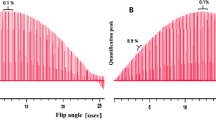
Abstract
Quantitative nuclear magnetic resonance (qNMR) with Internal Standard named as AQARI (Accurate QuAntitative NMR with Internal standard material) has been adopted by the Japanese Pharmacopoeia and the Japanese Standard of Food Additives as an official analytical method because of reliability and efficiency. We have developed Certified Reference Material (CRM) suitable for AQARI and utilitized AQARI with developed CRM to characterize analytical standards and certified reference materials (CRMs) for use in developing qNMR and chromatographic calibration standards. AQARI was used to determine the chemical purity of analytical standards for more than 500 compounds, including the following seven Japanese Pharmacopoeia crude drug products: magnolol, geniposide, paeonol, magnoflorine Iodide, saikosaponin b2, (E)-cinnamic acid and rosmarinic acid.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Department of food safety, ministry of health, labor and welfare, Introduction of the Positive List Systems for Agricultural Chemical Residues in Food (2006).
T. Ihara, T. Saito, N. Sugimoto, Synthesiology. 2: 12–22 (2009).
T. Suematsu, H. Goda, N. Sugimoto, T. Miura et al., qNMR Primary Guide. 1: 19–22 (2015).
Grzegorz Maniara, Kannan Rajamoorthi, Srinivasan Rajan, Gerald W. Stockton, Anal. Chem. 70: 4921–4928 (1998).
Saito T, Ihara T, Koike M, Kinugasa S, Fujimine Y, Nose K, Hirai, Accred Qual Assur. 14: 79–86 (2009).
The Japanese Pharmacopoeia 16th Ed., Supplement 2 (2014).
The Cabinet Office and the Ministry of Health, Labor and Welfare, Order to partially revise the Ordinance for Enforcement of the Food Sanitation Act and the Ministerial Ordinance concerning Compositional Standards, Etc. for Milk and Milk Products: Order No. 5 (2011)., and Ministry of Health, Labor and Welfare, Notification Specifications and Standards for Food and Food Additives: Notification No. 307, 011 (2011).
T. Saito, T. Ihara, T. Miura, Y. Yamada, K. Chiba, Accred Qual Assur. 16: 421–428 (2011).
General requirements for the competence of testing and calibration laboratories, ISO/IEC 17025 (2005).
The Japanese Pharmacopoeia 16th Ed., Supplement 2:18 (2014).
The Japanese Pharmacopoeia 16th Ed., Supplement 2:20 (2014).
The Japanese Pharmacopoeia 16th Ed., Supplement 2:21 (2014).
The Japanese Pharmacopoeia 16th Ed., Supplement 2:12 (2014).
Fujiwara T, Anai T, Nagayama K, J Magn Reson A. 104: 103–105 (1993).
Pauli, G. F., et al., J. Nat Prod. 75(4): 834–851 (2012).
T. Suematsu, H. Goda, N. Sugimoto, T. Miura et al., qNMR Primary Guide. 1: 50–51 (2015).
T. Suematsu, H. Goda, N. Sugimoto, T. Miura et al., qNMR Primary Guide. 1: 101–102 (2015).
T. Suematsu, H. Goda, N. Sugimoto, T. Miura et al., qNMR Primary Guide. 1: 102–103 (2015).
JEOL RESONANCE, Alice 2 for qNMR and Mestrelab Research, Mnova NMR.
Wako Pure Chemical Industries, Ltd., Product list of analytical standard of pesticide and animal drug.
(2016), http://www.wako-chem.co.jp/siyaku/info/env/pdf/positivelist_1_1.pdf.
J. Hosoe, N. Sugimoto, T. Suematsu, Y. Yamada, T. Miura, M. Hayakawa, H. Suzuki, T. Katsuhara, H. Nishimura, T. Yamasihita, Y. Goda, Pharmaceutical and Medical Device Regulatory Science. 45: 243–250 (2014).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2017 Springer Nature Singapore Pte Ltd.
About this chapter
Cite this chapter
Miura, T., Sugimoto, N., Suematsu, T., Millis, K.K., Asakura, K., Yamada, Y. (2017). Analytical Standards Purity Determination Using Quantitative Nuclear Magnetic Resonance. In: Tomioka, K., Shioiri, T., Sajiki, H. (eds) New Horizons of Process Chemistry. Springer, Singapore. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-10-3421-3_20
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-10-3421-3_20
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Singapore
Print ISBN: 978-981-10-3420-6
Online ISBN: 978-981-10-3421-3
eBook Packages: Chemistry and Materials ScienceChemistry and Material Science (R0)