Abstract
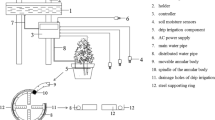
Elevated root-zone (RZ) [CO2] resulted in significantly higher maximal photosynthetic CO2 assimilation rate (A) but lower stomatal conductance (gs) in aeroponically grown temperate lettuce in the tropics. Higher midday leaf relative water content (RWC) was observed at elevated RZ [CO2]. Grown at 20 °C-RZ temperature (RZT), all plants accumulated more biomass than at ambient (A)-RZT. The increase of biomass was greater in roots than in shoots supported by lower shoot/root ratio under elevated RZ [CO2]. The percentage increase in biomass under elevated RZ [CO2] was greater at A-RZT although the total biomass was higher at 20 °C-RZT. NO3 − and total reduced N concentrations of shoot and root, total leaf soluble and Rubisco protein were significantly higher in all elevated RZ [CO2] plants than in ambine RZ [CO2] (360 ppm) at both RZTs. Roots, however, under each RZ [CO2] at A-RZT had significantly higher NO3 − and total reduced N concentration than at 20 °C-RZT. At each RZ [CO2], total leaf soluble and Rubisco protein concentration was significant greater at 20 °C-RZT than at A-RZT.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Preview
Unable to display preview. Download preview PDF.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
De Jong E, Schappert HJV (1972) Calculation of soil respiration and activity from CO2 profile in the soil. Soil Sci. 113: 328–333
He J, Austin PT, Lee SK (2010) Effects of elevated root zone CO2 and air temperature on photosynthetic gas exchange, nitrate uptake, and total reduced nitrogen content in aeroponically grown lettuce plants. J. Exp. Bot. 61: 3959–3969
He J, Austin PT, Nichols MA, Lee SK (2007) Elevated root-zone CO2 protects lettuce plants from midday depression of photosynthesis. Environ. Exp. Bot. 61, 94–110
Li Y, Gao Y, Xu X, Shen Q, Guo S (2009) Light-saturated photosynthetic rate in high-nitrogen rice (Oryza sativa L.) leaves is related to chloroplastic CO2 concentration. J. Exp. Bot. 60: 2351–2360
McGuire MA, Marshall JD, Teskey RO (2009) Assimilation of xylem-transported 13C-labelled CO2 in leaves and branches of sycamore (Platanus occidentalis L.). J. Exp. Bot. 60: 3809–3817
Norstadt FA, Porter LK (1984) Soil gases and temperatures: a beef cattle feedlot compared to alfalfa. Soil Sci. Soc. Am J. 48: 783–789
Pettersson R, McDonald JS (1994) Effects of nitrogen supply on the acclimation of photosynthesis to elevated CO2. Photosyn. Res. 39: 389–400
Teskey RO, McGuire MA (2005) CO2 transported in xylem sap affects CO2 efflux from Liquidambar styraciflua and Platanus occidentalis stems, and contributes to observed wound respiration phenomena. Trees: Structure and Function 19: 357–362
Viktor A, Cramer MD (2003) Variation in root-zone CO2 concentration modifies isotopic fractionation of carnon and nitrogen in tomato seedlings. New Phytol. 157: 45–54
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2013 Zhejiang University Press, Hangzhou and Springer-Verlag Berlin Heidelberg
About this paper
Cite this paper
He, J., Qin, L., Lee, S.K. (2013). Effects of Elevated Root-Zone CO2 and Root-Zone Temperature on Productivity and Photosynthesis of Aeroponically Grown Lettuce Plants. In: Photosynthesis Research for Food, Fuel and the Future. Advanced Topics in Science and Technology in China. Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-642-32034-7_152
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-642-32034-7_152
Publisher Name: Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg
Print ISBN: 978-3-642-32033-0
Online ISBN: 978-3-642-32034-7
eBook Packages: Biomedical and Life SciencesBiomedical and Life Sciences (R0)