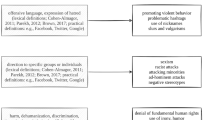
Zusammenfassung
From a computer science perspective, addressing on-line hate speech is a challenging task that is attracting the attention of both industry (mainly social media platform owners) and academia. In this chapter, we provide an overview of state-of-the-art data-science approaches – how they define hate speech, which tasks they solve to mitigate the phenomenon, and how they address these tasks. We limit our investigation mostly to (semi-)automatic detection of hate speech, which is the task that the majority of existing computer science works focus on. Finally, we summarize the challenges and the open problems in the current data-science research and the future directions in this field. Our aim is to prepare an easily understandable report, capable to promote the multidisciplinary character of hate speech research. Researchers from other domains (e.g., psychology and sociology) can thus take advantage of the knowledge achieved in the computer science domain but also contribute back and help improve how computer science is addressing that urgent and socially relevant issue which is the prevalence of hate speech in social media.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
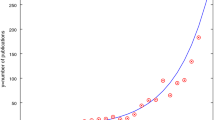
Similar content being viewed by others
References
CBS News (2018, May 1). Facebook Testing out a “Hate Speech”-Button, Inadvertently Launches its Live. CBS News. Retrieved from https://www.cbsnews.com/news/facebook-hate-speech-button-accidentally-launches-2018-05-01.
Chandra, N., Khatri, S. K., & Som, S. (2017). Anti Social Comment Classification Based on kNN Algorithm. In Proceedings of International Conference on Reliability, Infocom Technologies and Optimization – ICRITO 2017 (S. 348–354). Noida, India: IEEE.
Chatzakou, D., Kourtellis, N., Blackburn, J., De Cristofaro, E., Stringhini, G., & Vakali, A. (2017). Hate is not Binary: Studying Abusive Behavior of #GamerGate on Twitter. In Proceedings of the 28th ACM Conference on Hypertext and Social Media – HT 2017 (S. 65–74). New York, USA: ACM Press.
Council of the European Union (2008). Council Framework Decision 2008/913/JHA. Retrieved from https://eur-lex.europa.eu/legal-content/en/ALL/?uri=CELEX%3A32008F0913.
Davidson, T., Warmsley, D., Macy, M., & Weber, I. (2017). Automated Hate Speech Detection and the Problem of Offensive Language. In Proceedings of the 11th International Conference on Web and Social Media – ICWSM 2017 (S. 512–515). Montréal, Canada: AAAI.
del Rey, A. M. (2015). Mathematical Modeling of the Propagation of Malware: A Review. Security and Communication Networks, 8, (S. 2561–2579).
European Union Agency for Fundamental Rights (2016). Ensuring Justice for Hate Crime Victims: Professional Perspectives. Retrieved from https://fra.europa.eu/en/publication/2016/ensuring-justice-hate-crime-victims-professional-perspectives.
Facebook (2020). Community standards – Hate speech. Retrieved from https://facebook.com/communitystandards/hate_speech.
Fortuna, P., & Nunes, S. (2018). A Survey on Automatic Detection of Hate Speech in Text. ACM Computing Surveys, 51(4), (S. 1–30).
Gitari, N. D., Zuping, Z., Damien, H., & Long, J. (2015). A Lexicon-Based Approach for Hate Speech Detection. International Journal of Multimedia and Ubiquitous Engineering, 10(4), (S. 215–230).
Greisch, J. (2020). The Logic of Hatred and its Social and Historical Expressions: From the Great Witch-Hunt to Terror and Present-Day Djihadism. Continental Philosophy Review. (S. 1–9).
Liu, H., Burnap, P., Alorainy, W., Williams, M. L., Burnap, P., & Williams, M. L. (2019). Fuzzy Multi-task Learning for Hate Speech Type Identification. In Proceedings of the World Wide Web Conference – WWW 2019. (S. 3006–3012). New York, USA: ACM Press.
MacAvaney S., Yao, H.-R., Yang, E., Russell, K., Goharian, N., & Frieder, O. (2019). Hate Speech Detection: Challenges and solutions. PLoS ONE, 14(8).
Mathew, B., Dutt, R., Goyal, P., & Mukherjee, A. (2019). Spread of Hate Speech in Online Social Media. In Proceedings of the 10th ACM Conference on Web Science – WebSci 2019. (S. 173–182). New York, USA: ACM Press.
Mondal, M., Silva, L. A., & Benevenuto, F. (2017). A Measurement Study of Hate Speech in Social Media. In Proceedings of the 28th ACM Conference on Hypertext and Social Media – HT 2017. (S. 85–94). New York, USA: ACM Press.
Ousidhoum, N., Lin, Z., Zhang, H., Song, Y., & Yeung, D. (2019). Multilingual and Multi-Aspect Hate Speech Analysis. In Proceedings of the 2019 Conference on Empirical Methods in Natural Language Processing and the 9th International Joint Conference on Natural Language Processing (EMNLP-IJCNLP). (S. 4667–4676). New York, USA: Association for Computational Linguistics.
Pater, J. A., Kim, M. K., Mynatt, E. D., & Fiesler, C. (2016). Characterizations of Online Harassment. In Proceedings of the 19th International Conference on Supporting Group Work – GROUP 2016. (S. 369–374). New York, USA: ACM Press.
Poria, S., Cambria, E., Hazarika, D., & Vij, P. (2017). A Deeper Look into Sarcastic Tweets Using Deep Convolutional Neural Networks. In Proceedings of the 26th International Conference on Computational Linguistics – COLING 2016. (S. 1601–1612). New York, USA: Association for Computational Linguistics.
Sakama, C., Caminada, M., & Herzig, A. (2014). A Formal Account of Dishonesty. Journal of the IGPL, 23(2), (S. 259–294).
Schmidt, A., & Wiegand, M. (2017). A Survey on Hate Speech Detection using Natural Language Processing. In Proceedings of the Fifth International Workshop on Natural Language Processing for Social Media. (S. 1–10). New York, USA: Association for Computational Linguistics.
Schmidt, E. (2015). Eric Schmidt on how to Build a Better Web. The New York Times. Retrieved from https://www.nytimes.com/2015/12/07/opinion/eric-schmidt-on-how-to-build-a-better-web.html.
Singh, M. P., & Asher, N. M. (1993). A Logic of Intentions and Beliefs. Journal of Philosophical Logic, 22(5), (S. 513–544).
Srba, I., Moro, R., Simko, J., Sevcech, J., Chuda, D., Navrat, P., & Bielikova, M. (2019). Monant: Universal and Extensible Platform for Monitoring, Detection and Mitigation of Antisocial Behaviour. In Proceedings of Workshop on Reducing Online Misinformation Exposure (ROME 2019). (S. 1–7).
Sternberg, R. J. (2020). Perspectives on Hate: How It Originates, Develops, Manifests, and Spreads. American Psychological Association.
Švec, A., Pikuliak, M., Šimko, M., & Bieliková, M. (2018). Improving Moderation of Online Discussions via Interpretable Neural Models. In Proceedings of the Second Workshop on Abusive Language Online – ALW 2018 at EMNLP. (S. 60–65). New York, USA: Association for Computational Linguistics.
Wachs, S., Gámez-Guadix, M., Wright, M. F., Görzig, A., & Schubarth, W. (2020). How do Adolescents Cope with Cyberhate? Psychometric Properties and Socio-Demographic Differences of a Coping with Cyberhate Scale. Computers in Human Behavior, 104, (S. 106–167).
Wachs, S., Wright, M. F., & Vazsonyi, A. T. (2019). Understanding the Overlap between Cyberbullying and Cyberhate Perpetration: Moderating Effects of Toxic Online Disinhibition. Criminal Behaviour and Mental Health, 29(3), (S. 179–188).
Waseem, Z. (2016). Are You a Racist or Am I Seeing Things? Annotator Influence on Hate Speech Detection on Twitter. In Proceedings of the First Workshop on NLP and Computational Social Science. (S. 138–142). New York, USA: Association for Computational Linguistics.
Waseem, Z., Davidson, T., Warmsley, D., & Weber, I. (2017). Understanding Abuse: A Typology of Abusive Language Detection Subtasks. In Proceedings of the First Workshop on Abusive Language Online (S. 78–84). New York, USA: Association for Computational Linguistics.
Waseem, Z., & Hovy, D. (2016). Hateful Symbols or Hateful People? Predictive Features for Hate Speech Detection on Twitter. In Proceedings of the NAACL Student Research Workshop. (S. 88–93). New York, USA: Association for Computational Linguistics.
Zampieri, M., Malmasi, S., Nakov, P., Rosenthal, S., Farra, N., & Kumar, R. (2019). Predicting the Type and Target of Offensive Posts in Social Media. In Proceedings of the 2019 Conference of the North American Chapter of the Association for Computational Linguistics: Human Language Technologies. (S. 1415–1420). New York, USA: Association for Computational Linguistics.
Zhang, Z., & Luo, L. (2018). Hate Speech Detection: A Solved Problem? The Challenging Case of Long Tail on Twitter. Semantic Web, 10(5), (S. 925–945).
Acknowledgements
This work was partially supported by TAILOR, a project funded by EU Horizon 2020 research and innovation programme under GA No 952215; by the Scientific Grant Agency of the Slovak Republic, under the contracts No. VG 1/0725/19 and VG 1/0667/18; and by the FNR POC Project NoCry
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2021 Springer Fachmedien Wiesbaden GmbH, ein Teil von Springer Nature
About this chapter
Cite this chapter
Srba, I., Lenzini, G., Pikuliak, M., Pecar, S. (2021). Addressing Hate Speech with Data Science: An Overview from Computer Science Perspective. In: Wachs, S., Koch-Priewe, B., Zick, A. (eds) Hate Speech - Multidisziplinäre Analysen und Handlungsoptionen. Springer VS, Wiesbaden. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-658-31793-5_14
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-658-31793-5_14
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer VS, Wiesbaden
Print ISBN: 978-3-658-31792-8
Online ISBN: 978-3-658-31793-5
eBook Packages: Education and Social Work (German Language)