Abstract
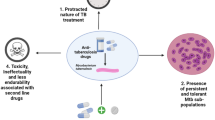
One third of the world population is infected latently with tuberculosis, a bacterial disease caused by Mycobacterium tuberculosis (MTB). Ten percent of this latent infection may lead to active TB. With the advent of drug resistance against conventional antibiotics, there is an urgent need for new therapeutics that can target and treat tuberculosis, especially multidrug-resistant tuberculosis and extensively drug-resistant tuberculosis. Antimycobacterial peptides, having low immunogenicity, high affinity to bacterial cell envelopes and diverse mode of action, have shown to be promising candidates in this regard. Some of the challenges faced by these peptides include difficulty in delivery to the target sites traversing the unique mycobacterial cell wall, stability of the peptides at physiological conditions and degradation by cytoplasmic proteases. This chapter will discuss the structure, composition, isolation and mode of synthesis of potential antimycobacterial peptides isolated from various sources as well as the methods used to overcome some of the challenges in delivery and bioavailability.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Agerberth B, Lee JY, Bergman T, Carlquist M, Boman HG, Mutt V, Jornvall H (1991) Amino acid sequence of PR-39. Isolation from pig intestine of a new member of the family of proline-arginine-rich antibacterial peptides. Eur J Biochem 202:849–854
Ahlstedt (1995) Clinical application of eosinophilic cationic protein in asthma. Allergy Asthma Proc 16:59–62
Alonso S, Pethe K, Russell DG, Purdy GE (2007) Lysosomal killing of Mycobacterium mediated by ubiquitin-derived peptides is enhanced by autophagy. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 104:6031–6036
Andreu D, Carreno C, Linde C, Boman HG, Andersson M (1999) Identification of an anti-mycobacterial domain in NK-lysin and granulysin. Biochem J 344(Pt 3):845–849
Boix E, Salazar VA, Torrent M, Pulido D, Nogués MV, Moussaoui M (2012) Structural determinants of the eosinophil cationic protein antimicrobial activity. Biol Chem 393:801–815
Boman HG, Agerberth B, Boman A (1993) Mechanisms of action on Escherichia coli of cecropin P1 and PR-39, two antibacterial peptides from pig intestine. Infect Immun 61:2978–2984
Bowdish DM, Davidson DJ, Hancock RE (2006) Immunomodulatory properties of defensins and cathelicidins. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol 306:27–66
Brennan PJ (2003) Structure, function, and biogenesis of the cell wall of Mycobacterium tuberculosis. Tuberculosis (Edinburgh) 83:91–97
Brogden KA, Ackermann M, McCray PB Jr, Tack BF (2003) Antimicrobial peptides in animals and their role in host defences. Int J Antimicrob Agents 22:465–478
Bystrom J, Amin K, Bishop-Bailey D (2011) Analysing the eosinophil cationic protein – a clue to the function of the eosinophil granulocyte. Respir Res 12:10
Carmona G, Rodriguez A, Juarez D, Corzo G, Villegas E (2013) Improved protease stability of the antimicrobial peptide Pin2 substituted with D-amino acids. Protein J 32:456–466
Carroll J, Draper LA, O’Connor PM, Coffey A, Hill C, Ross RP, Cotter PD, O’Mahony J (2012) Comparison of the activities of the lantibiotics nisin and lacticin 3147 against clinically significant mycobacteria. Int J Antimicrob Agents 36:132–136
Castaneda-Sanchez JI, Garcia-Perez BE, Munoz-Duarte AR, Baltierra-Uribe SL, Mejia-Lopez H, Lopez-Lopez C, Bautista-De Lucio VM, Robles-Contreras A, Luna-Herrera J (2013) Defensin production by human limbo-corneal fibroblasts infected with mycobacteria. Pathogens 2:13–32
Cotter PD, Hill C, Ross RP (2005) Bacteriocins: developing innate immunity for food. Nat Rev Microbiol 3:777–788
de Oliveira PC, de Lima PO, Oliveira DT, Pereira MC (2012) Eosinophil cationic protein: overview of biological and genetic features. DNA Cell Biol 31:1442–1446
Duplantier AJ, van Hoek ML (2013) The human cathelicidin antimicrobial peptide LL-37 as a potential treatment for polymicrobial infected wounds. Front Immunol 4:143
Foss MH, Powers KM, Purdy GE (2012) Structural and functional characterization of mycobactericidal ubiquitin-derived peptides in model and bacterial membranes. Biochemistry 51:9922–9929
Frothingham R, Hills HG, Wilson KH (1994) Extensive DNA sequence conservation throughout the Mycobacterium tuberculosis complex. J Clin Microbiol 32:1639–1643
Ganz T, Selsted ME, Szklarek D, Harwig SS, Daher K, Bainton DF, Lehrer RI (1985) Defensins. Natural peptide antibiotics of human neutrophils. J Clin Investig 76:1427–1435
Harder J, Schroder JM (2002) RNase 7, a novel innate immune defense antimicrobial protein of healthy human skin. J Biol Chem 277:46779–46784
Huang YC, Lin YM, Chang TW, Wu SJ, Lee YS, Chang MD, Chen C, Wu SH, Liao YD (2007) The flexible and clustered lysine residues of human ribonuclease 7 are critical for membrane permeability and antimicrobial activity. J Biol Chem 282:4626–4633
Iwatsuki M, Uchida R, Takakusagi Y, Matsumoto A, Jiang CL, Takahashi Y, Arai M, Kobayashi S, Matsumoto M, Inokoshi J, Tomoda H, Omura S (2007) Lariatins, novel anti-mycobacterial peptides with a lasso structure, produced by Rhodococcus jostii K01-B0171. J Antibiot (Tokyo) 60:357–363
Jiang Z, Higgins MP, Whitehurst J, Kisich KO, Voskuil MI, Hodges RS (2011) Anti-tuberculosis activity of alpha-helical antimicrobial peptides: de novo designed L- and D-enantiomers versus L- and D-LL-37. Protein Pept Lett 18:241–252
Kalita A, Verma I, Khuller GK (2004) Role of human neutrophil peptide-1 as a possible adjunct to antituberculosis chemotherapy. J Infect Dis 190:1476–1480
Khara JS, Priestman M, Uhia I, Hamilton MS, Krishnan N, Wang Y, Yang YY, Langford PR, Newton SM, Robertson BD, Ee PL (2016) Unnatural amino acid analogues of membrane-active helical peptides with anti-mycobacterial activity and improved stability. J Antimicrob Chemother 71:2181–2191
Kieffer AE, Goumon Y, Ruh O, Chasserot-Golaz S, Nullans G, Gasnier C, Aunis D, Metz-Boutigue MH (2003) The N- and C-terminal fragments of ubiquitin are important for the antimicrobial activities. FASEB J 17:776–778
Kisich KO, Heifets L, Higgins M, Diamond G (2001) Antimycobacterial agent based on mRNA encoding human beta-defensin 2 enables primary macrophages to restrict growth of Mycobacterium tuberculosis. Infect Immun 69:2692–2699
Kolodkin-Gal I, Romero D, Cao S, Clardy J, Kolter R, Losick R (2010) D-amino acids trigger biofilm disassembly. Science 328:627–629
Koten B, Simanski M, Glaser R, Podschun R, Schroder JM, Harder J (2009) RNase 7 contributes to the cutaneous defense against Enterococcus faecium. PLoS One 4:e6424
Krensky AM, Clayberger C (2009) Biology and clinical relevance of granulysin. Tissue Antigens 73:193–198
Lawlor C, O'Connor G, O'Leary S, Gallagher PJ, Cryan SA, Keane J, O'Sullivan MP (2016) Treatment of mycobacterium tuberculosis-infected macrophages with poly(lactic-co-glycolic acid) microparticles drives NFkappaB and autophagy dependent bacillary killing. PLoS One 11:e0149167
Linch SN, Kelly AM, Danielson ET, Pero R, Lee JJ, Gold JA (2009) Mouse eosinophils possess potent antibacterial properties in vivo. Infect Immun 77:4976–4982
Linde CM, Hoffner SE, Refai E, Andersson M (2001) In vitro activity of PR-39, a proline-arginine-rich peptide, against susceptible and multi-drug-resistant Mycobacterium tuberculosis. J Antimicrob Chemother 47:575–580
Liu PT, Modlin RL (2008) Human macrophage host defense against Mycobacterium tuberculosis. Curr Opin Immunol 20:371–376
Liu PT, Stenger S, Tang DH, Modlin RL (2007) Cutting edge: vitamin D-mediated human antimicrobial activity against Mycobacterium tuberculosis is dependent on the induction of cathelicidin. J Immunol 179:2060–2063
Martineau AR, Wilkinson KA, Newton SM, Floto RA, Norman AW, Skolimowska K, Davidson RN, Sorensen OE, Kampmann B, Griffiths CJ, Wilkinson RJ (2007) IFN-gamma- and TNF-independent vitamin D-inducible human suppression of mycobacteria: the role of cathelicidin LL-37. J Immunol 178:7190–7198
McAuliffe O, Ryan MP, Ross RP, Hill C, Breeuwer P, Abee T (1998) Lacticin 3147, a broad-spectrum bacteriocin which selectively dissipates the membrane potential. Appl Environ Microbiol 64:439–445
McGrath DM, Barbu EM, Driessen WH, Lasco TM, Tarrand JJ, Okhuysen PC, Kontoyiannis DP, Sidman RL, Pasqualini R, Arap W (2013) Mechanism of action and initial evaluation of a membrane active all-D-enantiomer antimicrobial peptidomimetic. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 110:3477–3482
Mendez-Samperio P (2010) The human cathelicidin hCAP18/LL-37: a multifunctional peptide involved in mycobacterial infections. Peptides 31:1791–1798
Miteva M, Andersson M, Karshikoff A, Otting G (1999) Molecular electroporation: a unifying concept for the description of membrane pore formation by antibacterial peptides, exemplified with NK-lysin. FEBS Lett 462:155–158
Mohanram H, Bhattacharjya S (2016) ‘Lollipop’-shaped helical structure of a hybrid antimicrobial peptide of temporin B-lipopolysaccharide binding motif and mapping cationic residues in antibacterial activity. Biochim Biophys Acta 1860:1362–1372
Morvan A, Bachere E, Da Silva PP, Pimenta P, Mialhe E (1994) In vitro activity of the antimicrobial peptide magainin 1 against Bonamia ostreae, the intrahemocytic parasite of the flat oyster Ostrea edulis. Mol Mar Biol Biotechnol 3:327–333
Mueller H, Fae KC, Magdorf K, Ganoza CA, Wahn U, Guhlich U, Feiterna-Sperling C, Kaufmann SH (2011) Granulysin-expressing CD4+ T cells as candidate immune marker for tuberculosis during childhood and adolescence. PLoS One 6:e29367
Ojha AK, Baughn AD, Sambandan D, Hsu T, Trivelli X, Guerardel Y, Alahari A, Kremer L, Jacobs WR Jr, Hatfull GF (2008) Growth of Mycobacterium tuberculosis biofilms containing free mycolic acids and harbouring drug-tolerant bacteria. Mol Microbiol 69:164–174
Okada M, Kita Y, Nakajima T, Kanamaru N, Hashimoto S, Nagasawa T, Kaneda Y, Yoshida S, Nishida Y, Nakatani H, Takao K, Kishigami C, Nishimatsu S, Sekine Y, Inoue Y, Matsumoto M, McMurray DN, De la Cruz EC, Tan EV, Abalos RM, Burgos JA, Saunderson P, Sakatani M (2011) Novel therapeutic vaccine: granulysin and new DNA vaccine against Tuberculosis. Human Vaccin 7(Suppl):60–67
Pazgier M, Hoover DM, Yang D, Lu W, Lubkowski J (2006) Human beta-defensins. Cell Mol Life Sci 63:1294–1313
Pena SV, Krensky AM (1997) Granulysin, a new human cytolytic granule-associated protein with possible involvement in cell-mediated cytotoxicity. Semin Immunol 9:117–125
Pitabut N, Sakurada S, Tanaka T, Ridruechai C, Tanuma J, Aoki T, Kantipong P, Piyaworawong S, Kobayashi N, Dhepakson P, Yanai H, Yamada N, Oka S, Okada M, Khusmith S, Keicho N (2013) Potential function of granulysin, other related effector molecules and lymphocyte subsets in patients with TB and HIV/TB co infection. Int J Med Sci 10:1003–1014
Pokorny A, Almeida PF (2005) Permeabilization of raft-containing lipid vesicles by delta-lysin: a mechanism for cell sensitivity to cytotoxic peptides. Biochemistry 44:9538–9544
Pulido D, Torrent M, Andreu D, Nogues MV, Boix E (2013) Two human host defense ribonucleases against mycobacteria, the eosinophil cationic protein (RNase 3) and RNase 7. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 57:3797–3805
Purdy GE, Niederweis M, Russell DG (2009) Decreased outer membrane permeability protects mycobacteria from killing by ubiquitin-derived peptides. Mol Microbiol 73:844–857
Rivas-Santiago CE, Rivas-Santiago B, Leon DA, Castaneda-Delgado J, Hernandez Pando R (2011) Induction of beta-defensins by l-isoleucine as novel immunotherapy in experimental murine tuberculosis. Clin Exp Immunol 164:80–89
Samuchiwal SK, Tousif S, Singh DK, Kumar A, Ghosh A, Bhalla K, Prakash P, Kumar S, Bhattacharyya M, Moodley P, Das G, Ranganathan A (2014) A peptide fragment from the human COX3 protein disrupts association of Mycobacterium tuberculosis virulence proteins ESAT-6 and CFP10, inhibits mycobacterial growth and mounts protective immune response. BMC Infect Dis 14:355
Santos P, Gordillo A, Osses L, Salazar LM, Soto CY (2012) Effect of antimicrobial peptides on ATPase activity and proton pumping in plasma membrane vesicles obtained from mycobacteria. Peptides 36:121–128
Sharma S, Verma I, Khuller GK (2000) Antibacterial activity of human neutrophil peptide-1 against Mycobacterium tuberculosis H37Rv: in vitro and ex vivo study. Eur Respir J 16:112–117
Sharma S, Verma I, Khuller GK (2001) Therapeutic potential of human neutrophil peptide 1 against experimental tuberculosis. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 45:639–640
Shi J, Ross CR, Chengappa MM, Blecha F (1994) Identification of a proline-arginine-rich antibacterial peptide from neutrophils that is analogous to PR-39, an antibacterial peptide from the small intestine. J Leukoc Biol 56:807–811
Shi J, Ross CR, Leto TL, Blecha F (1996) PR-39, a proline-rich antibacterial peptide that inhibits phagocyte NADPH oxidase activity by binding to Src homology 3 domains of p47 phox. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 93:6014–6018
Silva JP, Goncalves C, Costa C, Sousa J, Silva-Gomes R, Castro AG, Pedrosa J, Appelberg R, Gama FM (2016) Delivery of LLKKK18 loaded into self-assembling hyaluronic acid nanogel for tuberculosis treatment. J Control Release 235:112–124
Sosunov V, Mischenko V, Eruslanov B, Svetoch E, Shakina Y, Stern N, Majorov K, Sorokoumova G, Selishcheva A, Apt A (2007) Antimycobacterial activity of bacteriocins and their complexes with liposomes. J Antimicrob Chemother 59:919–925
Stenger S, Hanson DA, Teitelbaum R, Dewan P, Niazi KR, Froelich CJ, Ganz T, Thoma-Uszynski S, Melian A, Bogdan C, Porcelli SA, Bloom BR, Krensky AM, Modlin RL (1998) An antimicrobial activity of cytolytic T cells mediated by granulysin. Science 282:121–125
Toro JC, Hoffner S, Linde C, Andersson M, Andersson J, Grundstrom S (2006) Enhanced susceptibility of multidrug resistant strains of Mycobacterium tuberculosis to granulysin peptides correlates with a reduced fitness phenotype. Microbes Infect 8:1985–1993
Venge P, Bystrom J, Carlson M, Hakansson L, Karawacjzyk M, Peterson C, Seveus L, Trulson A (1999) Eosinophil cationic protein (ECP): molecular and biological properties and the use of ECP as a marker of eosinophil activation in disease. Clin Exp Allergy 29:1172–1186
Waghu FH, Gopi L, Barai RS, Ramteke P, Nizami B, Idicula-Thomas S (2014) CAMP: collection of sequences and structures of antimicrobial peptides. Nucleic Acids Res 42:D1154–D1158
Wang G (2015) Improved methods for classification, prediction, and design of antimicrobial peptides. Methods Mol Biol 1268:43–66
Wang Z, Choice E, Kaspar A, Hanson D, Okada S, Lyu SC, Krensky AM, Clayberger C (2000) Bactericidal and tumoricidal activities of synthetic peptides derived from granulysin. J Immunol 165:1486–1490
Wei L, Wu J, Liu H, Yang H, Rong M, Li D, Zhang P, Han J, Lai R (2013) A mycobacteriophage-derived trehalose-6,6′-dimycolate-binding peptide containing both antimycobacterial and anti-inflammatory abilities. FASEB J 27:3067–3077
Wenzel M, Chiriac AI, Otto A, Zweytick D, May C, Schumacher C, Gust R, Albada HB, Penkova M, Kramer U, Erdmann R, Metzler-Nolte N, Straus SK, Bremer E, Becher D, Brotz-Oesterhelt H, Sahl HG, Bandow JE (2014) Small cationic antimicrobial peptides delocalize peripheral membrane proteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 111:E1409–E1418
World Health Organization (2013) Global tuberculosis report 2013: www.who.int/tb
World Health Organization (2015) Global tuberculosis report 2015: www.who.int/tb
Yeaman MR, Yount NY (2003) Mechanisms of antimicrobial peptide action and resistance. Pharmacol Rev 55:27–55
Zasloff M (1987) Magainins, a class of antimicrobial peptides from Xenopus skin: isolation, characterization of two active forms, and partial cDNA sequence of a precursor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 84:5449–5453
Zhang J, Dyer KD, Rosenberg HF (2003) Human RNase 7: a new cationic ribonuclease of the RNase A superfamily. Nucleic Acids Res 31:602–607
Zhao X, Wu H, Lu H, Li G, Huang Q (2013) LAMP: a database linking antimicrobial peptides. PLoS One 8:e66557
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2017 Springer Nature Singapore Pte Ltd.
About this chapter
Cite this chapter
Thayil, S.M., Kesavan, A.K. (2017). Antimycobacterial Peptides. In: Sugathan, S., Pradeep, N., Abdulhameed, S. (eds) Bioresources and Bioprocess in Biotechnology. Springer, Singapore. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-10-4284-3_15
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-10-4284-3_15
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Singapore
Print ISBN: 978-981-10-4282-9
Online ISBN: 978-981-10-4284-3
eBook Packages: Biomedical and Life SciencesBiomedical and Life Sciences (R0)