Abstract
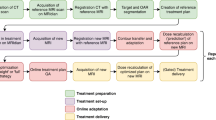
Background: For image-guided radiotherapy (IGRT) of prostate cancer, the current standard is online image guidance which can effectively correct setup errors and inter-fraction rigid organ motion. However, planning margins are still necessary for deformation and intra-fraction motion. Objectives: The purpose is to investigate an adaptive planning technique incorporating offline dose feedback to manage interfraction motion and residuals from online corrections. Methods: Repeated CT scans from 28 patients were studied. Online IG was simulated by matching center-of-mass of prostate. A seven-beam IMRT plan with zero margins was designed for each patient. Dose distribution at each fraction was evaluated based on actual target and OARs from that fraction. Cumulative dose was calculated using deformable registration and compared to initial plan. If deviation exceeded pre-defined 2% threshold in prostate D99, an adaptive planning technique called dose compensation was invoked, in which cumulative dose was fed back to the planning system and dose deficit was made up through boost radiation in future fractions through IMRT. Results: If 2% under-dose is allowed at the end of course, then 11 patients fail. If the same criteria is assessed at the end of each week (every 5 fractions), then 14 patients fail. The average dose deficit for these 14 patients was 4.4%. They improved to 2% after weekly compensation. Ten (out of 14) patients passed criterion after weekly dose compensation; 3 failed marginally; one failed significantly (10% deficit). A more aggressive compensation frequency (every 3 fractions) could reduce the dose deficit to the acceptable level for this patient. The doses to OARs were not significantly different from online IG only without dose compensation. Conclusions: We demonstrated an offline dose compensation technique in prostate IGRT which can effectively account for residual uncertainties uncorrectable in online IG. Dose compensation allows further margin reduction and critical organs sparing.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Preview
Unable to display preview. Download preview PDF.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2013 Springer-Verlag Berlin Heidelberg
About this paper
Cite this paper
Wu, Q., Liu, H. (2013). Adaptive Dose-Compensation Technique for Image-Guided Radiotherapy of Prostate Cancer. In: Long, M. (eds) World Congress on Medical Physics and Biomedical Engineering May 26-31, 2012, Beijing, China. IFMBE Proceedings, vol 39. Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-642-29305-4_491
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-642-29305-4_491
Publisher Name: Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg
Print ISBN: 978-3-642-29304-7
Online ISBN: 978-3-642-29305-4
eBook Packages: EngineeringEngineering (R0)