Abstract
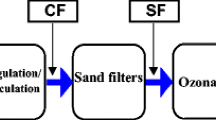
Monitoring of the various forms of natural organic matter (NOM) content (dissolved organic carbon (DOC), biodegradable organic carbon (BDOC), assimilable organic carbon (AOC)) and changes of these characteristics after the different water purification stages has been carried out in Dnieper river at different seasons. Maximum BDOC value was reached in May 2010 and was 4.1 mg/L. It has been recommended to use a rational combination of oxidation processes (ozonation) with following coagulation with the use of pressure reagent flotation and enhanced posttreatment on the biologically active carbon to produce the biologically stable water from the polluted source.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Arnold, E.G., S.C. Lenore, and D.E. Andrew. 1992. Standard methods for the examination of water and wastewater, 18th ed. Washington, DC: American Public Health Association.
Hu, J.Y., Z.S. Wang, W.J. Ng, and S.L. Ong. 1999. The effect of water treatment processes on the biological stability of potable water. Water Research 33: 2587–2592.
Raczyk-Stanisławiak, U., J. Świetlik, A. Dabrowska, and J. Nawrocki. 2004. Biodegradability of organic by-products after natural organic matter oxidation with ClO2—Case study. Water Research 38: 1044–1054.
Szlachta, M., and W. Adamski. 2009. Effect of natural organic matter removal be integrated processes: Alum coagulation and PAC-adsorption. Water Science and Technology 59(10): 1951–1957.
Trulleyova, S., and M. Rulik. 2004. Determination of biodegradable dissolved organic carbon in waters: Comparison of batch methods. Science of the Total Environment 332: 253–260.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2013 Zhejiang University Press and Springer Science+Business Media Dordrecht
About this paper
Cite this paper
Samsoni-Todorova, O., Klymenko, N., Savchyna, L. (2013). Production of Biologically Stable Safe Drinking Water from Polluted Surface Water Sources. In: Xu, J., Wu, J., He, Y. (eds) Functions of Natural Organic Matter in Changing Environment. Springer, Dordrecht. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-94-007-5634-2_162
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-94-007-5634-2_162
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Dordrecht
Print ISBN: 978-94-007-5633-5
Online ISBN: 978-94-007-5634-2
eBook Packages: Earth and Environmental ScienceEarth and Environmental Science (R0)