Abstract
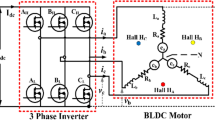
Brushless DC motor has permanent magnets in the rotor side that rotates around fixed armature. The current rotates in armature continuously as it is electronically commutated. The motor’s efficiency will otherwise reduce due to commutation angle errors. The novelty of the work is to reduce commutation errors that are obtained based on commutation point phase shift and the dc-link current difference. Based on these relationship analysis is made under ideal, advanced and delayed commutations. The self-compensation method of commutation instant deviation delays the commutation angle by 10º thus reducing the impact caused by commutation ripple thereby improving dynamic response and control. The dc-link current difference decrease gradually and phase deviation converges to correct the commutation angle. The proposed correction method can achieve ideal commutation effect thereby attaining fast convergence speed, current and torque.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Niasar Alij, H., Vaheda, M., Moghbalina, H.: Position control for a four-switch, BLDC motor drive without the use of a phase shifter. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 23(8), 3078–3086 (2008)
Park, J.S., Jungshin, M., Ki, H.W., Youlani, M.J.: Position tracking observer power control for sensorless drive permanent magnet synchronous machine. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 26(7), 2585–2597 (2014)
Po-ngamnaig, S., Sanwinch, S.: Performance improvement of full-order observers for PMSM drive. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 37(7), 588–604 (2012)
Tiwari, V., Rani, B.L.: Torque ripple reducing technique in BLDC motor with unideal back EMF method. In: Proceedings of 2nd International Conference on Emerging Trends Engineering technology (ICETET), pp. 687–690 (2010)
Kangshi, S., Sungshi, K.: Torque control of BLDC with nonideal trapezoidal back EMF. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 10(2), 796–802 (1994)
Bhogineni, S., Rajagopal, K.: Position control in a brushless DC motor based on average line to line voltages. In: Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference On Power Electronics, Drives and Energy Systems, pp. 1–6 (2012)
Ogasahara, S., Akagini, H.: An approach to position sensorless drive for brushless DC motors. IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl. 27(5), 928–933 (1992)
Urasaki, N., Senjyungthang, T., Uezato, K., Sungabasi, T.: Adaptive dead-time compensation strategy for a PMSM drive. IEEE Trans. Energy Convers. 22(4), 271–280 (2008)
Hu, T., Jung, K., Ehsanigom, M.: An error analysis for ataining position estimation for BLDC motor drive. In: Proc. Conf. Rec. Ind. Appl. Conf., vol. 1, pp. 611–617 (2003)
Pellechangnou, G., Gugulung, P., Arnandoshi, E., et al.: A Self-Commissioning Algorithm for Compensating Inverter Nonlinearity in Sensorless Induction Motors. IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl. 47(8), 1415–1424 (2012)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2018 Springer Nature Singapore Pte Ltd.
About this paper
Cite this paper
Pillai, M.S., Vijina, K. (2018). A Novel Self Correction Torque and Commutation Ripples Reduction in BLDC Motor. In: Zelinka, I., Senkerik, R., Panda, G., Lekshmi Kanthan, P. (eds) Soft Computing Systems. ICSCS 2018. Communications in Computer and Information Science, vol 837. Springer, Singapore. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-13-1936-5_74
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-13-1936-5_74
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Singapore
Print ISBN: 978-981-13-1935-8
Online ISBN: 978-981-13-1936-5
eBook Packages: Computer ScienceComputer Science (R0)