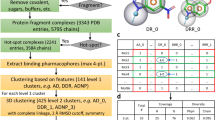
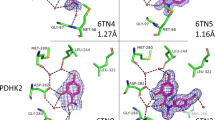
Abstract
Since its conception in the early 1990s, fragment-based drug discovery (FBDD) has become established as a powerful tool for identifying new, chemically tractable pharmacophores. Unlike traditional methods that focus primarily on initial potency, FBDD stresses efficiency of binding and exploration of a highly diverse chemical space. Small fragment library sizes (∼1,000 compounds) and the weak binding affinity of fragments have spurred the use of biophysical methods not readily applicable to screening of traditional compound libraries (greater than 100,000 compounds). X-ray crystallography is a powerful, yet under-appreciated, biophysical method for systematic identification of small molecule binding and discovery of potential inhibitory sites in a macromolecular target. Indeed, due to tremendous improvements in methodologies and technologies involved in X-ray data collection and analysis, it is now possible to collect data on a complete fragment library for a given macromolecular target during a single trip to a current generation synchrotron. Here we highlight some key insights and innovations learned from fragment screening campaigns targeting influenza and HIV-1 polymerases.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Hajduk PJ, Greer J (2007) A decade of fragment-based drug design: strategic advances and lessons learned. Nat Rev Drug Discov 6:211–219
Hesterkamp T, Whittaker M (2008) Fragment-based activity space: smaller is better. Curr Opin Chem Biol 12:260–268
Erlanson DA, Wells JA, Braisted AC (2004) Tethering: fragment-based drug discovery. Annu Rev Biophys Biomol Struct 33:199–223
Bauman JD, Patel D, Arnold E (2012) Fragment screening and HIV therapeutics. Top Curr Chem 317:181–200
Begley DW, Davies DR, Hartley RC, Hewitt SN, Rychel AL, Myler PJ, Van Voorhis WC, Staker BL, Stewart LJ (2011) Probing conformational states of glutaryl-CoA dehydrogenase by fragment screening. Acta Crystallogr Sect F: Struct Biol Cryst Commun 67:1060–1069
Howard N, Abell C, Blakemore W, Chessari G, Congreve M, Howard S, Jhoti H, Murray CW, Seavers LCA, van Montfort RLM (2006) Application of fragment screening and fragment linking to the discovery of novel thrombin inhibitors. J Med Chem 49:1346–1355
Bodoor K, Boyapati V, Gopu V, Boisdore M, Allam K, Miller J, Treleaven WD, Weldeghiorghis T, Aboul-ela F (2009) Design and implementation of an ribonucleic acid (RNA) directed fragment library. J Med Chem 52:3753–3761
Wang Y-S, Strickland C, Voigt JH, Kennedy ME, Beyer BM, Senior MM, Smith EM, Nechuta TL, Madison VS, Czarniecki M, McKittrick BA, Stamford AW, Parker EM, Hunter JC, Greenlee WJ, Wyss DF (2010) Application of fragment-based NMR screening, X-ray crystallography, structure-based design, and focused chemical library design to identify novel microM leads for the development of nM BACE-1 (beta-site APP cleaving enzyme 1) inhibitors. J Med Chem 53:942–950
Congreve M, Carr R, Murray C, Jhoti H (2003) A “rule of three” for fragment-based lead discovery? Drug Discov Today 8:876–877
Congreve M, Chessari G, Tisi D, Woodhead AJ (2008) Recent developments in fragment-based drug discovery. J Med Chem 51:3661–3680
Köster H, Craan T, Brass S, Herhaus C, Zentgraf M, Neumann L, Heine A, Klebe G (2011) A small nonrule of 3 compatible fragment library provides high hit rate of endothiapepsin crystal structures with various fragment chemotypes. J Med Chem 54:7784–7796
Zartler T (2013) What’s the fire behind the smoke? http://practicalfragments.blogspot.com/2013/04/whats-fire-behind-smoke.html. Accessed 9 Apr 2014
Jhoti H, Williams G, Rees DC, Murray CW (2013) The “rule of three” for fragment-based drug discovery: where are we now? Nat Rev Drug Discov 12:644–645
Verlinde CLMJ, Fan E, Shibata S, Zhang Z, Sun Z, Deng W, Ross J, Kim J, Xiao L, Arakaki T, Bosch J, Caruthers JM, Larson ET, LeTrong I, Napuli A, Kelley A, Mueller N, Zucker F, Van Voorhis WC, Buckner FS, Merritt EA, Hol WGJ (2009) Fragment-based cocktail crystallography by the Medical Structural Genomics of Pathogenic Protozoa Consortium. Curr Top Med Chem 9:1678–1687
Nienaber VL, Richardson PL, Klighofer V, Bouska JJ, Giranda VL, Greer J (2000) Discovering novel ligands for macromolecules using X-ray crystallographic screening. Nat Biotechnol 18:1105–1108
Hartshorn M, Murray C, Cleasby A, Frederickson M, Tickle I, Jhoti H (2005) Fragment-based lead discovery using X-ray crystallography. J Med Chem 48:403–413
Spurlino JC (2011) Fragment screening purely with protein crystallography. Methods Enzymol 493:321–356
Perryman AL, Zhang Q, Soutter HH, Rosenfeld R, McRee DE, Olson AJ, Elder JE, David Stout C (2010) Fragment-based screen against HIV protease. Chem Biol Drug Des 75:257–268
Davies TG, Tickle IJ (2011) Fragment screening using X-Ray crystallography. Top Curr Chem 317:33–59
Bauman JD, Patel D, Dharia C, Fromer M, Ahmed S, Frenkel Y, Eck JT, Ho W, Das K, Shatkin A, Arnold E (2013) Detecting allosteric sites of HIV-1 reverse transcriptase by X-ray crystallographic fragment screening. J Med Chem 56:2738–2746
Bauman JD, Patel D, Baker SF, Vijayan RSK, Xiang A, Parhi AK, Martínez-Sobrido L, Lavoie EJ, Das K, Arnold E (2013) Crystallographic fragment screening and structure-based optimization yields a new class of influenza endonuclease inhibitors. ACS Chem Biol 8:2501–2508
Bauman JD, Das K, Ho WC, Baweja M, Himmel DM, Arthur D, Clark J, Oren DA, Boyer PL, Hughes SH, Shatkin AJ, Arnold E (2008) Crystal engineering of HIV-1 reverse transcriptase for structure-based drug design. Nucleic Acids Res 36:5083–5092
Flocco MM, Mowbray SL (1994) Planar stacking interactions of arginine and aromatic side-chains in proteins. J Mol Biol 235:709–717
Kuroda DG, Bauman JD, Challa JR, Patel D, Troxler T, Das K, Arnold E, Hochstrasser RM (2013) Snapshot of the equilibrium dynamics of a drug bound to HIV-1 reverse transcriptase. Nat Chem 5:174–181
Shin G, Yost SA, Miller MT, Elrod EJ, Grakoui A, Marcotrigiano J (2012) Structural and functional insights into alphavirus polyprotein processing and pathogenesis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 109:16534–16539
Mueller-Dieckmann C, Kauffmann B, Weiss MS (2011) Trimethylamine N-oxide as a versatile cryoprotective agent in macromolecular crystallography. J Appl Crystallogr 44:433–436
Blaney J, Nienaber V, Burley SK (2006) Fragment-based lead discovery and optimisation using X- ray crystallography, computational chemistry, and high-throughput organic synthesis. In: Jahnke W, Erlanson DA (eds) Fragment-based approaches in drug discovery. Methods and principles in medicinal chemistry. Wiley–VCH, Weinheim, pp 215–248
Dalvit C, Flocco M, Veronesi M, Stockman BJ (2002) Fluorine-NMR competition binding experiments for high-throughput screening of large compound mixtures. Comb Chem High Throughput Screen 5:605–611
Tiefenbrunn T, Forli S, Happer M, Gonzalez A, Tsai Y, Soltis M, Elder JH, Olson AJ, Stout CD (2014) Crystallographic fragment – based drug discovery: use of a brominated fragment library targeting HIV protease. Chem Biol Drug Des 83:141–148
Yuan P, Bartlam M, Lou Z, Chen S, Zhou J, He X, Lv Z, Ge R, Li X, Deng T, Fodor E, Rao Z, Liu Y (2009) Crystal structure of an avian influenza polymerase PA(N) reveals an endonuclease active site. Nature 458:909–913
Dias A, Bouvier D, Crépin T, McCarthy AA, Hart DJ, Baudin F, Cusack S, Ruigrok RWH (2009) The cap-snatching endonuclease of influenza virus polymerase resides in the PA subunit. Nature 458:914–918
Dubois RM, Slavish PJ, Baughman BM, Yun M-K, Bao J, Webby RJ, Webb TR, White SW (2012) Structural and biochemical basis for development of influenza virus inhibitors targeting the PA endonuclease. PLoS Pathog 8:e1002830
Doan L, Handa B, Roberts NA, Klumpp K (1999) Metal ion catalysis of RNA cleavage by the influenza virus endonuclease. Biochemistry 38:5612–5619
Crépin T, Dias A, Palencia A, Swale C, Cusack S, Ruigrok RWH (2010) Mutational and metal binding analysis of the endonuclease domain of the influenza virus polymerase PA subunit. J Virol 84:9096–9104
Syson KK, Tomlinson CC, Chapados BRB, Sayers JRJ, Tainer JAJ, Williams NHN, Grasby JAJ (2008) Three metal ions participate in the reaction catalyzed by T5 flap endonuclease. J Biol Chem 283:28741–28746
Ivanov I, Tainer JA, McCammon JA (2007) Unraveling the three-metal-ion catalytic mechanism of the DNA repair enzyme endonuclease IV. Proc Natl Acad Sci 104:1465–1470
Sam MDM, Perona JJJ (1999) Catalytic roles of divalent metal ions in phosphoryl transfer by EcoRV endonuclease. Biochemistry 38:6576–6586
Kovall RA, Matthews BW (1999) Type II restriction endonucleases: structural, functional and evolutionary relationships. Curr Opin Chem Biol 3:578–583
Horton NC, Newberry KJ, Perona JJ (1998) Metal ion-mediated substrate-assisted catalysis in type II restriction endonucleases. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 95:13489–13494
Horton NC, Perona JJ (2004) DNA cleavage by EcoRV endonuclease: two metal ions in three metal ion binding sites. Biochemistry 43:6841–6857
Parhi AK, Xiang A, Bauman JD, Patel D, Vijayan RSK, Das K, Arnold E, Lavoie EJ (2013) Phenyl substituted 3-hydroxypyridin-2(1H)-ones: inhibitors of influenza A endonuclease. Bioorg Med Chem 21:6435–6446
Acknowledgement
EA is grateful to the National Institutes of Health for support from grants R37 AI027690 (MERIT Award) and P50 GM103368. We also thank our collaborators in RT studies, both past and present.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2015 Springer Science+Business Media Dordrecht
About this paper
Cite this paper
Bauman, J.D., Patel, D., Arnold, E. (2015). Adventures in Small Molecule Fragment Screening by X-ray Crystallography. In: Scapin, G., Patel, D., Arnold, E. (eds) Multifaceted Roles of Crystallography in Modern Drug Discovery. NATO Science for Peace and Security Series A: Chemistry and Biology. Springer, Dordrecht. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-94-017-9719-1_15
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-94-017-9719-1_15
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Dordrecht
Print ISBN: 978-94-017-9718-4
Online ISBN: 978-94-017-9719-1
eBook Packages: Biomedical and Life SciencesBiomedical and Life Sciences (R0)