Abstract
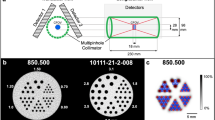
Single photon emission computed tomography (SPECT) using a pixelated Cadmium Telluride (CdTe) detector is a promising technology for high-resolution, small animal imaging. This study demonstrates the feasibility of using our high resolution SPECT system with CdTe in quantitative study in mouse brain. The CdTe detector had 0.35 mm x 0.35 mm2 pixels, which is similar to the size of the available detector (PID350, AJAT, Finland). The CdTe detector was 44.8 mm x 44.8 mm2 with 128 x 128 pixels and was 1 mm thick. The intrinsic resolutions of CdTe and was 0.35 mm. The parallel hole collimator of lead was 25 mm high, and the septum was 0.2 mm high. The parallel hole collimator was hexagonal with a 0.5 mm radius. A voxelized MOBY phantom was used to model the mouse brain for the quantitative dopamine transporters (DAT) binding study. A SPECT brain scan of the MOBY phantom was simulated using our system with CdTe. All SPECT images were obtained using 120 projection views acquired from 0° to 360° with a 3° step. Slices were reconstructed using an Ordered Subsets Expectation Maximization (OS-EM) with 8 iterations and 4 subsets. We investigated the quality of the images from our system in terms of spatial resolution (FWHM), sensitivity, signal-to-noise ratio (SNR), and contrastto-noise ratio (CNR). The spatial resolution of our new SPECT with a CdTe detector was about 2.32 mm at 3 cm. The sensitivity at 3 cm was 23.22 counts/sec/MBq. The SNR and CNR of the image from the CdTe detector were 0.8 and 0.74, respectively. These results demonstrate that SPECT imaging using a pixelated CdTe detector is applicable in quantitative study of neurorecptor binding sites in the mouse brain.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Preview
Unable to display preview. Download preview PDF.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2013 Springer-Verlag Berlin Heidelberg
About this paper
Cite this paper
Park, S.J., Lee, C.L., Kim, H.J. (2013). Feasibility of Quantitative Mouse Brain Study using High Resolution SPECT with CdTe: a Simulation Study. In: Long, M. (eds) World Congress on Medical Physics and Biomedical Engineering May 26-31, 2012, Beijing, China. IFMBE Proceedings, vol 39. Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-642-29305-4_281
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-642-29305-4_281
Publisher Name: Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg
Print ISBN: 978-3-642-29304-7
Online ISBN: 978-3-642-29305-4
eBook Packages: EngineeringEngineering (R0)