, Sasai Y. Self-organized formation of polarized cortical tissues from ESCs and its active manipulation by extrinsic signals. Cell Stem Cell. 2008;3:519–32.
Sato T, Vries RG, Snippert HJ, van de Wetering M, Barker N, Stange DE, van Es JH, Abo A, Kujala P, Peters PJ, Clevers H. Single Lgr5 stem cells build crypt-villus structures in vitro without a mesenchymal niche. Nature. 2009;459:262–5.
Eiraku M, Takata N, Ishibashi H, Kawada M, Sakakura E, Okuda S, Sekiguchi K, Adachi T, Sasai Y. Self-organizing optic-cup morphogenesis in three-dimensional culture. Nature. 2011;472:51–6.
Spence JR, Mayhew CN, Rankin SA, Kuhar MF, Vallance JE, Tolle K, Hoskins EE, Kalinichenko VV, Wells SI, Zorn AM, Shroyer NF, Wells JM. Directed differentiation of human pluripotent stem cells into intestinal tissue in vitro. Nature. 2011;470:105–9.
Takebe T, Sekine K, Enomura M, Koike H, Kimura M, Ogaeri T, Zhang RR, Ueno Y, Zheng YW, Koike N, Aoyama S, Adachi Y, Taniguchi H. Vascularized and functional human liver from an iPSC-derived organ bud transplant. Nature. 2013;499:481–4.
Lancaster MA, Renner M, Martin CA, Wenzel D, Bicknell LS, Hurles ME, Homfray T, Penninger JM, Jackson AP, Knoblich JA. Cerebral organoids model human brain development and microcephaly. Nature. 2013;501:373–9.
Taguchi A, Kaku Y, Ohmori T, Sharmin S, Ogawa M, Sasaki H, Nishinakamura R. Redefining the in vivo origin of metanephric nephron progenitors enables generation of complex kidney structures from pluripotent stem cells. Cell Stem Cell. 2014;14:53–67.
Takasato M, Er PX, Becroft M, Vanslambrouck JM, Stanley EG, Elefanty AG, Little MH. Directing human embryonic stem cell differentiation towards a renal lineage generates a self-organizing kidney. Nat Cell Biol. 2014;16:118–26.
Si-Tayeb K, Noto FK, Sepac A, Sedlic F, Bosnjak ZJ, Lough JW, Duncan SA. Generation of human induced pluripotent stem cells by simple transient transfection of plasmid DNA encoding reprogramming factors. BMC Dev Biol. 2010;10:81.
Swistowski A, Peng J, Liu Q, Mali P, Rao MS, Cheng L, Zeng X. Efficient generation of functional dopaminergic neurons from human induced pluripotent stem cells under defined conditions. Stem Cells. 2010;28:1893–904.
Deng J, Shoemaker R, Xie B, Gore A, LeProust EM, Antosiewicz-Bourget J, Egli D, Maherali N, Park IH, Yu J, Daley GQ, Eggan K, Hochedlinger K, Thomson J, Wang W, Gao Y, Zhang K. Targeted bisulfite sequencing reveals changes in DNA methylation associated with nuclear reprogramming. Nat Biotechnol. 2009;27:353–60.
Shinozawa T, Yoshikawa HY, Takebe T. Reverse engineering liver buds through self-driven condensation and organization towards medical application. Dev Biol. 2016;420:221–9.
Huch M, Gehart H, van Boxtel R, Hamer K, Blokzijl F, Verstegen MM, Ellis E, van Wenum M, Fuchs SA, de Ligt J, van de Wetering M, Sasaki N, Boers SJ, Kemperman H, de Jonge J, Ijzermans JN, Nieuwenhuis EE, Hoekstra R, Strom S, Vries RR, van der Laan LJ, Cuppen E, Clevers H. Long-term culture of genome-stable bipotent stem cells from adult human liver. Cell. 2015;160(1–2):299–312.
Sampaziotis F, de Brito MC, Madrigal P, Bertero A, Saeb-Parsy K, Soares FAC, Schrumpf E, Melum E, Karlsen TH, Bradley JA, Gelson WT, Davies S, Baker A, Kaser A, Alexander GJ, Hannan NRF, Vallier L. Cholangiocytes derived from human induced pluripotent stem cells for disease modeling and drug validation. Nat Biotechnol. 2015;33(8):845–52.
Ogawa M, Ogawa S, Bear CE, Ahmadi S, Chin S, Li B, Grompe M, Keller G, Kamath BM, Ghanekar A. Directed differentiation of cholangiocytes from human pluripotent stem cells. Nat Biotechnol. 2015;33(8):853–61.
Takebe T, Enomura M, Yoshizawa E, Kimura M, Koike H, Ueno Y, Matsuzaki T, Yamazaki T, Toyohara T, Osafune K, Nakauchi H, Yoshikawa HY, Taniguchi H. Vascularized and complex organ buds from diverse tissues via mesenchymal cell-driven condensation. Cell Stem Cell. 2015;16:556–65.
Lancaster MA, Knoblich JA. Organogenesis in a dish: modeling development and disease using organoid technologies. Science. 2014;345:1247125.
Elkabetz Y, Panagiotakos G, Al Shamy G, Socci ND, Tabar V, Studer L. Human ES cell-derived neural rosettes reveal a functionally distinct early neural stem cell stage. Genes Dev. 2008;22:152–65.
Zhang SC, Wernig M, Duncan ID, Brüstle O, Thomson JA. In vitro differentiation of transplantable neural precursors from human embryonic stem cells. Nat Biotechnol. 2001;19:112–33.
Muguruma K, Nishiyama A, Kawakami H, Hashimoto K, Sasai Y. Self-organization of polarized cerebellar tissue in 3D culture of human pluripotent stem cells. Cell Rep. 2015;10(4):537–50.
Lancaster MA, Corsini NS, Wolfinger S, Gustafson EH, Phillips AW, Burkard TR, Otani T, Livesey FJ, Knoblich JA. Guided self-organization and cortical plate formation in human brain organoids. Nat Biotechnol. 2017;35(7):659–66.
Nakano T, Ando S, Takata N, Kawada M, Muguruma K, Sekiguchi K, Saito K, Yonemura S, Eiraku M, Sasai Y. Self-formation of optic cups and storable stratified neural retina from human ESCs. Cell Stem Cell. 2012;10:771–85.
Zhong X, Gutierrez C, Xue T, Hampton C, Vergara MN, Cao LH, Peters A, Park TS, Zambidis ET, Meyer JS, Gamm DM, Yau KW, Canto-Soler MV. Generation of three-dimensional retinal tissue with functional photoreceptors from human iPSCs. Nat Commun. 2014;5:4047.
Quadrato G, Nguyen T, Macosko EZ, Sherwood JL, Min Yang S, Berger DR, Maria N, Scholvin J, Goldman M, Kinney JP, Boyden ES, Lichtman JW, Williams ZM, McCarroll SA, Arlotta P. Cell diversity and network dynamics in photosensitive human brain organoids. Nature. 2017;545(7652):48–53.
Weiss P, Taylor AC. Reconstitution of complete organs from single-cell supsensions of chick embryos in advanced stages of differentiation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1960;46:1177–85.
Clevers H. Modeling development and disease with organoids. Cell. 2016;165:1586–97.
Mae SI, Shono A, Shiota F, Yasuno T, Kajiwara M, Gotoda-Nishimura N, Arai S, Sato-Otubo A, Toyoda T, Takahashi K, Nakayama N, Cowan CA, Aoi T, Ogawa S, McMahon AP, Yamanaka S, Osafune K. Monitoring and robust induction of nephrogenic intermediate mesoderm from human pluripotent stem cells. Nat Commun. 2013;4:1367.
Xia Y, Nivet E, Sancho-Martinez I, Gallegos T, Suzuki K, Okamura D, Wu MZ, Dubova I, Esteban CR, Montserrat N, Campistol JM, Izpisua Belmonte JC. Directed differentiation of human pluripotent cells to ureteric bud kidney progenitor-like cells. Nat Cell Biol. 2013;15:1507–15.
Samira M, Akiko M, Thomas CF, Sauveur SFJ, Mariko H, Tadanori M, Kristen R, Seyoon C, Richard N, Miles I, Tohid F, Sandeep K, James CW, George MC, Ingber DE. Mature induced-pluripotent-stem-cell-derived human podocytes reconstitute kidney glomerular-capillary-wall function on a chip. Nat Biomed Eng. 2017;1:0069.
Heath JK. Transcriptional networks and signaling pathways that govern vertebrate intestinal development. Curr Top Dev Biol. 2010;90:159–92.
Gjorevski N, Sachs N, Manfrin A, Giger S, Bragina ME, Ordóñez-Morán P, Clevers H, Lutolf MP. Designer matrices for intestinal stem cell and organoid culture. Nature. 2016;539(7630):560–4.
Miura S, Suzuki A. Generation of mouse and human organoid-forming intestinal progenitor cells by direct lineage reprogramming. Cell Stem Cell. 2017;21(4):456–71.
McCracken KW, Catá EM, Crawford CM, Sinagoga KL, Schumacher M, Rockich BE, Tsai YH, Mayhew CN, Spence JR, Zavros Y, Wells JM. Modelling human development and disease in pluripotent stem-cell-derived gastric organoids. Nature. 2014;516:400–4.
Bartfeld S, Bayram T, van de Wetering M, Huch M, Begthel H, Kujala P, Vries R, Peters PJ, Clevers H. In vitro expansion of human gastric epithelial stem cells and their responses to bacterial infection. Gastroenterology. 2015;148:126–136.e6.
McCracken KW, Aihara E, Martin B, Crawford CM, Broda T, Treguier J, Zhang X, Shannon JM, Montrose MH, Wells JM. Wnt/β-catenin promotes gastric fundus specification in mice and humans. Nature. 2017;541(7636):182–7.
Greggio C, de Franceschi F, Figueiredo-Larsen M, Gobaa S, Ranga A, Semb H, Lutolf M, Grapin-Botton A. Artificial three-dimensional niches deconstruct pancreas development in vitro. Development. 2013;140(21):4452–62.
Huch M, Bonfanti P, Boj SF, Sato T, Loomans CJ, van de Wetering M, Sojoodi M, Li VS, Schuijers J, Gracanin A, Ringnalda F, Begthel H, Hamer K, Mulder J, van Es JH, de Koning E, Vries RG, Heimberg H, Clevers H. Unlimited in vitro expansion of adult bi-potent pancreas progenitors through the Lgr5/R-spondin axis. EMBO J. 2013;32(20):2708–21.
Boj SF, Hwang CI, Baker LA, Chio II, Engle DD, Corbo V, Jager M, Ponz-Sarvise M, Tiriac H, Spector MS, Gracanin A, Oni T, Yu KH, van Boxtel R, Huch M, Rivera KD, Wilson JP, Feigin ME, Öhlund D, Handly-Santana A, Ardito-Abraham CM, Ludwig M, Elyada E, Alagesan B, Biffi G, Yordanov GN, Delcuze B, Creighton B, Wright K, Park Y, Morsink FH, Molenaar IQ, Borel Rinkes IH, Cuppen E, Hao Y, Jin Y, Nijman IJ, Iacobuzio-Donahue C, Leach SD, Pappin DJ, Hammell M, Klimstra DS, Basturk O, Hruban RH, Offerhaus GJ, Vries RG, Clevers H, Tuveson DA. Organoid models of human and mouse ductal pancreatic cancer. Cell. 2015;160(1–2):324–38.
Broutier L, Andersson-Rolf A, Hindley CJ, Boj SF, Clevers H, Koo BK, Huch M. Culture and establishment of self-renewing human and mouse adult liver and pancreas 3D organoids and their genetic manipulation. Nat Protoc. 2016;11(9):1724–43.
Mondrinos MJ, Jones PL, Finck CM, Lelkes PI. Engineering de novo assembly of fetal pulmonary organoids. Tissue Eng Part A. 2014;20:2892–907.
Rock JR, Onaitis MW, Rawlins EL, et al. Basal cells as stem cells of the mouse trachea and human airway epithelium. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2009;106:12771–5.
Dye BR, Dedhia PH, Miller AJ, Nagy MS, White ES, Shea LD, Spence JR. A bioengineered niche promotes in vivo engraftment and maturation of pluripotent stem cell derived human lung organoids. Elife. 2016;5:e19732.
Lee JH, Tammela T, Hofree M, Choi J, Marjanovic ND, Han S, Canner D, Wu K, Paschini M, Bhang DH, Jacks T, Regev A, Kim CF. Anatomically and functionally distinct lung mesenchymal populations marked by Lgr5 and Lgr6. Cell. 2017;170(6):1149–63.
Chen YW, Huang SX, de Carvalho ALRT, Ho SH, Islam MN, Volpi S, Notarangelo LD, Ciancanelli M, Casanova JL, Bhattacharya J, Liang AF, Palermo LM, Porotto M, Moscona A, Snoeck HW. A three-dimensional model of human lung development and disease from pluripotent stem cells. Nat Cell Biol. 2017;19(5):542–9.
McCauley KB, Hawkins F, Serra M, Thomas DC, Jacob A, Kotton DN. Efficient derivation of functional human airway epithelium from pluripotent stem cells via temporal regulation of Wnt signaling. Cell Stem Cell. 2017;20(6):844–57.
Hogan BLM, Barkauskas CE, Chapman HA, et al. Repair and regeneration of the respiratory system: complexity, plasticity, and mechanisms of lung stem cell function. Cell Stem Cell. 2014;15:123–38.
del Moral P-M, Warburton D. Explant culture of mouse embryonic whole lung, isolated epithelium, or mesenchyme under chemically defined conditions as a system to evaluate the molecular mechanism of branching morphogenesis and cellular differentiation. Methods Mol Biol. 2010;633:71–9.
Nikolić MZ, Rawlins EL. Lung organoids and their use to study cell-cell interaction. Curr Pathobiol Rep. 2017;5(2):223–31.
Zhang S, Zhou X, Chen T, et al. Single primary fetal lung cells generate alveolar structures in vitro. In Vitro Cell Dev Biol Anim. 2014;50:87–93.
Sucre JMS, Wilkinson D, Vijayaraj P, et al. A threedimensional human model of the fibroblast activation that accompanies bronchopulmonary dysplasia identifies Notch-mediated pathophysiology. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 2016;310:L889–98.
Fang Y, Eglen RM. Three-dimensional cell cultures in drug discovery and development. SLAS Discov. 2017;22:456–72.
Sutherland RM, McCredie JA, Inch WR. Growth of multicell spheroids in tissue culture as a model of nodular carcinomas. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1971;46:113–20.
Ghosh S, Joshi MB, Ivanov D, Feder-Mengus C, Spagnoli GC, Martin I, Erne P, Resink TJ. Use of multicellular tumor spheroids to dissect endothelial cell-tumor cell interactions: a role for T-cadherin in tumor angiogenesis. FEBS Lett. 2007;581:4523–8.
Febles NK, Ferrie AM, Fang Y. Label-free single cell kinetics of the invasion of spheroidal colon cancer cells through 3D Matrigel. Anal Chem. 2014;86:8842–9.
Chandrasekaran S, Deng H, Fang Y. PTEN deletion potentiates invasion of colorectal cancer spheroidal cells through 3D Matrigel. Integr Biol. 2015;7:324–34.
Senkowski W, Zhang X, Olofsson MH, Isacson R, Höglund U, Gustafsson M, Nygren P, Linder S, Larsson R, Fryknäs M. Three-dimensional cell culture-based screening identifies the anthelmintic drug nitazoxanide as a candidate for treatment of colorectal cancer. Mol Cancer Ther. 2015;14:1504–16.
Kenny HA, Lal-Nag M, White EA, Shen M, Chiang CY, Mitra AK, Zhang Y, Curtis M, Schryver EM, Bettis S, Jadhav A, Boxer MB, Li Z, Ferrer M, Lengyel E. Quantitative high throughput screening using a primary human three-dimensional organotypic culture predicts in vivo efficacy. Nat Commun. 2015;6:6220.
Qian X, Nguyen HN, Song MM, Hadiono C, Ogden SC, Hammack C, Yao B, Hamersky GR, Jacob F, Zhong C, Yoon KJ, Jeang W, Lin L, Li Y, Thakor J, Berg DA, Zhang C, Kang E, Chickering M, Nauen D, Ho CY, Wen Z, Christian KM, Shi PY, Maher BJ, Wu H, Jin P, Tang H, Song H, Ming GL. Brain-region-specific organoids using mini-bioreactors for modeling ZIKV exposure. Cell. 2016;165:1238–54.
Scannell JW, Blanckley A, Boldon H, Warrington B. Diagnosing the decline in pharmaceutical R&D efficiency. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2012;11(3):191–200.
Shi Y, Inoue H, Wu JC, Yamanaka S. Induced pluripotent stem cell technology: a decade of progress. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2017;16:115–30.
Choi SM, Kim Y, Shim JS, Park JT, Wang RH, Leach SD, Liu JO, Deng C, Ye Z, Jang YY. Efficient drug screening and gene correction for treating liver disease using patient-specific stem cells. Hepatology. 2013;57:2458–68.
Rashid T, Takebe T, Nakauchi H. Novel strategies for liver therapy using stem cells. Gut. 2015;64:1–4.
Tafaleng EN, Chakraborty S, Han B, Hale P, Wu W, Soto-Gutierrez A, Feghali-Bostwick CA, Wilson AA, Kotton DN, Nagaya M, Strom SC, Roy-Chowdhury J, Stolz DB, Perlmutter DH, Fox IJ. Induced pluripotent stem cells model personalized variations in liver disease resulting from α1-antitrypsin deficiency. Hepatology. 2015;62:147–57.
Hay M, Thomas DW, Craighead JL, Economides C, Rosenthal J. Clinical development success rates for investigational drugs. Nat Biotechnol. 2014;32:40–51.
Reuben A, Koch DG, Lee WM, Acute Liver Failure Study Group. Drug-induced acute liver failure: results of a U.S. multicenter, prospective study. Hepatology. 2010;52:2065–76.
Amacher DE. Serum transaminase elevations as indicators of hepatic injury following the administration of drugs. Regul Toxicol Pharmacol. 1998;27:119–30.
Navarro VJ, Senior JR. Drug-related hepatotoxicity. N Engl J Med. 2006;354:731–9.
Bell CC, Hendriks DF, Moro SM, Ellis E, Walsh J, Renblom A, Fredriksson Puigvert L, Dankers AC, Jacobs F, Snoeys J, Sison-Young RL, Jenkins RE, Nordling Å, Mkrtchian S, Park BK, Kitteringham NR, Goldring CE, Lauschke VM, Ingelman-Sundberg M. Characterization of primary human hepatocyte spheroids as a model system for drug-induced liver injury, liver function and disease. Sci Rep. 2016;6:25187.
Sjogren AK, Liljevald M, Glinghammar B, Sagemark J, Li XQ, Jonebring A, Cotgreave I, Brolén G, Andersson TB. Critical differences in toxicity mechanisms in induced pluripotent stem cell-derived hepatocytes, hepatic cell lines and primary hepatocytes. Arch Toxicol. 2014;88:1427–37.
Krueger W, Boelsterli UA, Rasmussen TP. Stem cell strategies to evaluate idiosyncratic drug-induced liver injury. J Clin Transl Hepatol. 2014;2:143–52.
Morizane R, Lam AQ, Freedman BS, Kishi S, Valerius MT, Bonventre JV. Nephron organoids derived from human pluripotent stem cells model kidney development and injury. Nat Biotechnol. 2015;33:1193–200.
Ranga A, Gjorevski N, Lutolf MP. Drug discovery through stem cell-based organoid models. Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2014;69–70:19–28.
Workman MJ, Mahe MM, Trisno S, Poling HM, Watson CL, Sundaram N, Chang CF, Schiesser J, Aubert P, Stanley EG, Elefanty AG, Miyaoka Y, Mandegar MA, Conklin BR, Neunlist M, Brugmann SA, Helmrath MA, Wells JM. Engineered human pluripotent-stem-cell-derived intestinal tissues with a functional enteric nervous system. Nat Med. 2017;23(1):49–59.
Li L, Fukunaga-Kalabis M, Herlyn M. The three-dimensional human skin reconstruct model: a tool to study normal skin and melanoma progression. J Vis Exp. 2011;54:2937.
Huh D, Matthews BD, Mammoto A, Montoya-Zavala M, Hsin HY, Ingber DE. Reconstituting organ-level lung functions on a chip. Science. 2010;328:1662–8.
Aref AR, Huang RY, Yu W, Chua KN, Sun W, Tu TY, Bai J, Sim WJ, Zervantonakis IK, Thiery JP, Kamm RD. Screening therapeutic EMT blocking agents in a three-dimensional microenvironment. Integr Biol. 2013;5:381–9.
Takebe T, Zhang B, Radisic M. Synergistic engineering: organoids meet organs-on-a-chip. Cell Stem Cell. 2017;21:297–300.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2019 Springer Nature Singapore Pte Ltd.
About this chapter
Cite this chapter
Nio, Y., Takebe, T. (2019). Organoid Models of Development and Disease Towards Therapy. In: Inoue, H., Nakamura, Y. (eds) Medical Applications of iPS Cells . Current Human Cell Research and Applications. Springer, Singapore. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-13-3672-0_9
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-13-3672-0_9
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Singapore
Print ISBN: 978-981-13-3671-3
Online ISBN: 978-981-13-3672-0
eBook Packages: MedicineMedicine (R0)