Abstract
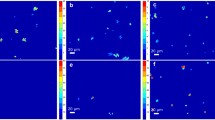
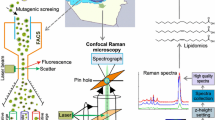
The environmental impacts from consumption of fossil fuels have raised interest in finding renewable energy resources throughout the globe. Much focus has been placed on optimizing microalgae to efficiently produce compounds that can substitute for fossil fuels. However, the path to achieving economical feasibility of this substitution is likely to require strain optimization through mutagenesis screens as well as other available approaches and tools. Rapid characterization of the type of fatty acid expressed at a single-cell level can help identify screened cells with the desired lipid characteristics such as chain length and saturation status. Confocal Raman microscopy is a powerful tool for physicochemical characterization of biological samples. It enables single-cell, in vivo monitoring of various cellular components in a rapid, quantitative, label-free, and nondestructive manner. In this chapter, we describe recent advances in this method, which have resulted in remarkable enhancements in the sensitivity, specificity, and spatiotemporal resolution of the technique. We utilize this technique for analyzing lipid content of algal isolates obtained through a mutagenesis screen of the green alga, Chlamydomonas reinhardtii, for increased lipid production at the single-cell level. Our results demonstrate cell-to-cell variation in structural features of expressed lipids among the screened C. reinhardtii mutants, while clonal isolates show little to no variability in expressed lipids. The lack of stochasticity in expression of lipids in clonal populations of C. reinhardtii is a desired feature when accompanied by expression of fatty acids suitable for use as biofuel feedstock.
R. Abdrabu, S.K. Sharma, B. Khraiwesh and K. Jijakli—These authors contributed equally to this work.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
Notes
- 1.
We note that the accumulated lipids are expected to be in the from triacylglycerides [45].
References
Castruita M, Casero D, Karpowicz SJ, Kropat J, Vieler A, Hsieh SI, Yan W, Cokus S, Loo JA, Benning C, Pellegrini M, Merchant SS (2011) Systems biology approach in Chlamydomonas reveals connections between copper nutrition and multiple metabolic steps. Plant Cell. doi:10.1105/tpc.111.084400
Lv H, Qu G, Qi X, Lu L, Tian C, Ma Y (2013) Transcriptome analysis of Chlamydomonas reinhardtii during the process of lipid accumulation. Genomics 101(4):229–237. doi:10.1016/j.ygeno.2013.01.004
Merchant SS, Prochnik SE, Vallon O, Harris EH, Karpowicz SJ, Witman GB, Terry A, Salamov A, Fritz-Laylin LK, Marechal-Drouard L, Marshall WF, Qu LH, Nelson DR, Sanderfoot AA, Spalding MH, Kapitonov VV, Ren Q, Ferris P, Lindquist E, Shapiro H, Lucas SM, Grimwood J, Schmutz J, Cardol P, Cerutti H, Chanfreau G, Chen CL, Cognat V, Croft MT, Dent R, Dutcher S, Fernandez E, Fukuzawa H, Gonzalez-Ballester D, Gonzalez-Halphen D, Hallmann A, Hanikenne M, Hippler M, Inwood W, Jabbari K, Kalanon M, Kuras R, Lefebvre PA, Lemaire SD, Lobanov AV, Lohr M, Manuell A, Meier I, Mets L, Mittag M, Mittelmeier T, Moroney JV, Moseley J, Napoli C, Nedelcu AM, Niyogi K, Novoselov SV, Paulsen IT, Pazour G, Purton S, Ral JP, Riano-Pachon DM, Riekhof W, Rymarquis L, Schroda M, Stern D, Umen J, Willows R, Wilson N, Zimmer SL, Allmer J, Balk J, Bisova K, Chen CJ, Elias M, Gendler K, Hauser C, Lamb MR, Ledford H, Long JC, Minagawa J, Page MD, Pan J, Pootakham W, Roje S, Rose A, Stahlberg E, Terauchi AM, Yang P, Ball S, Bowler C, Dieckmann CL, Gladyshev VN, Green P, Jorgensen R, Mayfield S, Mueller-Roeber B, Rajamani S, Sayre RT, Brokstein P, Dubchak I, Goodstein D, Hornick L, Huang YW, Jhaveri J, Luo Y, Martinez D, Ngau WC, Otillar B, Poliakov A, Porter A, Szajkowski L, Werner G, Zhou K, Grigoriev IV, Rokhsar DS, Grossman AR (2007) The Chlamydomonas genome reveals the evolution of key animal and plant functions. Science 318(5848):245–250. doi:10.1126/science.1143609
Hannon M, Gimpel J, Tran M, Rasala B, Mayfield S (2010) Biofuels from algae: challenges and potential. Biofuels 1(5):763–784
Radakovits R, Jinkerson RE, Darzins A, Posewitz MC (2010) Genetic engineering of algae for enhanced biofuel production. Eukaryot Cell 9(4):486–501. doi:10.1128/EC.00364-09
Wijffels RH, Barbosa MJ (2010) An outlook on microalgal biofuels. Science 329(5993):796–799. doi:10.1126/science.1189003
Jijakli K, Abdrabu R, Khraiwesh B, Nelson D, Koussa J, Salehi-Ashtiani K (2015) Molecular genetic techniques for algal bioengineering. In: Moheimani NR, McHenry MP, de Boer K, Bahri PA (eds) Biomass and biofuels from microalgae. Biofuel and biorefinery technologies, vol 2. Springer, Cham, pp 155–171. doi:10.1007/978-3-319-16640-7_9
Khraiwesh B, Jijakli K, Swift J, Chaiboonchoe A, Abdrabu R, Chao P-W, Yen L, Salehi-Ashtiani K (2015) Prospective applications of synthetic biology for algal bioproduct optimization. In: Moheimani NR, McHenry MP, de Boer K, Bahri PA (eds) Biomass and biofuels from microalgae. Biofuel and biorefinery technologies, vol 2. Springer, Cham, pp 137–154. doi:10.1007/978-3-319-16640-7_8
Salehi-Ashtiani K, Koussa J, Dohai B, Chaiboonchoe A, Cai H, Dougherty KD, Nelson D, Jijakli K, Khraiwesh B (2015) Toward applications of genomics and metabolic modeling to improve algal biomass productivity. In: Moheimani NR, McHenry MP, de Boer K, Bahri PA (eds) Biomass and biofuels from microalgae. Biofuel and biorefinery technologies, vol 2. Springer, Switzerland, pp 173–189. doi:10.1007/978-3-319-16640-7_10
Koussa J, Chaiboonchoe A, Salehi-Ashtiani K (2014) Computational approaches for microalgal biofuel optimization: a review. Biomed Res Int 2014:649453. doi:10.1155/2014/649453
Fagerer SR, Schmid T, Ibanez AJ, Pabst M, Steinhoff R, Jefimovs K, Urban PL, Zenobi R (2013) Analysis of single algal cells by combining mass spectrometry with Raman and fluorescence mapping. Analyst 138(22):6732–6736. doi:10.1039/C3AN01135F
Wu H, Volponi JV, Oliver AE, Parikh AN, Simmons BA, Singh S (2011) In vivo lipidomics using single-cell Raman spectroscopy. Proc Natl Acad Sci 108(9):3809–3814. doi:10.1073/pnas.1009043108
Popescu G, Park K, Mir M, Bashir R (2014) New technologies for measuring single cell mass. Lab Chip 14(4):646–652. doi:10.1039/c3lc51033f
Fritzsch FSO, Dusny C, Frick O, Schmid A (2012) Single-cell analysis in biotechnology, systems biology, and biocatalysis. Annu Rev Chem Biomol Eng 3(1):129–155. doi:10.1146/annurev-chembioeng-062011-081056
Lindstrom S, Andersson-Svahn H (2010) Overview of single-cell analyses: microdevices and applications. Lab Chip 10(24):3363–3372. doi:10.1039/C0LC00150C
Sweedler J, Arriaga E (2007) Single cell analysis. Anal Bioanal Chem 387(1):1–2. doi:10.1007/s00216-006-0921-4
Lange BM (2005) Single-cell genomics. Curr Opin Plant Biol 8(3):236–241. doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.pbi.2005.03.015
Saliba AE, Westermann AJ, Gorski SA, Vogel J (2014) Single-cell RNA-seq: advances and future challenges. Nucleic Acids Res 42(14):8845–8860. doi:10.1093/nar/gku555
Woyke T, Jarett J (2015) Function-driven single-cell genomics. Microb Biotechnol 8(1):38–39. doi:10.1111/1751-7915.12247
Bonke M, Turunen M, Sokolova M, Vähärautio A, Kivioja T, Taipale M, Björklund M, Taipale J (2013) Transcriptional networks controlling the cell cycle. G3: Genes Genomes Genet 3(1):75–90. doi:10.1534/g3.112.004283
Ghazalpour A, Bennett B, Petyuk VA, Orozco L, Hagopian R, Mungrue IN, Farber CR, Sinsheimer J, Kang HM, Furlotte N, Park CC, Wen PZ, Brewer H, Weitz K, Camp DG 2nd, Pan C, Yordanova R, Neuhaus I, Tilford C, Siemers N, Gargalovic P, Eskin E, Kirchgessner T, Smith DJ, Smith RD, Lusis AJ (2011) Comparative analysis of proteome and transcriptome variation in mouse. PLoS Genet 7(6):e1001393. doi:10.1371/journal.pgen.1001393
Nagaraj N, Wisniewski JR, Geiger T, Cox J, Kircher M, Kelso J, Paabo S, Mann M (2011) Deep proteome and transcriptome mapping of a human cancer cell line. Mol Syst Biol 7:548. doi:10.1038/msb.2011.81
Washburn MP, Koller A, Oshiro G, Ulaszek RR, Plouffe D, Deciu C, Winzeler E, Yates JR 3rd (2003) Protein pathway and complex clustering of correlated mRNA and protein expression analyses in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 100(6):3107–3112. doi:10.1073/pnas.0634629100
Walley JW, Shen Z, Sartor R, Wu KJ, Osborn J, Smith LG, Briggs SP (2013) Reconstruction of protein networks from an atlas of maize seed proteotypes. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 110(49):E4808–E4817. doi:10.1073/pnas.1319113110
Tang F, Lao K, Surani MA (2011) Development and applications of single-cell transcriptome analysis. Nat Methods 8(4 Suppl):S6–11. doi:10.1038/nmeth.1557
Hebenstreit D (2012) Methods, challenges and potentials of single cell RNA-seq. Biology (Basel) 1(3):658–667. doi:10.3390/biology1030658
Petry R, Schmitt M, Popp J (2003) Raman spectroscopy—a prospective tool in the life sciences. Chemphyschem: Eur J Chem Phys Phys Chem 4:14–30. doi:10.1002/cphc.200390004
Li M, Yang L, Bai Y, Liu H (2014) Analytical methods in lipidomics and their applications. Anal Chem 86:161–175. doi:10.1021/ac403554h
Pořízka P, Prochazková P, Prochazka D, Sládková L, Novotný J, Petrilak M, Brada M, Samek O, Pilát Z, Zemánek P, Adam V, Kizek R, Novotný K, Kaiser J (2014) Algal biomass analysis by laser-based analytical techniques—a review. Sensors 14:17725–17752. doi:10.3390/s140917725
Wei X, Jie D, Cuello JJ, Johnson DJ, Qiu Z, He Y (2014) Microalgal detection by Raman microspectroscopy. TrAC Trends Anal Chem 53:33–40. doi:10.1016/j.trac.2013.09.012
Wu H, Volponi JV, Oliver AE, Parikh AN, Simmons BA, Singh S (2011) In vivo lipidomics using single-cell Raman spectroscopy. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 108:3809–3814. doi:10.1073/pnas.1009043108
Hosokawa M, Ando M, Mukai S, Osada K, Yoshino T, Hamaguchi H-O, Tanaka T (2014) In vivo live cell imaging for the quantitative monitoring of lipids by using Raman microspectroscopy. Anal Chem 86:8224–8230
Heraud P, Beardall J, McNaughton D, Wood BR (2007) In vivo prediction of the nutrient status of individual microalgal cells using Raman microspectroscopy. FEMS Microbiol Lett 275:24–30. doi:10.1111/j.1574-6968.2007.00861.x
Kaczor A, Turnau K, Baranska M (2011) In situ Raman imaging of astaxanthin in a single microalgal cell. Analyst 136:1109–1112. doi:10.1039/c0an00553c
Li S, Li L, Zeng Q, Zhang Y, Guo Z, Liu Z, Jin M, Su C, Lin L, Xu J, Liu S (2015) Characterization and noninvasive diagnosis of bladder cancer with serum surface enhanced Raman spectroscopy and genetic algorithms. Sci Rep 5. doi:10.1038/srep09582
Sathyavathi R, Saha A, Soares JS, Spegazzini N, McGee S, Rao Dasari R, Fitzmaurice M, Barman I (2015) Raman spectroscopic sensing of carbonate intercalation in breast microcalcifications at stereotactic biopsy. Sci Rep 5. doi:10.1038/srep09907
Tolstik T, Marquardt C, Beleites C, Matthäus C, Bielecki C, Bürger M, Krafft C, Dirsch O, Settmacher U, Popp J, Stallmach A (2015) Classification and prediction of HCC tissues by Raman imaging with identification of fatty acids as potential lipid biomarkers. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol 141(3):407–418. doi:10.1007/s00432-014-1818-9
Christian K, Johanna M, Werner A, Kathrin B, Tesfay GM, Robert H, Abbas A, Stefan W, Andreas B, Wilhelm NF, Florian S (2014) Raman difference spectroscopy: a non-invasive method for identification of oral squamous cell carcinoma. Biomed Opt Express 5(9):3252–3265. doi:10.1364/BOE.5.003252
von Erlach TC, Hedegaard MAB, Stevens MM (2015) High resolution Raman spectroscopy mapping of stem cell micropatterns. Analyst 140(6):1798–1803. doi:10.1039/C4AN02346C
Spiro TG (1974) Resonance Raman spectroscopy. New structure probe for biological chromophores. Acc Chem Res 7:339–344. doi:10.1021/ar50082a004
Kneipp K, Kneipp H, Itzkan I, Dasari RR, Feld MS (2002) Surface-enhanced Raman scattering and biophysics. J Phys: Condens Matter 14:R597–R624. doi:10.1088/0953-8984/14/18/202
Puppels GJ, Mul FFMD, Otto C, Greve J, Robert-Nicoud M, Arndt-Jovin DJ, Jovin TM (1990) Studying single living cells and chromosomes by confocal Raman microspectroscopy. Nature 347:301–303
Freudiger CW, Min W, Saar BG, Lu S, Holtom GR, He C, Tsai JC, Kang JX, Xie XS (2008) Label-free biomedical imaging with high sensitivity by stimulated Raman scattering microscopy. Science (New York, N.Y.) 322. doi:10.1126/science.1165758
Le TT, Yue S, Cheng J-X (2010) Shedding new light on lipid biology with coherent anti-Stokes Raman scattering microscopy. J Lipid Res 51:3091–3102. doi:10.1194/jlr.R008730
Merchant SS, Kropat J, Liu B, Shaw J, Warakanont J (2012) TAG, you’re it! Chlamydomonas as a reference organism for understanding algal triacylglycerol accumulation. Curr Opin Biotechnol 23(3):352–363. doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.copbio.2011.12.001
Gorman DS, Levine RP (1965) Cytochrome f and plastocyanin: their sequence in the photosynthetic electron transport chain of Chlamydomonas reinhardii. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 54(6):1665–1669
Small GD, Greimann CS (1977) Photoreactivation and dark repair of ultraviolet light-induced pyrimidine dimers in chloroplast DNA. Nucleic Acids Res 4(8):2893–2902
Tillich UM, Lehmann S, Schulze K, Duhring U, Frohme M (2012) The optimal mutagen dosage to induce point-mutations in Synechocystis sp. PCC6803 and its application to promote temperature tolerance. PLoS ONE 7(11):e49467. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0049467
Zayadan BK, Purton S, Sadvakasova AK, Userbaeva AA, Bolatkhan K (2014) Isolation, mutagenesis, and optimization of cultivation conditions of microalgal strains for biodiesel production. Russ J Plant Physiol 61(1):124–130. doi:10.1134/S102144371401018X
Hyka P, Lickova S, Přibyl P, Melzoch K, Kovar K (2013) Flow cytometry for the development of biotechnological processes with microalgae. Biotechnol Adv 31(1):2–16. doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.biotechadv.2012.04.007
Sharma et al (2015) Biotechnol Biofuels 8:164. doi:10.1186/s13068-015-0349-1
Terashima M, Freeman ES, Jinkerson RE, Jonikas MC (2015) A fluorescence-activated cell sorting-based strategy for rapid isolation of high-lipid Chlamydomonas mutants. Plant J 81(1):147–159. doi:10.1111/tpj.12682
Xie B, Stessman D, Hart JH, Dong H, Wang Y, Wright DA, Nikolau BJ, Spalding MH, Halverson LJ (2014) High-throughput fluorescence-activated cell sorting for lipid hyperaccumulating Chlamydomonas reinhardtii mutants. Plant Biotechnol J 12(7):872–882. doi:10.1111/pbi.12190
Brennan L, Blanco Fernández A, Mostaert AS, Owende P (2012) Enhancement of BODIPY505/515 lipid fluorescence method for applications in biofuel-directed microalgae production. J Microbiol Methods 90(2):137–143. doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.mimet.2012.03.020
Cooper MS, Hardin WR, Petersen TW, Cattolico RA (2010) Visualizing “green oil” in live algal cells. J Biosci Bioeng 109(2):198–201. doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.jbiosc.2009.08.004
Hyka P, Lickova S, Přibyl P, Melzoch K, Kovar K (2013) Flow cytometry for the development of biotechnological processes with microalgae. Biotechnol Adv 31:2–16
Meier M, Wokaun A, Vo-Dinh T (1985) Silver particles on stochastic quartz substrates providing tenfold increase in Raman enhancement. J Phys Chem 89(10):1843–1846. doi:10.1021/j100256a002
Kim S, Kim H, Ko D, Yamaoka Y, Otsuru M, Kawai-Yamada M, Ishikawa T, Oh H-M, Nishida I, Li-Beisson Y, Lee Y (2013) Rapid induction of lipid droplets in Chlamydomonas reinhardtii and Chlorella vulgaris by Brefeldin A. PLoS ONE 8:e81978. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0081978
Kobayashi N, Noel E, Barnes A, Rosenberg J, DiRusso C, Black P, Oyler GA (2013) Rapid detection and quantification of triacylglycerol by HPLC-ELSD in Chlamydomonas reinhardtii and Chlorella strains. Lipids 48:1035–1049. doi:10.1007/s11745-013-3828-9
Msanne J, Xu D, Reddy A, Casas-mollano JA, Awada T, Cahoon EB, Cerutti H (2012) Metabolic and gene expression changes triggered by nitrogen deprivation in the photoautotrophically grown microalgae Chlamydomonas reinhardtii and Coccomyxa sp. C-169. Phytochemistry 75:50–59. doi:10.1016/j.phytochem.2011.12.007
Siaut M, Cuiné S, Cagnon C, Fessler B, Nguyen M, Carrier P, Beyly A, Beisson F, Triantaphylidès C, Li-beisson Y, Peltier G (2011) Oil accumulation in the model green alga Chlamydomonas reinhardtii: characterization, variability between common laboratory strains and relationship with starch reserves. BMC Biotechnol 11:7. doi:10.1186/1472-6750-11-7
Luo Q, Li Y, Wang W, Fei X, Deng X (2015) Genome-wide survey and expression analysis of Chlamydomonas reinhardtii U-box E3 ubiquitin ligases (CrPUBs) reveal a functional lipid metabolism module. PLoS ONE 10(3):e0122600. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0122600
Bielskienė K, Bagdonienė L, Mozūraitienė J, Kazbarienė B, Janulionis E (2015) E3 ubiquitin ligases as drug targets and prognostic biomarkers in melanoma. Medicina 51(1):1–9. doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.medici.2015.01.007
Acknowledgments
Financial support for this work was provided by New York University Abu Dhabi (NYUAD) Institute grant G1205, NYUAD Research Enhancement Fund AD060, and NYUAD Faculty Research Funds (AD060, VP012, and AD008).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2016 Springer-Verlag Berlin Heidelberg
About this chapter
Cite this chapter
Abdrabu, R. et al. (2016). Single-Cell Characterization of Microalgal Lipid Contents with Confocal Raman Microscopy. In: Tseng, FG., Santra, T. (eds) Essentials of Single-Cell Analysis. Series in BioEngineering. Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-662-49118-8_14
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-662-49118-8_14
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg
Print ISBN: 978-3-662-49116-4
Online ISBN: 978-3-662-49118-8
eBook Packages: EngineeringEngineering (R0)