Abstract:
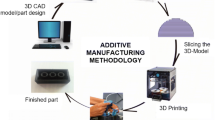
This chapter describes and discusses the carbon footprint assessment of two additive manufacturing (AM) processes. The first process is the fused deposition modeling (FDM) process. The second process is the curved FDM process which is a process that has been adopted from the FDM process itself to overcome the stairstepping effects of the traditional layer-by-layer processes. The focus of this study is to explore the carbon footprint of both the technologies and its implications.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Wohler’s Report (2010) An in-depth global study on the advances in additive manufacturing technologies and applications. ISBN:0-9754429-6-1
Wen PZ, Huang WM, Wu C-K (2008) Modified fast algorithm for STL file slicing. J Comput Appl 28:1766–1768
Gao W, et al (2015) The status, challenges, and future of additive manufacturing in engineering. Comput Aided Des 69:65–89
Wuyi ZBWSC (2004) Algorithm for rapid slicing STL model. J Beijing Univ Aeronaut Astronaut 4:011
Brown AC, De Beer D (2013) Development of a stereolithography (STL) slicing and G-code generation algorithm for an entry level 3-D printer. In: Africon, 2013. IEEE
Choi SH, Kwok FKT (1999) A memory efficient slicing algorithm for large STL files. In: Proceedings of solid freeform fabrication symposium
Tata K, et al (1998) Efficient slicing for layered manufacturing. Rapid Prototyp J 4(4):151–167
Chakraborty D, Reddy BA, Choudhury AR (2008) Extruder path generation for curved layer fused deposition modeling. Comput Aided Des 40(2):235–243
Klosterman DA, et al (1999) Development of a curved layer LOM process for monolithic ceramics and ceramic matrix composites. Rapid Prototyp J 5(2):61–71
Singamneni S, et al (2012) Modeling and evaluation of curved layer fused deposition. J Mater Process Technol 212(1):27–35
Guan HW, et al (2015) Influence of fill gap on flexural strength of parts fabricated by curved layer fused deposition modeling. Procedia Technol 20:243–248
International Organisation for Standardization (ISO) (2013) ISO/TS 14067:2013 greenhouse gases—carbon footprint of products—requirements and guidelines for quantification and communication
CLP Annual Report (2014) https://www.clpgroup.com/en/Sustainability-site/Report%20Archive%20%20Year%20Document/SR_In_Essense_2014_en.pdf
Interational Organisation for Standardization (ISO) (2006) ISO 14040: 2006 environmental management—life cycle assessment—principles and framework
Acknowledgements
We would like to thank the Hong Kong Polytechnic University for supporting this project under the code G-YM77.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2016 Springer Science+Business Media Singapore
About this chapter
Cite this chapter
Muthu, S.S., Mahesh, S.M. (2016). Carbon Footprint Assessment of Additive Manufacturing: Flat and Curved Layer-by-Layer Approaches. In: Muthu, S., Savalani, M. (eds) Handbook of Sustainability in Additive Manufacturing. Environmental Footprints and Eco-design of Products and Processes. Springer, Singapore. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-10-0606-7_5
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-10-0606-7_5
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Singapore
Print ISBN: 978-981-10-0604-3
Online ISBN: 978-981-10-0606-7
eBook Packages: Earth and Environmental ScienceEarth and Environmental Science (R0)