Abstract
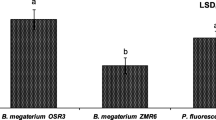
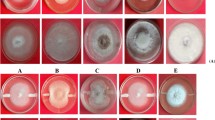
The study of root-associated bacteria and their antagonistic potential is important not only for understanding their ecological role in the rhizosphere and the interaction with plants but also for the suppression of soilborne plant pathogens. In this context, a total of 206 fluorescent pseudomonads (FPs) were isolated from rice rhizosphere from southern part of Tamil Nadu. Initially 113 isolates were found which were active against Rhizoctonia solani, of which 89 were strongly active against R. solani with zone of inhibition range from 10 to 32 mm. Production of lytic enzymes such as chitinase, cellulase, protease, amylase and pectinase was reported along with other characteristics including phosphate solubilisation and siderophore formation in 89 antagonistic fluorescent pseudomonads. Antagonistic fluorescent pseudomonads were also tested towards other fungal pathogens such as Macrophomina phaseolina, Fusarium oxysporum, Fusarium udum and Alternaria alternata. Among 89 the strain VSMKU-4046 has high antagonistic potential against R. solani. Strain VSMKU-4046 significantly controls sheath blight of rice compared to control using sclerotia of R. solani through detached leaf assay. The lesion length around the sclerotium was measured, and ShB severity was rated by the relative lesion height (RLH) method with the following formula:% RLH = 100 x Total height of lesions / Total leaf height. \(\%\text{RLH}=100\times\text{total}\text{height}\text{of}\text{lesions}/\text{total}\text{leaf}\text{height}\)
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Yang Q, Lin F, Feng S, Wang L, Pan Q. Recent progress on molecular mapping and cloning of Blast resistance genes in rice (Oryza sativa L.). Scia Agric Sin. 2009;42:1601–15.
Ou SH. Rice diseases. Kew survey: Commonwealth Mycological Institute; 1985. p. 256–368.
Padaria JC, Singh A. Molecular characterization of soil bacteria antagonistic to Rhizoctonia solani, sheath blight of rice. J Environ Sci Health B. 2009;44:397–402.
Shanmugaiah V. Biocontrol potential of phenazine-1- carboxamide producing plant growth promoting rhizobacterium, Pseudomonas aeruginosa MML2212 against sheath blight disease of rice. Ph.D. thesis, University of Madras, Chennai, India; 2007.
Shanmugaiah V, Mathivanan N, Varghese B. Purification, crystal structure and antimicrobial activity of phenazine-1-carboxamide produced by a growth-promoting biocontrol bacterium, Pseudomonas aeruginosa MML2212. J Appl Microbiol. 2010;108(703–711):703.
Defago G, Hass D. Pseudomonads as antagonists of soil borne plant pathogens: modes of action and genetic analysis. Soil Biol Biochem. 1990;6:249–92.
Egamberdiyeva D. The effect of plant growth promoting bacteria on growth and nutrient uptake of maize in two different soils. Appl Soil Ecol. 2007;36(Suppl 2–3):184–9.
Curl EA, Truelove B. The rhizosphere. Berlin/Heidelberg: Springer; 1986. p. 288.
Chaiharn M, Chunhaleuchanon S, Kozo A, Lumyong S. Screening of rhizobacteria for their plant growth promoting activities. KMITL Sci Technol J. 2008;8 suppl 1:18–23.
Han J, Sun L, Dong X, Cai Z, Sun X, Yang H, Wang Y, Song W. Characterization of a novel plant growth promoting bacteria strain Delftia tsuruhatensis HR4 both as a diazotroph and a potential biocontrol agent against various plant pathogens. Syst Appl Microbiol. 2005;28(1):66–76.
Gupta CP, Dubey RC, Kang SC, Maheshwari DK. Antibiosis mediated necrotrophic effect of Pseudomonas GRC2 against two fungal plant pathogens. Curr Sci India. 2001;81:91–4.
King EO, Ward MK, Raney DE. Two simple media for the demonstration of pyocyanin and fluorescein. J Lab Clin Med. 1954;44:301–7.
Haung MC, Hoes JA. Penetration and infection of sclerotinia sclerotiorum by coniothyrium minitans. Can J Bot. 1976;54:406–10.
Schwyn B, Neilands JB. Universal chemical assay for the detection and determination of siderophores. Anal Biochem. 1987;160(1):47–56.
Lorck H. Production of hydrocyanic acid by bacteria. Physiol Plant. 1948;1:142–6.
Patten C, Glick CR. Bacterial biosynthesis of indole-3-acetic acid. Can J Microbiol. 1996;42:207–20.
Shanmugaiah V, Ramesh S, Jayaprakashvel M, Mathivanan N. Biocontrol and plant growth promoting potential of a Pseudomonas sp. MML2212 from the rice rhizosphere. In: Zeller W, Ullrich C, editors. Proceedings for the 1st international symposium on Biological Control of Bacterial Plant Diseases. Federal Institute of Biological Control, Dormstadt, Germany; 2006. pp. 320–324.
Nagarjkumar M, Bhaskaran R, Velazhahan R. Involvement of secondary metabolites and extracellular lytic enzymes produced by Pseudomonas fluorescens in inhibition of Rhizoctonia solani, the rice sheath blight pathogen. Microbiol Res. 2004;159:73–81.
Mathivanan N, Shanmugaiah V. Management of sheath blight disease in rice by Pseudomonas aeruginosa MML2212. In: Reddy MS, Wang Qi, editors. Proceedings for the 2nd Asian PGPR Conference, 21–24 Aug 2011, Beijing, PR China; 2011.
Devi VT, Malarvizhi R, Sakthivel N, Gnanamanickam SS. Biological control of sheath blight of rice in India with antagonistic bacteria. Plant Soil. 1989;119:325–30.
Pan XB, Rush MC, Sha XY, Xie QJ, Stetina SD, Oard JH. Major gene, nonallelic sheath blight resistance from the rice cultivars “Jamine 85” and “Tequing”. Crop Sci. 1999;39:338–46.
Williams ST, et al., editors. Bergey’s manual of determinative bacteriology. 9th ed. Baltimore: Williams and Wilkins Co.; 1994.
Pikovskaya RI. Mobilization of phosphorus in soil connection with the vital activity of some microbial species. Microbiologia. 1948;17:362–70.
Acknowledgement
The authors greatly thank University Grant Commission, New Delhi (F.No.39-214/2010) (SR), for financial assistance. We also would like to acknowledge the Head, Department of Microbial Technology, the Co-ordinator, NRCBS, School of Biological Sciences, Madurai Kamaraj University, Madurai, Tamil Nadu, India.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2012 Springer India
About this paper
Cite this paper
Kumar, C.S., Harikrishnan, H., Charulatha, R., Shanmugaiah, V. (2012). Evaluation of Pseudomonas sp. VSMKU-4046 for Suppression of Sheath Blight (ShB) of Rice in Detached Leaf Assay. In: Sabu, A., Augustine, A. (eds) Prospects in Bioscience: Addressing the Issues. Springer, India. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-81-322-0810-5_33
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-81-322-0810-5_33
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, India
Print ISBN: 978-81-322-0809-9
Online ISBN: 978-81-322-0810-5
eBook Packages: Biomedical and Life SciencesBiomedical and Life Sciences (R0)