Abstract
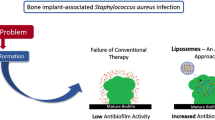
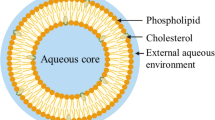
The prevention and treatment of bacterial contamination induced bone infection is challenging due to the lack of osteotropicity of available antimicrobials. This protocol describes a novel biomineral-binding liposomal (BBL) platform for the efficient delivery of antimicrobials to the skeletal tissues. The biomineral-binding lipid, alendronate-tri(ethylene- glycol)-cholesterol conjugate (ALN-TEG-Chol), was synthesized through Cu(I)-catalyzed Huisgen 1,3-dipolar cycloaddition, a versatile “click” reaction. Using ALN-TEG-Chol, BBL-containing antimicrobial oxacillin was then successfully developed using extrusion and sonication methods. Oxacillin-loaded BBL showed fast and strong binding to hydroxyapatite particles (model bone surface), and demonstrated significantly better preventive efficacy against bacterial colonization when challenged with Staphylococcus aureus when compared to that of free oxacillin and non-BBL. This suggests that the development of biomineral-binding liposomal formulations of antimicrobials may be used in conjunction with orthopedic implants or bone-grafting materials to prevent osteomyelitis associated with orthopedic surgery.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abraham SA, Waterhouse DN, Mayer LD, Cullis PR, Madden TD, Bally MB (2005) The liposomal formulation of doxorubicin. Methods Enzymol 391:71–97
Boucher H, Miller LG, Razonable RR (2010) Serious infections caused by methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus. Clin Infect Dis 51(Suppl 2):S183–S197
Diaz-Rodriguez P, Landin M, Rey-Rico A, Couceiro J, Coenye T, Gonzalez P, Serra J, Lopez-Alvarez M, Leon B (2011) Bio-inspired porous SiC ceramics loaded with vancomycin for preventing MRSA infections. J Mater Sci Mater Med 22(2):339–347
El-Husseiny M, Patel S, MacFarlane RJ, Haddad FS (2011) Biodegradable antibiotic delivery systems. J Bone Joint Surg Br 93(2):151–157
Gabizon A, Horowitz AT, Goren D, Tzemach D, Shmeeda H, Zalipsky S (2003) In vivo fate of folate-targeted polyethylene-glycol liposomes in tumor-bearing mice. Clin Cancer Res 9(17):6551–6559
Gaitanis A, Staal S (2010) Liposomal doxorubicin and nab-paclitaxel: nanoparticle cancer chemotherapy in current clinical use. Methods Mol Biol 624:385–392
Gast K, Zirwer D, Ladhoff AM, Schreiber J, Koelsch R, Kretschmer K, Lasch J (1982) Auto-oxidation-induced fusion of lipid vesicles. Biochim Biophys Acta 686(1):99–109
Hein CD, Liu XM, Wang D (2008) Click chemistry, a powerful tool for pharmaceutical sciences. Pharm Res 25(10):2216–2230
Immordino ML, Dosio F, Cattel L (2006) Stealth liposomes: review of the basic science, rationale, and clinical applications, existing and potential. Int J Nanomedicine 1(3):297–315
Jett BD, Hatter KL, Huycke MM, Gilmore MS (1997) Simplified agar plate method for quantifying viable bacteria. BioTechniques 23(4):648–650
Khoo X, O’Toole GA, Nair SA, Snyder BD, Kenan DJ, Grinstaff MW (2010) Staphylococcus aureus resistance on titanium coated with multivalent PEGylated-peptides. Biomaterials 31(35): 9285–9292
Kolb HC, Finn MG, Sharpless KB (2001) Click chemistry: diverse chemical function from a few good reactions. Angew Chem Int Ed Engl 40(11):2004–2021
Kumar VA, Fausto AK, Mitchell N, Robbins R (2007) Basic pathology, 8th edn. Elsevier Health Sciences, Philadelphia, pp 810–811
Lew DP, Waldvogel FA (1997) Osteomyelitis. N Engl J Med 336(14):999–1007
Liu XM, Thakur A, Wang D (2007) Efficient synthesis of linear multifunctional poly(ethylene glycol) by copper(I)-catalyzed Huisgen 1,3-dipolar cycloaddition. Biomacromolecules 8(9): 2653–2658
Liu XM, Wiswall AT, Rutledge JE, Akhter MP, Cullen DM, Reinhardt RA, Wang D (2008) Osteotropic beta-cyclodextrin for local bone regeneration. Biomaterials 29(11):1686–1692
Liu XM, Zhang Y, Chen F, Khutsishvili I, Fehringer EV, Marky LA, Bayles KW, Wang D (2012) Prevention of orthopedic device-associated osteomyelitis using oxacillin-containing biomineral-binding liposomes. Pharm Res 29(11):3169–3179
Ohvo-Rekila H, Ramstedt B, Leppimaki P, Slotte JP (2002) Cholesterol interactions with phospholipids in membranes. Prog Lipid Res 41(1):66–97
Pan H, Sima M, Kopeckova P, Wu K, Gao S, Liu J, Wang D, Miller SC, Kopecek J (2008) Biodistribution and pharmacokinetic studies of bone-targeting N-(2-hydroxypropyl)methacrylamide copolymer-alendronate conjugates. Mol Pharm 5(4):548–558
Rostovtsev VV, Green LG, Fokin VV, Sharpless KB (2002) A stepwise huisgen cycloaddition process: copper(I)-catalyzed regioselective “ligation” of azides and terminal alkynes. Angew Chem Int Ed Engl 41(14):2596–2599
Takahashi T, Yokogawa K, Sakura N, Nomura M, Kobayashi S, Miyamoto K (2008) Bone-targeting of quinolones conjugated with an acidic oligopeptide. Pharm Res 25(12):2881–2888
Tanaka KS, Houghton TJ, Kang T, Dietrich E, Delorme D, Ferreira SS, Caron L, Viens F, Arhin FF, Sarmiento I et al (2008) Bisphosphonated fluoroquinolone esters as osteotropic prodrugs for the prevention of osteomyelitis. Bioorg Med Chem 16(20):9217–9229
Torchilin VP (2005) Recent advances with liposomes as pharmaceutical carriers. Nat Rev Drug Discov 4(2):145–160
Wang D, Miller S, Sima M, Kopeckova P, Kopecek J (2003) Synthesis and evaluation of water-soluble polymeric bone-targeted drug delivery systems. Bioconjug Chem 14(5):853–859
Wang D, Miller SC, Kopecek J (2005) Targeted drug delivery for musculoskeletal diseases. Adv Drug Deliv Rev 57(7):935–937
Wu P, Grainger DW (2006) Drug/device combinations for local drug therapies and infection prophylaxis. Biomaterials 27(11):2450–2467
Yoshinari M, Kato T, Matsuzaka K, Hayakawa T, Shiba K (2010) Prevention of biofilm formation on titanium surfaces modified with conjugated molecules comprised of antimicrobial and titanium-binding peptides. Biofouling 26(1):103–110
Zhang S, Gangal G, Uludag H (2007) ‘Magic bullets’ for bone diseases: progress in rational design of bone-seeking medicinal agents. Chem Soc Rev 36(3):507–531
Acknowledgments
The preparation of this book chapter was supported in part by the National Institute of Arthritis and Musculoskeletal and Skin Diseases (NIAMS) of the National Institutes of Health under award number R01 AR62680. The content is solely the responsibility of the authors and does not necessarily represent the official views of the National Institutes of Health.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2018 Springer-Verlag GmbH Germany
About this entry
Cite this entry
Liu, XM., Ren, K., Wu, G., Wang, D. (2018). Preparation and Evaluation of Biomineral-Binding Antibiotic Liposomes. In: Lu, WL., Qi, XR. (eds) Liposome-Based Drug Delivery Systems. Biomaterial Engineering. Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-662-49231-4_17-1
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-662-49231-4_17-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg
Print ISBN: 978-3-662-49231-4
Online ISBN: 978-3-662-49231-4
eBook Packages: Springer Reference Chemistry and Mat. ScienceReference Module Physical and Materials ScienceReference Module Chemistry, Materials and Physics