Abstract
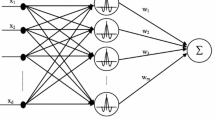
A variable translation wavelet neural network (VT-WNN) is a type of wavelet neural network that is able to adapt to the changes in the input. Different learning algorithms have been proposed such as backpropagation and hybrid wavelet-particle swarm optimization. However, most of them are time costly. This paper proposed a new learning mechanism for VT-WNN using random weights. To validate the performance of randomized VT-WNN, several experiments using benchmark data form UCI machine learning datasets were conducted. The experimental results show that RVT-WNN can work on a broad range of applications from the small size up to the large size with comparable performance to other well-known classifiers.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adamowski, J., Chan, H.F.: A wavelet neural network conjunction model for groundwater level forecasting. J. Hydrol. 407, 28–40 (2011)
Anam, K., Al-Jumaily, A.: Adaptive wavelet extreme learning machine (AW-ELM) for index finger recognition using two-channel electromyography. In: Loo, C.K., Yap, K.S., Wong, K.W., Teoh, A., Huang, K. (eds.) ICONIP 2014. LNCS, vol. 8834, pp. 471–478. Springer, Cham (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-12637-1_59
Anam, K., Al-Jumaily, A.: Evaluation of extreme learning machine for classification of individual and combined finger movements using electromyography on amputees and non-amputees. Neural Netw. 85, 51–68 (2017)
Antuvan, C.W., Bisio, F., Marini, F., et al.: Role of muscle synergies in real-time classification of upper limb motions using extreme learning machines. J. Neuroeng. Rehabil. 13, 76 (2016)
Asuncion, A., Newman, D.: The UCI Machine Learning Repository (2007)
Cao, J., Lin, Z., Huang, G.-B.: Composite function wavelet neural networks with extreme learning machine. Neurocomputing 73, 1405–1416 (2010)
Chen, C.-H.: Intelligent transportation control system design using wavelet neural network and PID-type learning algorithms. Expert Syst. Appl. 38, 6926–6939 (2011)
Huang, G., Song, S., Gupta, J.N., et al.: Semi-supervised and unsupervised extreme learning machines. IEEE Trans. Cybern. 44, 2405–2417 (2014)
Huang, G.-B., Zhu, Q.-Y., Siew, C.-K.: Extreme learning machine: theory and applications. Neurocomputing 70, 489–501 (2006)
Huang, G.B., Zhou, H., Ding, X., et al.: Extreme learning machine for regression and multiclass classification. IEEE Trans. Syst. Man Cybern. Part B (Cybern.) 42, 513–529 (2012)
Inoussa, G., Peng, H., Wu, J.: Nonlinear time series modeling and prediction using functional weights wavelet neural network-based state-dependent AR model. Neurocomputing 86, 59–74 (2012)
Ling, S.H., Iu, H., Leung, F.H.-F., et al.: Improved hybrid particle swarm optimized wavelet neural network for modeling the development of fluid dispensing for electronic packaging. IEEE Trans. Industr. Electron. 55, 3447–3460 (2008)
Pindoriya, N.M., Singh, S.N., Singh, S.K.: An adaptive wavelet neural network-based energy price forecasting in electricity markets. IEEE Trans. Power Syst. 23, 1423–1432 (2008)
Ramana, R.V., Krishna, B., Kumar, S., et al.: Monthly rainfall prediction using wavelet neural network analysis. Water Resources Manag. 27, 3697–3711 (2013)
Schmidt, W.F., Kraaijveld, M.A., Duin, R.P.: Feedforward neural networks with random weights. In: Proceedings of the11th IAPR International Conference on Pattern Recognition, pp. 1–4. IEEE (1992)
Senapati, M.R., Mohanty, A.K., Dash, S., et al.: Local linear wavelet neural network for breast cancer recognition. Neural Comput. Appl. 22, 125–131 (2013)
Subasi, A., Yilmaz, M., Ozcalik, H.R.: Classification of EMG signals using wavelet neural network. J. Neurosci. Methods 156, 360–367 (2006)
Zhang, L., Suganthan, P.N.: A survey of randomized algorithms for training neural networks. Inf. Sci. 364, 146–155 (2016). %@ 0020-0255
Zhou, B., Shi, A., Cai, F., Zhang, Y.: Wavelet neural networks for nonlinear time series analysis. In: Yin, F.-L., Wang, J., Guo, C. (eds.) ISNN 2004. LNCS, vol. 3174, pp. 430–435. Springer, Heidelberg (2004). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-540-28648-6_68
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2017 Springer Nature Singapore Pte Ltd.
About this paper
Cite this paper
Anam, K., Al-Jumaily, A. (2017). Evaluation of Randomized Variable Translation Wavelet Neural Networks. In: Mohamed, A., Berry, M., Yap, B. (eds) Soft Computing in Data Science. SCDS 2017. Communications in Computer and Information Science, vol 788. Springer, Singapore. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-10-7242-0_1
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-10-7242-0_1
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Singapore
Print ISBN: 978-981-10-7241-3
Online ISBN: 978-981-10-7242-0
eBook Packages: Computer ScienceComputer Science (R0)