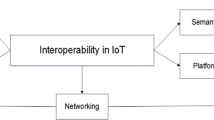
Abstract
An increase of 2.5 billion people is expected in urban areas by 2050, when 66% of the world population will reside here. It is therefore reasonable to assume a parallel growth in the smart city Internet of Things (IoT). A challenge, however, is presented in the interoperability between the devices deployed, limited due to the ad hoc and proprietary ways which systems have been rolled out to date. A standardized network infrastructure specific to the IoT can work towards resolving the challenges. This approach to operation, however, raises questions with regard to how an architecture may support different devices and applications simultaneously, and additionally be extensible to accommodate applications and devices not available at the time of the framework’s development. In this paper, these questions are explored, and an IoT infrastructure which accommodates the interoperability communication constraints and challenges today is proposed.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aloi, G., Caliciuri, G., Fortino, G., Gravina, R., Pace, P., Russo, W., Savaglio, C.: A mobile multi-technology gateway to enable IoT interoperability. In: IEEE 1st International Conference on Internet-of-Things Design and Implementation, IoTDI 2016, pp. 259–264 (2016)
Aloi, G., Caliciuri, G., Fortino, G., Gravina, R., Pace, P., Russo, W., Savaglio, C.: Enabling IoT interoperability through opportunistic smartphone-based mobile gateways. J. Netw. Comput. Appl. 81, 74–84 (2017)
Fortino, G., Savaglio, C., Palau, C.E., de Puga, J.S., Ghanza, M., Paprzycki, M., Montesinos, M., Liotta, A., Llop, M.: Towards multi-layer interoperability of heterogeneous IoT platforms: the INTER-IoT approach. In: Gravina, R., Palau, C., Manso, M., Liotta, A., Fortino, G. (eds.) Integration, Interconnection, and Interoperability of IoT Systems. Internet of Things, pp. 199–232. Springer, Cham (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-61300-0_10. ISBN 9783319612997
European Smart Cities: The Smart City Model. http://www.smart-cities.eu/model.html
Department for Business Innovation & Skills: Smart Cities: Background Paper, October 2013
European Commission: Smart Cities. http://ec.europa.eu/
Innovation Cities Program: Definition of a Smart City. http://www.innovation-cities.com/
Smart City Networks: Smart City Networks named Anaheim Convention Center’s Exclusive Telecommunications Provider, September 2014. http://www.smartcitynetworks.com/
Vander Veen, C.: Without Smart, Connected People There Are No Smart Cities, February 2015. http://www.govtech.com/
Department for Business Innovation & Skills: The Smart City Market: Opportunities for the UK, October 2013
Government of India Ministry of Urban Development; Homepage. http://moud.gov.in/
Ministry of Urban Development Government of India; Homepage. http://indiansmartcities.in/
EUROCITIES: Smart Cities. http://www.eurocities.eu/
Future Cities: Smart Cities. https://futurecities.catapult.org.uk/
Hamaguchi, K., Ma, Y., Takada, M., Nishjima, T., Shimura, T.: Telecommunication systems in smart cities. Hitachi Rev. 61(3), 152–158 (2012)
Cisco Systems: Smart City Framework a Systematic Process for Enabling Smart+Connected Communities, pp. 1–11, September 2012
IBM: Smarter Planet. http://www.ibm.com/smarterplanet/uk/en/
Smart Cities Council: Architecture 2030 Beta Testing Urban Planning Tool, May 2013. http://smartcitiescouncil.com/
AllSeen Alliance Homepage. https://allseenalliance.org/
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2018 ICST Institute for Computer Sciences, Social Informatics and Telecommunications Engineering
About this paper
Cite this paper
Peoples, C. (2018). A Standardizable Network Architecture Supporting Interoperability in the Smart City Internet of Things. In: Fortino, G., et al. Interoperability, Safety and Security in IoT. InterIoT SaSeIoT 2017 2017. Lecture Notes of the Institute for Computer Sciences, Social Informatics and Telecommunications Engineering, vol 242. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-93797-7_5
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-93797-7_5
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-319-93796-0
Online ISBN: 978-3-319-93797-7
eBook Packages: Computer ScienceComputer Science (R0)