Abstract
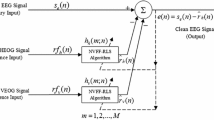
We developed a cascade of deep network and recursive least squares adaptive filter (DN-RLS) for electrooculogram (EOG) artifacts removal. The proposed method can be divided into offline stage and online stage. During the offline stage, EOG signals are used to train an DN to learn features of EOG signals. During the online stage, the learned DN is used to extract EOG artifacts from electroencephalogram (EEG), then a RLS filter is used to further remove EOG artifacts. The proposed method not only just needs few number of EEG channels in removal process, but also doesn’t need additional EOG recordings during online stage. We compared the proposed method to the independent component analysis (ICA) technique and a shallow network combined with RLS method. Experimental results show that the DN-RLS can learn features of EOG artifacts better and result in higher classification accuracy.
This project is supported by National Natural Science Foundation of China (31100709), the Shanghai Pujiang Program, China (No. 14PJ1431300) and Natural Science Foundation of Shanghai (No. 16ZR1424200).
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Nguyen, H.A.T., Musson, J., Li, F., et al.: EOG artifact removal using a wavelet neural network. Neurocomputing 97(1), 374–389 (2012)
Nijboer, F., Broermann, U.: Brain-computer interfaces for communication and control in locked-in patients. In: Graimann, B., Pfurtscheller, G., Allison, B. (eds.) Brain-Computer Interfaces. The Frontiers Collection, pp. 185–201. Springer, Heidelberg (2010)
Chen, M., Liu, Y., Zhang, L.: Classification of stroke patients’ motor imagery EEG with autoencoders in BCI-FES rehabilitation training system. In: Loo, C.K., Yap, K.S., Wong, K.W., Beng Jin, A.T., Huang, K. (eds.) ICONIP 2014, Part III. LNCS, vol. 8836, pp. 202–209. Springer, Heidelberg (2014)
Hassan, A., Song, X.: A study of kernel CSP-based motor imagery brain computer interface classification. In: Signal Processing in Medicine and Biology Symposium, pp. 1–4 (2012)
Jing, H., Wang, C.-S., Min, W.: Removal of EOG and EMG artifacts from EEG using combination of functional link neural network and adaptive neural fuzzy inference system. Neurocomputing 151, 278–287 (2015)
Devuyst, S., Dutoit, T., Ravet, T., Stenuit, P., Kerkhofs, M., Stanus, E.: Automatic processing of EEG-EOG-EMG artifacts in sleep stage classification. In: Lim, C.T., Goh, J.C.H. (eds.) ICBME 2008. IFMBE Proceedings, vol. 23, pp. 146–150. Springer, Heidelberg (2009)
Ai, G., Sato, N., Singh, B., et al.: Direction and viewing area-sensitive influence of EOG artifacts revealed in the EEG topographic pattern analysis. Cogn. Neurodyn. 10, 301–314 (2016)
Gratton, G., Coles, M.G.H., Donchin, E.: A new method for off-line removal of ocular artifact. Electroencephalogr. Clin. Neurophysiol. 55(4), 468–484 (1983)
Ghandeharion, H., Erfanian, A.: A fully automatic ocular artifact suppression from EEG data using higher order statistics: improved performance by wavelet analysis. Med. Eng. Phys. 32(7), 720–729 (2010)
Ahmed, S., Merino, L.M., Mao, Z., et al.: A deep learning method for classification of images RSVP events with EEG data. In: Global Conference on Signal and Information Processing, pp. 33–36. IEEE (2013)
Hagemann, D., Naumann, E.: The effects of ocular artifacts on (lateralized) broadband power in the EEG. Clin. Neurophysiol. Off. J. Int. Fed. Clin. Neurophysiol. 112(2), 215–231 (2001)
Pizzagalli, D.A.: Electroencephalography and high-density electrophysiological source localization, pp. 56–84 (2007)
Vincent, P., Larochelle, H., Lajoie, I., et al.: Stacked denoising autoencoders: learning useful representations in a deep network with a local denoising criterion. J. Mach. Learn. Res. 11(6), 3371–3408 (2010)
Stacked Autoencoders. http://ufldl.stanford.edu/wiki/index.php/Stacked_Autoencoders
Rueda-Plata, D., Ramos-Pollán, R., González, F.A.: Supervised greedy layer-wise training for deep convolutional networks with small datasets. In: Núñez, M., Nguyen, N.T., Camacho, D., Trawiński, B. (eds.) ICCCI 2015, Part I. LNCS, vol. 9329, pp. 275–284. Springer International Publishing, Switzerland (2015)
Ng, A.: Sparse autoencoder. CS294A Lecture Notes, vol. 72, pp. 1–19 (2011)
He, D.P., Wilson, G., Russell, C.: Removal of ocular artifacts from electro-encephalogram by adaptive filtering. Med. Biol. Eng. Comput. 42(3), 407–412 (2004)
Leeb, R., Lee, F., Keinrath, C., et al.: Brain-computer communication: motivation, aim, and impact of exploring a virtual apartment. IEEE Trans. Neural Syst. Rehabil. Eng. 15(4), 473–482 (2007)
Leeb, R., Brunner, C., Mller-Putz, G.R.: BCI Competition 2008-Graz dataset B. Graz University of Technology (2008)
Klados, M.A., Bratsas, C., Frantzidis, C., et al.: A kurtosis-based automatic system using Naïve Bayesian classifier to identify ICA components contaminated by EOG or ECG artifacts. In: XII Mediterranean Conference on Medical and Biological Engineering and Computing, vol. 29, pp. 49–52 (2010)
Schlögl, A., Flotzinger, D., Pfurtscheller, G.: Adaptive autoregressive modeling used for single-trial EEG classification. Biomed. Tech. 42(6), 162–167 (1997)
Hortal, E., Iáñez, E., Úbeda, A., María Azorín, J., Fernández, E.: Training study approaches for a SVM-based BCI: adaptation to the model vs adaptation to the user. In: Manuel Ferrández Vicente, J., Ramón Álvarez Sánchez, J., de la Paz López, F., Toledo Moreo, F. (eds.) IWINAC 2013, Part I. LNCS, vol. 7930, pp. 131–140. Springer, Heidelberg (2013)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2016 Springer Science+Business Media Singapore
About this paper
Cite this paper
Yang, B., Duan, K., Zhang, T., Zhang, Y. (2016). EOG Artifacts Reduction from EEG Based on Deep Network and Recursive Least Squares Adaptive Filter. In: Zhang, L., Song, X., Wu, Y. (eds) Theory, Methodology, Tools and Applications for Modeling and Simulation of Complex Systems. AsiaSim SCS AutumnSim 2016 2016. Communications in Computer and Information Science, vol 645. Springer, Singapore. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-10-2669-0_44
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-10-2669-0_44
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Singapore
Print ISBN: 978-981-10-2668-3
Online ISBN: 978-981-10-2669-0
eBook Packages: Computer ScienceComputer Science (R0)