Abstract
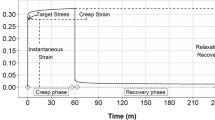
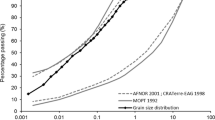
Hemp is made of highly deformable particles. Depending on the water content, on the particle size distribution, and on many other material parameters such as initial porosity and retting of the processed stalks, the mechanical behaviour of shiv in bulk can change significantly. In a compaction process, the mass per volume of the raw material increases with the applied stress and some creep or relaxation effects occur as observed in wood based materials. Hence, the mechanical properties of the bulk impact the packaging of the raw material as the shiv density inside the final mix and the in-service properties of the composite material. In this way, the bulk compressibility is primarily useful to manage the building processes, from transport of the raw material, to mixing and casting.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Arnaud, L., Gourlay, E.: Experimental study of parameters influencing mechanical properties of hemp concretes. Constr. Build. Mater. 28, 50–56 (2012)
Barbosa-Cànovas, G.V., Malavé, J., Peleg, M.: Density and compressibility of the selected food powder mixtures. J. Food Process Eng. 10(1), 1–19 (1987)
Ceyte, I.: Béton de chanvre, définition des caractéristiques mécaniques de la chènevotte. Travail de Fin d’Etudes, ENTPE (2008)
Cerezo, V.: Propriétés mécaniques, thermiques et acoustiques d’un matériau à base de particules végétales: approche expérimentale et modélisation théorique, Ph.D. Thesis, ENTPE - INSA de Lyon (2005)
Chevanan, N., Womac, A.R., Bitra, V.S.P., Igathinathane, C., Yang, Y.T., Miu, P.I., Sokhansanj, S.: Bulk density and compaction behaviour of knife mill chopped switchgrass, wheat straw, and corn stover. Bioresour. Technol. 101, 207–214 (2010)
Chtourou, H., Guillot, M., Gakwaya, A.: Modelling of metal powder compaction process using the cap model. Part I. Experimental material characterisation and validation. Int. J. Solids Struct. 39, 1059–1075 (2002)
Cooper, A.R., Eaton, L.E.: Compaction behaviour of several ceramic powders. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 45(3), 97–101 (1962)
Doremus, P., Toussaint F., Alvain O.: Simple tests standard procedure for the characterisation of green compacted powder, In: Proceedings of the Nato Advanced Research Workshop on Recent Developments in Computer Modelling of Powder Metallurgy Processes, pp. 29–41, Kiev (2001)
Emami, S., Tabil, L.G.: Friction and compression characteristics of chickpea flour and components. Powder Tech. 175, 14–21 (2007)
Jacky, J.: The coefficient of earth pressure at rest, J. Soc. Hung. Archit. Eng. pp. 355–358 (1944)
Janssen, H.A.: Versuche über Getreidedruck in Silozellen. Z. Ver. Dtsch. Ing. 39, 1045–1049 (1895)
Jones, W.D.: Fundamental Principle of Powder Metallurgy. Edward Arnold Publisher Ltd., London, UK (1960)
Jonsén, P., Häggblad, H.A.: Modelling and numerical investigation of the residual stress state in a green metal powder body. Powder Technol. 155(3), 196–208 (2005)
Kawakita, K., Lüdde, K.H.: Some considerations on powder compression equations. Powder Technol. 4, 61–68 (1971)
Leuenberger, H.: The compressibility and compactibility of powder systems. Int. J. Pharm. 12(1), 41–55 (1982)
Mani, S., Tabil, L.G., Sokhansanj, S.: Grinding performance and physical properties of wheat and barley straws, corn stover and switchgrass. Biomass Bioenergy 27, 339–352 (2004)
Modnet, P.M.: Methods and measurements group. Measurement of friction for powder compaction modelling. Powder Metall. 43(4), 364–374 (2000)
Nguyen, T.T., Picandet, V., Amziane, S., Baley, C.: Influence of compactness and hemp hurd characteristics on the mechanical properties of lime and hemp concrete. Eur. J. of Env. Civil Eng. 13, 1039–1050 (2009)
Nguyen, T.T.: Contribution à l’étude de la formulation et du procédé de fabrication d’éléments de construction en béton de chanvre. Doctoral Thesis, Université de Bretagne Sud, Ecole Doctorale SICMA, Lorient. Avaiable online: http://web.univ-ubs.fr/limatb/lab/ (2010)
Nguyen, T.T., Picandet, V., Carré, P., Lecompte, T., Amziane, S., Baley, C.: Effect of compaction on mechanical and thermal properties of hemp concrete. E. J. of Env. Civil Eng. 14, 545–560 (2010)
O’Dogherty, M.J.: A review of the mechanical behaviour of straw when compressed to high densities. J. Agric. Eng. Res. 44, 241–265 (1989)
Perrot A., Lanos C., Estellé P., Melinge Y.: Ram extrusion force for a frictional plastic material: model prediction and application to cement paste. Rheol Acta 45(4), 457–467 (2006)
Picandet, V.: Characterization of plant-based aggregates (Chap. 2). In: Amziane, S., Arnaud, L., (eds.) Bio-Aggregate-Based Building Materials: Applications to Hemp Concretes, pp. 27–74. Wiley Inc., London (2013)
Seeling, P., Wulff, J.: Pressing operation in fabrication of articles by powder metallurgy. Trans. Am. Inst. Min. Metall. Eng. 166, 492–505 (1946)
Sinka, I.C., Cunningham, J.C., Zavaliangos, A.: The effect of wall friction in the compaction of pharmaceutical tablets with curved faces: a validation study of the Drucker-Prager Cap model. Powder Technol. 133, 33–43 (2003)
Tronet, P.: Contribution à l’étude des matériaux chaux-chanvre: influence du compactage sur les propriétés, Ph.D. Thesis, Université de Bretagne-Sud (2014)
Tronet, P., Lecompte, T., Picandet, V., Baley, C.: Study of lime hemp composite precasting by compaction of fresh mix - An instrumented die to measure friction and stress state, Powder Tech. 258(14), 285–296 (2014)
Walker, E.E.: The properties of powders—part VI: the compressibility of powders. Trans. Faraday Soc. 19(1), 73–82 (1923)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2017 RILEM
About this chapter
Cite this chapter
Picandet, V. (2017). Bulk Density and Compressibility. In: Amziane, S., Collet, F. (eds) Bio-aggregates Based Building Materials . RILEM State-of-the-Art Reports, vol 23. Springer, Dordrecht. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-94-024-1031-0_5
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-94-024-1031-0_5
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Dordrecht
Print ISBN: 978-94-024-1030-3
Online ISBN: 978-94-024-1031-0
eBook Packages: EngineeringEngineering (R0)