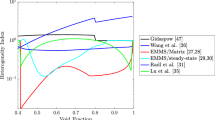
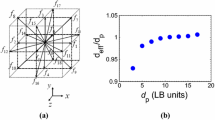
Abstract
The characterization of fluidized beds is still a challenging task for macroscopic modeling issues and industrial applications. The macroscopic models require to be fed with parameters or laws that are not well understood or even impossible to estimate as soon as the solid fraction is larger than 0.1. The aim of the present work is to investigate Direct Numerical Simulation [1] of unsteady particle flows in order to solve all the time and space scales of the flow and the particles and to allow for the estimate of unknown macroscopic or stochastic characteristics of the flow. In the DNS, the particles are fully resolved, i.e. the particle diameter is larger than the grid size and to the smallest hydrodynamic scale. A benchmark experimental fluidized bed [2] is simulated and analyzed in terms of macroscopic and Lagrangian characteristics. Comparisons of numerical solutions to measurements are achieved with success.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Preview
Unable to display preview. Download preview PDF.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Vincent, S., Brändle de Motta, J.C., Sarthou, A., Estivalezes, J.-L., Simonin, O., Climent, E.: A Lagrangian VOF tensorial penalty method for the DNS of resolved particle-laden flows. Under Correction in Journal of Computational Physics (2012)
Aguilar Corona, A.: Agitation of particles in a liquid fluidized bed. Experimental study. PhD thesis, Toulouse University (2008)
Ferrante, A., Elghobashi, S.: On the physical mechanisms of two-way coupling in particle-laden isotropic turbulence. Physics of Fluids 15, 315–329 (2003)
Ahmed, A.M., Elghobashi, S.: Direct numerical simulation of particle dispersion in homogeneous turbulent shear flows. Physics of Fluids 13, 3346–3364 (2001)
Fede, P., Simonin, O.: Numerical study of the subgrid fluid turbulence effects on the statistics of heavy colliding particles. Physics of Fluids 18, 45103–45120 (2006)
Hu, H.H., Joseph, D.D., Crochet, M.J.: Direct Simulation of Fluid Particle Motions. Theoretical and Computational Fluid Mechanics 3, 285–306 (1992)
Fadlun, E.A., Verzicco, R., Orlandi, P., Mohd-Yusofz, J.: Combined Immersed-Boundary Finite-Difference Methods for Three-Dimensional Complex Flow Simulations. Journal of Computational Physics 161, 35–60 (2000)
Kim, J., Kim, D., Choi, H.: An immersed-boundary finite-volume method for simulations of flow in complex geometries. Journal of Computational Physics 171, 132–150 (2001)
Takagi, S., Oguz, H.N., Zhang, Z., Prosperetti, A.: PHYSALIS: a new method for particle simulation Part II: two-dimensional Navier-Stokes flow around cylinders. Journal of Computational Physics 187, 371–390 (2003)
Coquerelle, M., Cottet, G.H.: A vortex level set method for the two-way coupling of an incompressible fluid with colliding rigid bodies. Journal of Computational Physics 227, 9121–9137 (2008)
Simeonov, J.A., Calantoni, J.: A pressure boundary integral method for direct fluid-particle simulations on Cartesian grids. Journal of Computational Physics 230, 1749–1765 (2011)
Höfler, K., Schwarzer, S.: Navier-Stokes simulation with constraint forces: Finite-difference method for particle-laden flows and complex geometries. Physical Review E 61, 7146–7160 (2000)
Maury, B.: Direct simulations of 2D fluid-particle flows in biperiodic domains. Journal of Computational Physics 156, 325–351 (1999)
Glowinski, R., Pan, T.W., Hesla, T.I., Joseph, D.D., Périaux, J.: A fictitious domain approach to the direct numerical simulation of incompressible viscous flow past moving rigid bodies: application to particulate flow. Journal of Computational Physics 169, 363–426 (2001)
Zhang, Z., Prosperetti, A.: A second-order method for three-dimensional particle simulation. Journal of Computational Physics 210, 292–324 (2005)
Uhlmann, M.: An immersed boundary method with direct forcing for the simulation of particulate flows. Journal of Computational Physics 209(2), 448–476 (2005)
Uhlmann, M.: Interface-resolved direct numerical simulation of vertical particulate channel flow in the turbulent regime. Physics of Fluids 20(5), 053305 (2008)
Ten Cate, A., Derksen, J.J., Portela, L.M., Van Der Akker, E.A.: Fully resolved simulations of colliding monodisperse spheres in forced isotropic turbulence. Journal of Fluid Mechanics 519, 233–271 (2004)
Gao, H., Wang, L.-P.: Lattice Boltzmann simulation of turbulent flow laden with finite-size particles. In: Proceedings of the 7th International Conference on Multiphase Flows, ICMF 2010 (2010)
Lucci, F., Ferrante, A., Elghobashi, S.: Modulation of isotropic turbulence by particles of Taylor length-scale size. Journal of Fluid Mechanics 650, 5–55 (2010)
Lucci, F., Ferrante, A., Elghobashi, S.: Is Stokes number an appropriate indicator for turbulence modulation by particles of Taylor-length-scale size? Physics of Fluids 23, 025101:1–025101:7 (2011)
Ritz, J.-B., Caltagirone, J.P.: A numerical continuous model for the hydrodynamics of fluid particle systems. International Journal for Numerical Methods in Fluids 30, 1067–1090 (1999)
Randrianarivelo, T.N., Pianet, G., Vincent, S., Caltagirone, J.-P.: Numerical modelling of the solid particle motion using a new penalty method. International Journal for Numerical Methods in Fluids 47, 1245–1251 (2005)
Randrianarivelo, T.N., Vincent, S., Simonin, O., Caltagirone, J.-P.: A DNS approach dedicated to the analysis of fluidized beds. Fluid Mechanics Applications 81, 207–214 (2007)
Khadra, K., Angot, P., Parneix, S., Caltagirone, J.P.: Fictitious domain approach for numerical modelling of Navier-Stokes equations. International Journal for Numerical Methods in Fluids 34, 651–684 (2000)
Richardson, J.F., Zaki, W.N.: Sedimentation and fluidization. Part 1. Transactions of the Institution of Chemical Engineering 32, 35–53 (1954)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2014 Springer-Verlag Berlin Heidelberg
About this paper
Cite this paper
Vincent, S., Estivalezes, J.L., de Motta, J.C.B., Simonin, O., Masbernat, O. (2014). Analysis of Unsteady Lagrangian and Eulerian Characteristics of a Liquid Fluidized Bed by Direct Numerical Simulation. In: Deville, M., Estivalezes, JL., Gleize, V., Lê, TH., Terracol, M., Vincent, S. (eds) Turbulence and Interactions. Notes on Numerical Fluid Mechanics and Multidisciplinary Design, vol 125. Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-662-43489-5_21
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-662-43489-5_21
Publisher Name: Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg
Print ISBN: 978-3-662-43488-8
Online ISBN: 978-3-662-43489-5
eBook Packages: Physics and AstronomyPhysics and Astronomy (R0)