Abstract
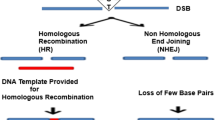
Targetable nucleases, including zinc-finger nucleases (ZFNs), transcription activator-like effector nucleases (TALENs), and clustered regularly interspaced short palindromic repeat (CRISPR)/CRISPR-associated (Cas), induce DNA double-strand breaks (DSBs) into user-defined sites. DSBs are immediately repaired through the evolutionarily conserved pathways of error-prone non-homologous end joining (NHEJ) or homology-directed repair (HDR). With the utilization of these repair processes, researchers have been able to disrupt specific genes, add exogenous DNA elements into intended genomic sites, introduce single-nucleotide substitutions, and perform many other applications. Consequently, this “genome editing” technology has revolutionized the life science field. In addition, this technology has the potential to improve agricultural products and be applicable to therapeutic use.
Here, we will introduce a brief history of targetable nuclease-mediated genome editing and the applications of the tools that the technology provides. In this chapter, we will primarily focus on ZFNs and TALENs, which are artificial proteins composed of a specific DNA-binding domain and a restriction enzyme FokI DNA-cleavage domain. We will also review the properties and construction methods of these nucleases.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aitman TJ, Critser JK, Cuppen E et al (2008) Progress and prospects in rat genetics: a community view. Nat Genet 40:516–522
Bedell VM, Wang Y, Campbell JM et al (2012) In vivo genome editing using a high-efficiency TALEN system. Nature 491:114–118
Beumer K, Bhattacharyya G, Bibikova M et al (2006) Efficient gene targeting in Drosophila with zinc-finger nucleases. Genetics 172:2391–2403
Beumer KJ, Trautman JK, Bozas A et al (2008) Efficient gene targeting in Drosophila by direct embryo injection with zinc-finger nucleases. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 105:19821–19826
Bhakta MS, Henry IM, Ousterout DG et al (2013) Highly active zinc-finger nucleases by extended modular assembly. Genome Res 23:530–538
Bibikova M, Golic M, Golic KG, Carroll D (2002) Targeted chromosomal cleavage and mutagenesis in Drosophila using zinc-finger nucleases. Genetics 161:1169–1175
Boch J, Bonas U (2010) Xanthomonas AvrBs3 family-type III effectors: discovery and function. Annu Rev Phytopathol 48:419–436
Boch J, Scholze H, Schornack S et al (2009) Breaking the code of DNA binding specificity of TAL-type III effectors. Science 326:1509–1512
Bogdanove AJ, Schornack S, Lahaye T (2010) TAL effectors: finding plant genes for disease and defense. Curr Opin Plant Biol 13:394–401
Carlson DF, Tan W, Lillico SG et al (2012) Efficient TALEN-mediated gene knockout in livestock. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 109:17382–17387
Carroll D (2014) Genome engineering with targetable nucleases. Annu Rev Biochem 83:409–439
Cermak T, Doyle EL, Christian M et al (2011) Efficient design and assembly of custom TALEN and other TAL effector-based constructs for DNA targeting. Nucleic Acids Res 39:e82–e82
Chen F, Pruett-Miller SM, Huang Y et al (2011) High-frequency genome editing using ssDNA oligonucleotides with zinc-finger nucleases. Nat Methods 8:753–755
Chen S, Oikonomou G, Chiu CN et al (2013) A large-scale in vivo analysis reveals that TALENs are significantly more mutagenic than ZFNs generated using context-dependent assembly. Nucleic Acids Res 41:2769–2778
Christian M, Cermak T, Doyle EL et al (2010) Targeting DNA double-strand breaks with TAL effector nucleases. Genetics 186:757–761
Christian ML, Demorest ZL, Starker CG et al (2012) Targeting G with TAL effectors: a comparison of activities of TALENs constructed with NN and NK repeat variable di-residues. PLoS One 7:e45383
Cong L, Zhou R, Kuo Y-C et al (2012) Comprehensive interrogation of natural TALE DNA-binding modules and transcriptional repressor domains. Nat Commun 3:968
Cong L, Ran FA, Cox D et al (2013) Multiplex genome engineering using CRISPR/Cas systems. Science 339:819–823
Cui X, Ji D, Fisher DA et al (2010) Targeted integration in rat and mouse embryos with zinc-finger nucleases. Nat Biotechnol 29:64–67
Dahlem TJ, Hoshijima K, Jurynec MJ et al (2012) Simple methods for generating and detecting locus-specific mutations induced with TALENs in the zebrafish genome. PLoS Genet 8:e1002861
Desjarlais JR, Berg JM (1992) Redesigning the DNA-binding specificity of a zinc finger protein: a data base-guided approach. Proteins 12:101–104
Ding Q, Lee Y-K, Schaefer EAK et al (2013) A TALEN genome-editing system for generating human stem cell-based disease models. Cell Stem Cell 12:238–251
Doyon Y, Vo TD, Mendel MC et al (2010) Enhancing zinc-finger-nuclease activity with improved obligate heterodimeric architectures. Nat Methods 8:74–79
Dreier B, Beerli RR, Segal DJ et al (2001) Development of zinc finger domains for recognition of the 5“-ANN-3” family of DNA sequences and their use in the construction of artificial transcription factors. J Biol Chem 276:29466–29478
Dreier B, Fuller RP, Segal DJ et al (2005) Development of zinc finger domains for recognition of the 5‘-CNN-3’ family DNA sequences and their use in the construction of artificial transcription factors. J Biol Chem 280:35588–35597
Emery DW (2011) The use of chromatin insulators to improve the expression and safety of integrating gene transfer vectors. Hum Gene Ther 22:761–774
Foley JE, Yeh J-RJ, Maeder ML et al (2009) Rapid mutation of endogenous zebrafish genes using zinc finger nucleases made by Oligomerized Pool ENgineering (OPEN). PLoS One 4:e4348
Fu Y, Foden JA, Khayter C et al (2013) High-frequency off-target mutagenesis induced by CRISPR-Cas nucleases in human cells. Nat Biotechnol 31:822–826
Gabriel R, Lombardo A, Arens A et al (2011) An unbiased genome-wide analysis of zinc-finger nuclease specificity. Nat Biotechnol 29:816–823
Greisman HA, Pabo CO (1997) A general strategy for selecting high-affinity zinc finger proteins for diverse DNA target sites. Science 275:657–661
Guilinger JP, Pattanayak V, Reyon D et al (2014) Broad specificity profiling of TALENs results in engineered nucleases with improved DNA-cleavage specificity. Nat Methods 11:429–435
Gupta A, Hall VL, Kok FO et al (2013) Targeted chromosomal deletions and inversions in zebrafish. Genome Res 23:1008–1017
Hayashi T, Sakamoto K, Sakuma T et al (2014) Transcription activator-like effector nucleases efficiently disrupt the target gene in Iberian ribbed newts (Pleurodeles waltl), an experimental model animal for regeneration. Dev Growth Differ 56:115–121
Händel E-M, Alwin S, Cathomen T (2008) Expanding or restricting the target site repertoire of zinc-finger nucleases: the inter-domain linker as a major determinant of target site selectivity. Mol Ther 17:104–111
Hockemeyer D, Soldner F, Beard C et al (2009) Efficient targeting of expressed and silent genes in human ESCs and iPSCs using zinc-finger nucleases. Nat Biotechnol 27:851–857
Hockemeyer D, Wang H, Kiani S et al (2011) Genetic engineering of human pluripotent cells using TALE nucleases. Nat Biotechnol 29:731–734
Hurt JA, Thibodeau SA, Hirsh AS et al (2003) Highly specific zinc finger proteins obtained by directed domain shuffling and cell-based selection. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 100:12271–12276
Isalan M, Klug A, Choo Y (2001) A rapid, generally applicable method to engineer zinc fingers illustrated by targeting the HIV-1 promoter. Nat Biotechnol 19:656–660
Ivics Z, Li MA, Mátés L et al (2009) Transposon-mediated genome manipulation in vertebrates. Nat Methods 6:415–422
Joung JK, Sander JD (2013) TALENs: a widely applicable technology for targeted genome editing. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 14:49–55
Kim CA, Berg JM (1996) A 2.2 A resolution crystal structure of a designed zinc finger protein bound to DNA. Nat Struct Biol 3:940–945
Kim YG, Cha J, Chandrasegaran S (1996) Hybrid restriction enzymes: zinc finger fusions to Fok I cleavage domain. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 93:1156–1160
Kim E, Kim S, Kim DH et al (2012) Precision genome engineering with programmable DNA-nicking enzymes. Genome Res 22:1327–1333
Kim Y, Kweon J, Kim A et al (2013) A library of TAL effector nucleases spanning the human genome. Nat Biotechnol 31:251–258
Klug A (2010) The discovery of zinc fingers and their applications in gene regulation and genome manipulation. Annu Rev Biochem 79:213–231
Konermann S, Brigham MD, Trevino AE et al (2013) Optical control of mammalian endogenous transcription and epigenetic states. Nature 500:472–476
Lee HJ, Kim E, Kim J-S (2010) Targeted chromosomal deletions in human cells using zinc finger nucleases. Genome Res 20:81–89
Li L, Wu LP, Chandrasegaran S (1992) Functional domains in Fok I restriction endonuclease. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 89:4275–4279
Li T, Huang S, Jiang WZ et al (2011) TAL nucleases (TALNs): hybrid proteins composed of TAL effectors and FokI DNA-cleavage domain. Nucleic Acids Res 39:359–372
Liu Q, Segal DJ, Ghiara JB, Barbas CF (1997) Design of polydactyl zinc-finger proteins for unique addressing within complex genomes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 94:5525–5530
Maeder ML, Thibodeau-Beganny S, Osiak A et al (2008) Rapid “open-source” engineering of customized zinc-finger nucleases for highly efficient gene modification. Mol Cell 31:294–301
Maeder ML, Angstman JF, Richardson ME et al (2013) Targeted DNA demethylation and activation of endogenous genes using programmable TALE-TET1 fusion proteins. Nat Biotechnol 31:1137–1142
Mahfouz MM, Li L, Shamimuzzaman M et al (2011) De novo-engineered transcription activator-like effector (TALE) hybrid nuclease with novel DNA binding specificity creates double-strand breaks. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 108:2623–2628
Mali P, Esvelt KM, Church GM (2013a) Cas9 as a versatile tool for engineering biology. Nat Methods 10:957–963
Mali P, Yang L, Esvelt KM et al (2013b) RNA-guided human genome engineering via Cas9. Science 339:823–826
Maresca M, Lin VG, Guo N, Yang Y (2012) Obligate ligation-gated recombination (ObLiGaRe): custom designed nucleases mediated targeted integration through non-homologous end joining. Genome Res 23:539–546
Mashimo T, Takizawa A, Voigt B et al (2010) Generation of knockout rats with X-linked severe combined immunodeficiency (X-SCID) using zinc-finger nucleases. PLoS One 5:e8870
Megason SG, Fraser SE (2007) Imaging in systems biology. Cell 130:784–795
Meister GE, Chandrasegaran S, Ostermeier M (2010) Heterodimeric DNA methyltransferases as a platform for creating designer zinc finger methyltransferases for targeted DNA methylation in cells. Nucleic Acids Res 38:1749–1759
Mendenhall EM, Williamson K, Reyon D et al (2013) Locus-specific editing of histone modifications at endogenous enhancers. Nat Biotechnol 31:1133–1136
Meng X, Wolfe SA (2006) Identifying DNA sequences recognized by a transcription factor using a bacterial one-hybrid system. Nat Protoc 1:30–45
Meng X, Noyes MB, Zhu LJ et al (2008) Targeted gene inactivation in zebrafish using engineered zinc-finger nucleases. Nat Biotechnol 26:695–701
Mercer AC, Gaj T, Fuller RP, Barbas CF (2012) Chimeric TALE recombinases with programmable DNA sequence specificity. Nucleic Acids Res 40:11163–11172
Meyer M, de Angelis MH, Wurst W, Kühn R (2010) Gene targeting by homologous recombination in mouse zygotes mediated by zinc-finger nucleases. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 107:15022–15026
Meyer M, Ortiz O, Hrabé de Angelis M et al (2012) Modeling disease mutations by gene targeting in one-cell mouse embryos. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 109:9354–9359
Miller JC, Holmes MC, Wang J et al (2007) An improved zinc-finger nuclease architecture for highly specific genome editing. Nat Biotechnol 25:778–785
Miller JC, Tan S, Qiao G et al (2011) A TALE nuclease architecture for efficient genome editing. Nat Biotechnol 29:143–148
Miyaoka Y, Chan AH, Judge LM et al (2014) Isolation of single-base genome-edited human iPs cells without antibiotic selection. Nat Methods 11:291–293
Moehle EA, Moehle EA, Rock JM et al (2007) Targeted gene addition into a specified location in the human genome using designed zinc finger nucleases. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 104:3055–3060
Moore M, Klug A, Choo Y (2001) Improved DNA binding specificity from polyzinc finger peptides by using strings of two-finger units. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 98:1437–1441
Moscou MJ, Bogdanove AJ (2009) A simple cipher governs DNA recognition by TAL effectors. Science 326:1501–1501
Ochiai H, Fujita K, Suzuki K-I et al (2010) Targeted mutagenesis in the sea urchin embryo using zinc-finger nucleases. Genes Cells 15:875–885
Ochiai H, Sakamoto N, Fujita K et al (2012) Zinc-finger nuclease-mediated targeted insertion of reporter genes for quantitative imaging of gene expression in sea urchin embryos. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 109:10915–10920
Ochiai H, Miyamoto T, Kanai A et al (2014) TALEN-mediated single-base-pair editing identification of an intergenic mutation upstream of BUB1B as causative of PCS (MVA) syndrome. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 111:1461–1466
Osakabe K, Osakabe Y, Toki S (2010) Site-directed mutagenesis in Arabidopsis using custom-designed zinc finger nucleases. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 107:12034–12039
Pattanayak V, Ramirez CL, Joung JK, Liu DR (2011) Revealing off-target cleavage specificities of zinc-finger nucleases by in vitro selection. Nat Methods 8:765–770
Perez EE, Wang J, Miller JC et al (2008) Establishment of HIV-1 resistance in CD4+ T cells by genome editing using zinc-finger nucleases. Nat Biotechnol 26:808–816
Pernstich C, Halford SE (2012) Illuminating the reaction pathway of the FokI restriction endonuclease by fluorescence resonance energy transfer. Nucleic Acids Res 40:1203–1213
Piganeau M, Ghezraoui H, De Cian A et al (2013) Cancer translocations in human cells induced by zinc finger and TALE nucleases. Genome Res 23:1182–1193
Porteus MH (2006) Mammalian gene targeting with designed zinc finger nucleases. Mol Ther 13:438–446
Ramirez CL, Foley JE, Wright DA et al (2008) Unexpected failure rates for modular assembly of engineered zinc fingers. Nat Methods 5:374–375
Ramirez CL, Certo MT, Mussolino C et al (2012) Engineered zinc finger nickases induce homology-directed repair with reduced mutagenic effects. Nucleic Acids Res 40:5560–5568
Reyon D, Khayter C, Regan MR et al. (2012a) Engineering designer transcription activator-like effector nucleases (TALENs) by REAL or REAL-Fast assembly. Curr Protoc Mol Biol Chapter 12:Unit 12.15. doi:10.1002/0471142727.mb1215s100
Reyon D, Tsai SQ, Khayter C et al (2012b) FLASH assembly of TALENs for high-throughput genome editing. Nat Biotechnol 30:460–465
Sakuma T, Hosoi S, Woltjen K et al (2013a) Efficient TALEN construction and evaluation methods for human cell and animal applications. Genes Cells 18:315–326
Sakuma T, Ochiai H, Kaneko T et al (2013b) Repeating pattern of non-RVD variations in DNA-binding modules enhances TALEN activity. Sci Rep 3:3379
Sander JD, Dahlborg EJ, Goodwin MJ et al (2010) Selection-free zinc-finger-nuclease engineering by context-dependent assembly (CoDA). Nat Methods 8:67–69
Sander JD, Cade L, Khayter C et al (2011) Targeted gene disruption in somatic zebrafish cells using engineered TALENs. Nat Biotechnol 29:697–698
Sanjana NE, Cong L, Zhou Y et al (2012) A transcription activator-like effector toolbox for genome engineering. Nat Protoc 7:171–192
Segal DJ, Dreier B, Beerli RR, Barbas CF (1999) Toward controlling gene expression at will: selection and design of zinc finger domains recognizing each of the 5“-GNN-3” DNA target sequences. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 96:2758–2763
Shukla VK, Doyon Y, Miller JC et al (2009) Precise genome modification in the crop species Zea mays using zinc-finger nucleases. Nature 459:437–441
Sirk SJ, Gaj T, Jonsson A et al (2014) Expanding the zinc-finger recombinase repertoire: directed evolution and mutational analysis of serine recombinase specificity determinants. Nucleic Acids Res 42:4755–4766
Smith J, Bibikova M, Whitby FG et al (2000) Requirements for double-strand cleavage by chimeric restriction enzymes with zinc finger DNA-recognition domains. Nucleic Acids Res 28:3361–3369
Soldner F, Laganière J, Cheng AW et al (2011) Generation of isogenic pluripotent stem cells differing exclusively at Two early onset Parkinson point mutations. Cell 146:318–331
Subramanya S, Kim S-S, Manjunath N, Shankar P (2010) RNA interference-based therapeutics for human immunodeficiency virus HIV-1 treatment: synthetic siRNA or vector-based shRNA? Expert Opin Biol Ther 10:201–213
Sugi T, Sakuma T, Ohtani Y, Yamamoto T (2014) Versatile strategy for isolating transcription activator-like effector nuclease-mediated knockout mutants in Caenorhabditis elegans. Dev Growth Differ 56:78–85
Szczepek M, Brondani V, Büchel J et al (2007) Structure-based redesign of the dimerization interface reduces the toxicity of zinc-finger nucleases. Nat Biotechnol 25:786–793
Tebas P, Stein D, Tang WW et al (2014) Gene editing of CCR5in autologous CD4 T cells of persons infected with HIV. N Engl J Med 370:901–910
Tesson L, Usal C, Ménoret S et al (2011) Knockout rats generated by embryo microinjection of TALENs. Nat Biotechnol 29:695–696
Tong C, Huang G, Ashton C et al (2012) Rapid and cost-effective gene targeting in rat embryonic stem cells by TALENs. J Genet Genomics 39:275–280
Urnov FD, Miller JC, Lee Y-L et al (2005) Highly efficient endogenous human gene correction using designed zinc-finger nucleases. Nature 435:646–651
Urnov FD, Rebar EJ, Holmes MC et al (2010) Genome editing with engineered zinc finger nucleases. Nat Rev Genet 11:636–646
Wang J, Friedman G, Doyon Y et al (2012) Targeted gene addition to a predetermined site in the human genome using a ZFN-based nicking enzyme. Genome Res 22:1316–1326
Wolfe SA, Nekludova L, Pabo CO (2000) DNA recognition by Cys2His2 zinc finger proteins. Annu Rev Biophys Biomol Struct 29:183–212
Wright DA, Thibodeau-Beganny S, Sander JD et al (2006) Standardized reagents and protocols for engineering zinc finger nucleases by modular assembly. Nat Protoc 1:1637–1652
Yates L, McMurray F, Zhang Y et al (2009) ENU mutagenesis as a tool for understanding lung development and disease. Biochem Soc Trans 37:838–842
Yusa K, Rashid ST, Strick-Marchand H et al (2011) Targeted gene correction of α1-antitrypsin deficiency in induced pluripotent stem cells. Nature 478:391–394
Zhang F, Cong L, Lodato S et al (2011) Efficient construction of sequence-specific TAL effectors for modulating mammalian transcription. Nat Biotechnol 29:149–153
Zou J, Maeder ML, Mali P et al (2009) Gene targeting of a disease-related gene in human induced pluripotent stem and embryonic stem cells. Cell Stem Cell 5:97–110
Zu Y, Tong X, Wang Z et al (2013) TALEN-mediated precise genome modification by homologous recombination in zebrafish. Nat Methods 10:329–331
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2015 Springer Japan
About this chapter
Cite this chapter
Ochiai, H., Yamamoto, T. (2015). Genome Editing Using Zinc-Finger Nucleases (ZFNs) and Transcription Activator-Like Effector Nucleases (TALENs). In: Yamamoto, T. (eds) Targeted Genome Editing Using Site-Specific Nucleases. Springer, Tokyo. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-4-431-55227-7_1
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-4-431-55227-7_1
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Tokyo
Print ISBN: 978-4-431-55226-0
Online ISBN: 978-4-431-55227-7
eBook Packages: Biomedical and Life SciencesBiomedical and Life Sciences (R0)