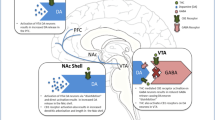
Abstract
The prevalence of cannabis use disorder (CUD) varies with age. Adolescents are particularly susceptible to negative consequences associated with heavy cannabis use. In this chapter, the age-related trends in CUD are discussed. Neurobiological risk factors associated with increased risk of developing a CUD are also discussed, including impulsivity/disinhibition, emotional dysregulation, and sensitivity to the rewarding properties of cannabis. Environmental risk factors such as low parental monitoring, parental cannabis use, and association with peers who use cannabis may contribute to cannabis use initiation in adolescence, indirectly influencing the development of CUD. Evidence for behavioral and pharmacological treatments for adolescent CUD is reviewed. More research is available on behavioral treatments for adolescent CUD, and these are often the first-line treatment options. Emerging evidence suggests promising pharmacological adjuncts for the treatment of adolescent CUD, however. Preliminary data examining these pharmacological treatments suggests that effective treatments for adults may not be appropriate or effective for adolescents and vice versa, though further research is necessary.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- CBT:
-
Cognitive behavioral therapy
- CUD:
-
Cannabis use disorder
- DSM:
-
Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders
- EFBT:
-
Ecological family-based therapy
- NAC:
-
N-acetylcysteine
- SUD:
-
Substance use disorder
References
Anderson KG, Sitney M, White HR. Marijuana motivations across adolescence: impacts on use and consequences. Subst Use Misuse. 2015;50:292–301. https://doi.org/10.3109/10826084.2014.977396.
Anthony J. The epidemiology of cannabis dependence. In: Roffman R, Stephens RS, editors. Cannabis dependence: its nature, consequences and treatment. New York: Cambridge; 2006. p. 58–105.
Azrin NH, Donohue B, Teichner GA, Crum T, Howell J, DeCato LA. A controlled evaluation and description of individual-cognitive problem solving and family-behavior therapies in dually-diagnosed conduct-disordered and substance-dependent youth. J Child Adolesc Subst Abuse. 2001;11:1–43. https://doi.org/10.1300/J029v11n01_01.
Bahr SJ, Hoffmann JP, Yang X. Parental and peer influences on the risk of adolescent drug use. J Prim Prev. 2005;26:529–51. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10935-005-0014-8.
Baker TB, Piper ME, McCarthy DE, Majeskie MR, Fiore MC. Addiction motivation reformulated: an affective processing model of negative reinforcement. Psychol Rev. 2004;111:33–51. https://doi.org/10.1037/0033-295x.111.1.33.
Battjes RJ, Gordon M, O’Grady KE, Kinlock TW, Katz EC, Sears EA. Evaluation of a group-based substance abuse treatment program for adolescents. J Subst Abus Treat. 2004;27:123–34. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jsat.2004.06.002.
Bentzley JP, Tomko RL, Gray KM. Low pretreatment impulsivity and high medication adherence increase the odds of abstinence in a trial of N-acetylcysteine in adolescents with cannabis use disorder. J Subst Abus Treat. 2016;63:72–7. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jsat.2015.12.003.
Blanco C, Rafful C, Wall MM, Ridenour TA, Wang S, Kendler KS. Towards a comprehensive developmental model of cannabis use disorders. Addiction. 2014;109:284–94. https://doi.org/10.1111/add.12382.
Bovasso GB. Cannabis abuse as a risk factor for depressive symptoms. Am J Psychiatry. 2001;158:2033–7. https://doi.org/10.1176/appi.ajp.158.12.2033.
Brook JS, Zhang C, Brook DW. Antisocial behavior at age 37: developmental trajectories of marijuana use extending from adolescence to adulthood. Am J Addict. 2011;20:509–15. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1521-0391.2011.00179.x.
Brook JS, Zhang C, Leukefeld CG, Brook DW. Marijuana use from adolescence to adulthood: developmental trajectories and their outcomes. Soc Psychiatry Psychiatr Epidemiol. 2016;51:1405–15. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00127-016-1229-0.
Calafat A, García F, Juan M, Becoña E, Fernández-Hermida JR. Which parenting style is more protective against adolescent substance use? Evidence within the European context. Drug Alcohol Depend. 2014;138:185–92. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.drugalcdep.2014.02.705.
Carpenter KM, Schreiber E, Church S, McDowell D. Drug Stroop performance: relationships with primary substance of use and treatment outcome in a drug-dependent outpatient sample. Addict Behav. 2006;31:174–81. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.addbeh.2005.04.012.
Casey B, Jones RM, Hare TA. The adolescent brain. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2008;1124:111–26. https://doi.org/10.1196/annals.1440.010.
Chen K, Kandel DB. Predictors of cessation of marijuana use: an event history analysis. Drug Alcohol Depend. 1998;50:109–21.
Choi NG, DiNitto DM, Marti CN. Older marijuana users: life stressors and perceived social support. Drug Alcohol Depend. 2016;169:56–63. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.drugalcdep.2016.10.012.
Choi NG, DiNitto DM, Marti CN. Nonmedical versus medical marijuana use among three age groups of adults: associations with mental and physical health status. Am J Addict. 2017;26:697–706. https://doi.org/10.1111/ajad.12598.
Cooper ZD, Haney M. Cannabis reinforcement and dependence: role of the cannabinoid CB1 receptor. Addict Biol. 2008;13:188–95. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1369-1600.2007.00095.x.
Creswell KG, Chung T, Clark DB, Martin CS. Solitary cannabis use in adolescence as a correlate and predictor of cannabis problems. Drug Alcohol Depend. 2015;156:120–5. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.drugalcdep.2015.08.027.
Cyders MA, Coskunpinar A. Measurement of constructs using self-report and behavioral lab tasks: is there overlap in nomothetic span and construct representation for impulsivity? Clin Psychol Rev. 2011;31:965–82. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cpr.2011.06.001.
Cyders MA, Smith GT, Spillane NS, Fischer S, Annus AM, Peterson C. Integration of impulsivity and positive mood to predict risky behavior: development and validation of a measure of positive urgency. Psychol Assess. 2007;19:107–18. https://doi.org/10.1037/1040-3590.19.1.107.
De La Haye K, Green HD, Pollard MS, Kennedy DP, Tucker JS. Befriending risky peers: factors driving adolescents’ selection of friends with similar marijuana use. J Youth Adolesc. 2015;44:1914–28. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10964-014-0210-z.
Dennis M, Godley SH, Diamond G, Tims FM, Babor T, Donaldson J, et al. The Cannabis Youth Treatment (CYT) study: main findings from two randomized trials. J Subst Abus Treat. 2004;27:197–213. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jsat.2003.09.005.
Ellickson PL, D’Amico EJ, Collins RL, Klein DJ. Marijuana use and later problems: when frequency of recent use explains age of initiation effects (and when it does not). Subst Use Misuse. 2005;40:343–59. https://doi.org/10.1081/JA-200049356.
Epstein M, Hill KG, Nevell AM, Guttmannova K, Bailey JA, Abbott RD, et al. Trajectories of marijuana use from adolescence into adulthood: environmental and individual correlates. Dev Psychol. 2015;51:1650–63. https://doi.org/10.1037/dev0000054.
Evenden JL. Varieties of impulsivity. Psychopharmacology. 1999;146:348–61. https://doi.org/10.1007/PL00005481.
Fergusson DM, Horwood LJ, Lynskey MT, Madden PA. Early reactions to cannabis predict later dependence. Arch Gen Psychiatry. 2003;60:1033–9. https://doi.org/10.1001/archpsyc.60.10.1033.
Gfroerer JC, Wu LT, Penne MA. Initiation of marijuana use: trends, patterns, and implications. Rockville: Department of Health and Human Services, Substance Abuse and Mental Health Services Administration, Office of Applied Studies; 2002.
Ghitza UE. ASPIRE model for treating cannabis and other substance use disorders: a novel personalized-medicine framework. Front Psych. 2014;5:180. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpsyt.2014.00180.
Gray KM, Carpenter MJ, Baker NL, DeSantis SM, Kryway E, Hartwell KJ, et al. A double-blind randomized controlled trial of N-acetylcysteine in cannabis-dependent adolescents. Am J Psychiatry. 2012;169:805–12. https://doi.org/10.1176/appi.ajp.2012.12010055.
Gray KM. New developments in understanding and treating adolescent marijuana dependence. Adolesc Psychiatry. 2013;3:297–306. https://doi.org/10.2174/221067660304140121173215.
Gray KM, Sonne SC, McClure EA, Ghitza UE, Matthews AG, McRae-Clark AL, et al. A randomized placebo-controlled trial of N-acetylcysteine for cannabis use disorder in adults. Drug Alcohol Depend. 2017;177:249–57. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.drugalcdep.2017.04.020.
Hammond CJ, Gray KM. Pharmacotherapy for substance use disorders in youths. J Child Adolesc Subst Abuse. 2016;25:292–316. https://doi.org/10.1080/1067828X.2015.1037517.
Han BH, Compton WM, Jones CM, Blanco C. Cannabis use and cannabis use disorders among youth in the United States, 2002–2014. J Clin Psychiatry. 2017;78:1404. https://doi.org/10.4088/JCP.16m10948.
Han BH, Sherman S, Mauro PM, Martins SS, Rotenberg J, Palamar JJ. Demographic trends among older cannabis users in the United States, 2006–13. Addiction. 2017;112:516–25. https://doi.org/10.1111/add.13670.
Haney M, Malcolm RJ, Babalonis S, Nuzzo PA, Cooper ZD, Bedi G, et al. Oral cannabidiol does not alter the subjective, reinforcing or cardiovascular effects of smoked cannabis. Neuropsychopharmacology. 2015;41:1974–82. https://doi.org/10.1038/npp.2015.367.
Harden KP, Tucker-Drob EM. Individual differences in the development of sensation seeking and impulsivity during adolescence: further evidence for a dual systems model. Dev Psychol. 2011;47:739–46. https://doi.org/10.1037/a0023279.
Hasin DS, Kerridge BT, Saha TD, Huang B, Pickering R, Smith SM, et al. Prevalence and correlates of DSM-5 cannabis use disorder, 2012-2013: findings from the national epidemiologic survey on alcohol and related conditions–III. Am J Psychiatry. 2016;173:588–99. https://doi.org/10.1176/appi.ajp.2015.15070907.
Hasin DS, Saha TD, Kerridge BT, Goldstein RB, Chou SP, Zhang H, et al. Prevalence of marijuana use disorders in the United States between 2001–2002 and 2012–2013. JAMA Psychiat. 2015;72:1235–42. https://doi.org/10.1001/jamapsychiatry.2015.1858.
Hendriks V, van der Schee E, Blanken P. Treatment of adolescents with a cannabis use disorder: main findings of a randomized controlled trial comparing multidimensional family therapy and cognitive behavioral therapy in the Netherlands. Drug Alcohol Depend. 2011;119:64–71. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.drugalcdep.2011.05.021.
Henggeler SW, Borduin CM, Melton GB, Mann BJ, et al. Effects of multisystemic therapy on drug use and abuse in serious juvenile offenders: a progress report from two outcome studies. Fam Dyn Addict Q. 1991;1:40–51.
Henggeler SW, Schoenwald SK, Borduin CM, Rowland MD, Cunningham PB. Multisystemic therapy for antisocial behavior in children and adolescents. New York: Guilford Press; 2009.
Hogue A, Henderson CE, Ozechowski TJ, Robbins MS. Evidence base on outpatient behavioral treatments for adolescent substance use: updates and recommendations 2007-2013. J Clin Child Adolesc Psychol. 2014;43:695–720. https://doi.org/10.1080/15374416.2014.915550.
Iacono WG, Malone SM, McGue M. Behavioral disinhibition and the development of early-onset addiction: common and specific influences. Annu Rev Clin Psychol. 2008;4:325–48. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev.clinpsy.4.022007.141157.
Jacobus J, Squeglia LM, Infante MA, Castro N, Brumback T, Meruelo AD, Tapert SF. Neuropsychological performance in adolescent marijuana users with co-occurring alcohol use: a three-year longitudinal study. Neuropsychology. 2015;29:829–43. https://doi.org/10.1037/neu0000203.
Johnson BA, Ait-Daoud N, Bowden CL, DiClemente CC, Roache JD, Lawson K, et al. Oral topiramate for treatment of alcohol dependence: a randomised controlled trial. Lancet. 2003;361:1677–85.
Johnson BA, Ait-Daoud N, Wang XQ, Penberthy JK, Javors MA, Seneviratne C, et al. Topiramate for the treatment of cocaine addiction: a randomized clinical trial. JAMA Psychiat. 2013;70:1338–46.
Johnston LD, Miech RA, O'Malley PM, Bachman JG, Schulenberg JE. Teen use of any illicit drug other than marijuana at new low, same true for alcohol. 2016. University of Michigan News Service: Ann Arbor. Retrieved 09/27/2017 from http://www.monitoringthefuture.org
Kaminer Y, Burleson JA. Psychotherapies for adolescent substance abusers: 15-month follow-up of a pilot study. Am J Addict. 1999;8:114–9. https://doi.org/10.1111/ajad.12634.
Kaminer Y, Burleson JA, Goldberger R. Cognitive-behavioral coping skills and psychoeducation therapies for adolescent substance abuse. J Nerv Ment Dis. 2002;190:737–45. https://doi.org/10.1097/01.nmd.0000038168.51591.b6.
Kandel DB, Raveis VH. Cessation of illicit drug use in young adulthood. Arch Gen Psychiatry. 1989;46(2):109–16.
Karschner EL, Darwin WD, McMahon RP, Liu F, Wright S, Goodwin RS, et al. Subjective and physiological effects after controlled Sativex and oral THC administration. Clin Pharmacol Ther. 2011;89:400–7. https://doi.org/10.1038/clpt.2010.318.
Kedzior KK, Laeber LT. A positive association between anxiety disorders and cannabis use or cannabis use disorders in the general population--a meta-analysis of 31 studies. BMC Psychiatry. 2014;14:136. https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-244x-14-136.
Kendler KS, Schmitt E, Aggen SH, Prescott CA. Genetic and environmental influences on alcohol, caffeine, cannabis, and nicotine use from early adolescence to middle adulthood. Arch Gen Psychiatry. 2008;65:674–82. https://doi.org/10.1001/archpsyc.65.6.674.
Kirisci L, Tarter R, Ridenour T, Zhai ZW, Fishbein D, Reynolds M, et al. Age of alcohol and cannabis use onset mediates the association of transmissible risk in childhood and development of alcohol and cannabis disorders: evidence for common liability. Exp Clin Psychopharmacol. 2013;21:38–45. https://doi.org/10.1037/a0030742.
Kirisci L, Tarter RE, Ridenour T, Reynolds M, Vanyukov M. Longitudinal modeling of transmissible risk in boys who subsequently develop cannabis use disorder. Am J Drug Alcohol Abuse. 2013;39:180–5. https://doi.org/10.3109/00952990.2013.774009.
Koob GF, Ahmed SH, Boutrel B, Chen SA, Kenny PJ, Markou A, et al. Neurobiological mechanisms in the transition from drug use to drug dependence. Neurosci Biobehav Rev. 2004;27:739–49. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neubiorev.2003.11.007.
Koob GF, Le Moal M. Drug addiction, dysregulation of reward, and allostasis. Neuropsychopharmacology. 2001;24:97–129. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0893-133x(00)00195-0.
Kosty DB, Seeley JR, Farmer RF, Stevens JJ, Lewinsohn PM. Trajectories of cannabis use disorder: risk factors, clinical characteristics and outcomes. Addiction. 2017;112:279–87. https://doi.org/10.1111/add.13557.
Kwako LE, Momenan R, Grodin EN, Litten RZ, Koob GF, Goldman D. Addictions neuroclinical assessment: a reverse translational approach. Neuropharmacology. 2017;122:254–64. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuropharm.2017.03.006.
Kwako LE, Momenan R, Litten RZ, Koob GF, Goldman D. Addictions neuroclinical assessment: a neuroscience-based framework for addictive disorders. Biol Psychiatry. 2016;80:179–89. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biopsych.2015.10.024.
Levine A, Clemenza K, Rynn M, Lieberman J. Evidence for the risks and consequences of adolescent cannabis exposure. J Am Acad Child Adolesc Psychiatry. 2017;56:214–25. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jaac.2016.12.014.
Liddle HA. Multidimensional family therapy for adolescent cannabis users, Cannabis youth treatment (CYT) series (Vol. 5). Rockville: Center for Substance Abuse Treatment, Substance Abuse and Mental Health Services Administration; 2002.
Lisdahl KM, Gilbart ER, Wright NE, Shollenbarger S. Dare to delay? The impacts of adolescent alcohol and marijuana use onset on cognition, brain structure, and function. Brain Reward Stress Syst Addict. 2015;53. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpsyt.2013.00053.
Lopez-Quintero C, de los Cobos JP, Hasin DS, Okuda M, Wang S, Grant BF, et al. Probability and predictors of transition from first use to dependence on nicotine, alcohol, cannabis, and cocaine: results of the National Epidemiologic Survey on Alcohol and Related Conditions (NESARC). Drug Alcohol Depend. 2011;115:120–30. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.drugalcdep.2010.11.004.
Martin-Santos R, Crippa JA, Batalla A, Bhattacharyya S, Atakan Z, Borgwardt S, et al. Acute effects of a single, oral dose of d9-tetrahydrocannabinol (THC) and cannabidiol (CBD) administration in healthy volunteers. Curr Pharm Des. 2012;18:4966–79.
Mason MJ, Zaharakis NM, Rusby JC, Westling E, Light JM, Mennis J, et al. A longitudinal study predicting adolescent tobacco, alcohol, and cannabis use by behavioral characteristics of close friends. Psychol Addict Behav. 2017;31:712. https://doi.org/10.1037/adb0000299.
Meier MH, Caspi A, Ambler A, Harrington H, Houts R, Keefe RS, et al. Persistent cannabis users show neuropsychological decline from childhood to midlife. Proc Natl Acad Sci. 2012;109:E2657–64.
Miller SM, Siegel JT, Hohman Z, Crano WD. Factors mediating the association of the recency of parent’s marijuana use and their adolescent children’s subsequent initiation. Psychol Addict Behav. 2013;27:848–53. https://doi.org/10.1037/a0032201.
Miranda R, Treloar H, Blanchard A, Justus A, Monti PM, Chun T, et al. Topiramate and motivational enhancement therapy for cannabis use among youth: a randomized placebo-controlled pilot study. Addict Biol. 2017;22:779–90. https://doi.org/10.1111/adb.12350.
Miranda R, Treloar H. Emerging pharmacologic treatments for adolescent substance use: challenges and new directions. Curr Addict Rep. 2016;3:145–56. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40429-016-0098-7.
Moffitt TE. Adolescence-limited and life-course-persistent antisocial behavior: a developmental taxonomy. Psychol Rev. 1993;100:674–701.
Mokrysz C, Freeman TP, Korkki S, Griffiths K, Curran HV. Are adolescents more vulnerable to the harmful effects of cannabis than adults? A placebo-controlled study in human males. Transl Psychiatry. 2016;6:e961. https://doi.org/10.1038/tp.2016.225.
Oncken C, Arias AJ, Feinn R, Litt M, Covault J, Sofuoglu M, Kranzler HR. Topiramate for smoking cessation: a randomized, placebo-controlled pilot study. Nicotine Tob Res. 2014;16:288–96.
Passarotti AM, Crane NA, Hedeker D, Mermelstein RJ. Longitudinal trajectories of marijuana use from adolescence to young adulthood. Addict Behav. 2015;45:301–8. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.addbeh.2015.02.008.
Patton GC, Coffey C, Carlin JB, Degenhardt L, Lynskey M, Hall W. Cannabis use and mental health in young people: cohort study. BMJ: Br Med J. 2002;325:1195–8.
Peters EN, Petry NM, Lapaglia DM, Reynolds B, Carroll KM. Delay discounting in adults receiving treatment for marijuana dependence. Exp Clin Psychopharmacol. 2013;21:46–54. https://doi.org/10.1037/a0030943.
Prince van Leeuwen A, Creemers HE, Verhulst FC, Ormel J, Huizink AC. Are adolescents gambling with cannabis use? A longitudinal study of impulsivity measures and adolescent substance use: The TRAILS study. J Stud Alcohol Drugs. 2011;72(1):70–8. https://doi.org/10.15288/jsad.2011.72.70.
Quinn PD, Harden KP. Differential changes in impulsivity and sensation seeking and the escalation of substance use from adolescence to early adulthood. Dev Psychopathol. 2013;25:223–39. https://doi.org/10.1017/S0954579412000284.
Ramesh D, Haney M, Cooper ZD. Marijuana’s dose-dependent effects in daily marijuana smokers. Exp Clin Psychopharmacol. 2013;21:287–93. https://doi.org/10.1037/a0033661.
Ray LA, Bujarski S, Roche DJ. Subjective response to alcohol as a research domain criterion. Alcohol Clin Exp Res. 2016;40:6–17. https://doi.org/10.1111/acer.12927.
Richter L, Pugh BS, Ball SA. Assessing the risk of marijuana use disorder among adolescents and adults who use marijuana. Am J Drug Alcohol Abuse. 2017;43:247–60. https://doi.org/10.3109/00952990.2016.1164711.
Rigter H, Henderson CE, Pelc I, Tossmann P, Phan O, Hendriks V, et al. Multidimensional family therapy lowers the rate of cannabis dependence in adolescents: a randomised controlled trial in Western European outpatient settings. Drug Alcohol Depend. 2013;130:85–93. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.drugalcdep.2012.10.013.
Rogosch FA, Oshri A, Cicchetti D. From child maltreatment to adolescent cannabis abuse and dependence: a developmental cascade model. Dev Psychopathol. 2010;22:883–97. https://doi.org/10.1017/S0954579410000520.
Ross CS, Brooks DR, Aschengrau A, Siegel MB, Weinberg J, Shrier LA. Positive and negative affect following marijuana use in naturalistic settings: an ecological momentary assessment study. Addict Behav. 2018;76:61–7. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.addbeh.2017.07.020.
Ryzin MJ, Fosco GM, Dishion TJ. Family and peer predictors of substance use from early adolescence to early adulthood: an 11-year prospective analysis. Addict Behav. 2012;37:1314–24. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.addbeh.2012.06.020.
Salas-Wright CP, Vaughn MG, Cummings-Vaughn LA, Holzer KJ, Nelson EJ, AbiNader M, et al. Trends and correlates of marijuana use among late middle-aged and older adults in the United States, 2002–2014. Drug Alcohol Depend. 2017;171:97–106. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.drugalcdep.2016.11.031.
Schrot RJ, Hubbard JR. Cannabinoids: Medical implications. Ann Med. 2016;48:128–41. https://doi.org/10.3109/07853890.2016.1145794.
Schwope DM, Bosker WM, Ramaekers JG, Gorelick DA, Huestis MA. Psychomotor performance, subjective and physiological effects and whole blood Delta(9)-tetrahydrocannabinol concentrations in heavy, chronic cannabis smokers following acute smoked cannabis. J Anal Toxicol. 2012;36:05–412. https://doi.org/10.1093/jat/bks044.
Scott JC, Wolf DH, Calkins ME, Bach EC, Weidner J, Ruparel K, et al. Cognitive functioning of adolescent and young adult cannabis users in the Philadelphia Neurodevelopmental Cohort. Psychol Addict Behav. 2017;31:423–34. https://doi.org/10.1037/adb0000268.
Shedler J, Block J. Adolescent drug use and psychological health: a longitudinal inquiry. Am Psychol. 1990;45:612.
Sher KJ, Bartholow BD, Wood MD. Personality and substance use disorders: a prospective study. J Consult Clin Psychol. 2000;68:818–29. https://doi.org/10.1037/0022-006X.68.5.818.
Sher KJ, Grekin ER, Williams NA. The development of alcohol use disorders. Annu Rev Clin Psychol. 2005;1:493–523. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev.clinpsy.1.102803.144107.
Simons J, Correia CJ, Carey KB. A comparison of motives for marijuana and alcohol use among experienced users. Addict Behav. 2000;25:153–60. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0306-4603(98)00104-X.
Simons J, Correia CJ, Carey KB, Borsari BE. Validating a five-factor marijuana motives measure: relations with use, problems, and alcohol motives. J Couns Psychol. 1998;45:265. https://doi.org/10.1037/0022-0167.45.3.265.
Slesnick N, Erdem G, Bartle-Haring S, Brigham GS. Intervention with substance-abusing runaway adolescents and their families: results of a randomized clinical trial. J Consult Clin Psychol. 2013;81:600–14. https://doi.org/10.1037/a0033463.
Slesnick N, Prestopnik JL. Comparison of family therapy outcome with alcohol-abusing, runaway adolescents. J Marital Fam Ther. 2009;35:255–77. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1752-0606.2009.00121.x.
Smith GT, Guller L, Zapolski TC. A comparison of two models of urgency: urgency predicts both rash action and depression in youth. Clin Psychol Sci. 2013;1:266–75. https://doi.org/10.1177/2167702612470647.
Squeglia LM, Gray KM. Alcohol and drug use and the developing brain. Curr Psychiatry Rep. 2016;18(5):1–10. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11920-016-0689-y.
Stanger C, Budney AJ, Kamon JL, Thostensen J. A randomized trial of contingency management for adolescent marijuana abuse and dependence. Drug Alcohol Depend. 2009;105:240–7. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.drugalcdep.2009.07.009.
Stanger C, Ryan SR, Fu H, Landes RD, Jones BA, Bickel WK, et al. Delay discounting predicts adolescent substance abuse treatment outcome. Exp Clin Psychopharmacol. 2012;20:205–12. https://doi.org/10.1037/a0026543.
Stautz K, Cooper A. Urgency traits and problematic substance use in adolescence: direct effects and moderation of perceived peer use. Psychol Addict Behav. 2014;28:487–97. https://doi.org/10.1037/a0034346.
Steinberg L, Albert D, Cauffman E, Banich M, Graham S, Woolard J. Age differences in sensation seeking and impulsivity as indexed by behavior and self-report: evidence for a dual systems model. Dev Psychol. 2008;44:1764–8. https://doi.org/10.1037/a0012955.
Swendsen J, Burstein M, Case B, Conway KP, Dierker L, He J, et al. Use and abuse of alcohol and illicit drugs in US adolescents: results of the National Comorbidity Survey–Adolescent Supplement. Arch Gen Psychiatry. 2012;69:390–8. https://doi.org/10.1001/archgenpsychiatry.2011.1503.
Tomko RL, Bountress KE, Gray KM. Personalizing substance use treatment based on pre-treatment impulsivity and sensation seeking: a review. Drug Alcohol Depend. 2016;167:1–7. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.drugalcdep.2016.07.022.
Tomko RL, Prisciandaro JJ, Kutty Falls S, Magid V. The structure of the UPPS-R-child impulsivity scale and its relations with substance use outcomes among treatment-seeking adolescents. Drug Alcohol Depend. 2016;161:276. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.drugalcdep.2016.02.010.
Van der Pol TM, Hoeve M, Noom MJ, Stams GJM, Doreleijers TAH, van Domburgh L, et al. Research review: The effectiveness of multidimensional family therapy in treating adolescents with multiple behavior problems – a meta-analysis. J Child Psychol Psychiatry. 2017;58:532–45. https://doi.org/10.1111/jcpp.12685.
Verdejo-García A, Lawrence AJ, Clark L. Impulsivity as a vulnerability marker for substance-use disorders: review of findings from high-risk research, problem gamblers and genetic association studies. Neurosci Biobehav Rev. 2008;32(4):777–810. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neubiorev.2007.11.003.
Vergés A, Haeny AM, Jackson KM, Bucholz KK, Grant JD, Trull TJ, et al. Refining the notion of maturing out: results from the national epidemiologic Survey on alcohol and related conditions. Am J Public Health. 2013;103:e67–73.
Wagner FA, Anthony JC. From first drug use to drug dependence: developmental periods of risk for dependence upon marijuana, cocaine, and alcohol. Neuropsychopharmacology. 2002;26:479–88. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0893-133X(01)00367-0.
Wagner FA, Anthony JC. Into the world of illegal drug use: exposure opportunity and other mechanisms linking the use of alcohol, tobacco, marijuana, and cocaine. Am J Epidemiol. 2002;155:918–25.
Waldron HB, Slesnick N, Brody JL, Turner CW, Peterson TR. Treatment outcomes for adolescent substance abuse at 4- and 7-month assessments. J Consult Clin Psychol. 2001;69(5):802–13. https://doi.org/10.1037/0022-006X.69.5.802.
Washburn IJ, Capaldi DM. Heterogeneity in men’s marijuana use in the 20s: adolescent antecedents and consequences in the 30s. Dev Psychopathol. 2015;27:279–91. https://doi.org/10.1017/S0954579414000686.
Weissman DG, Schriber RA, Fassbender C, et al. Earlier adolescent substance use onset predicts stronger connectivity between reward and cognitive control brain networks. Dev Cogn Neurosci. 2015;16:121–9. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.dcn.2015.07.002.
White HR, Beardslee J, Pardini D. Early predictors of maturing out of marijuana use among young men. Addict Behav. 2017;65:56–62. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.addbeh.2016.09.007.
Whiteside SP, Lynam DR. The five factor model and impulsivity: using a structural model of personality to understand impulsivity. Personal Individ Differ. 2001;30:669–89. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0191-8869(00)00064-7.
Winters KC, Fahnhorst T, Botzet A, Lee S, Lalone B. Brief intervention for drug-abusing adolescents in a school setting: outcomes and mediating factors. J Subst Abus Treat. 2012;42:279–88. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jsat.2011.08.005.
Wittchen HU, Frohlich C, Behrendt S, Gunther A, Rehm J, Zimmermann P, et al. Cannabis use and cannabis use disorders and their relationship to mental disorders: a 10-year prospective-longitudinal community study in adolescents. Drug Alcohol Depend. 2007;88(Suppl 1):S60–70. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.drugalcdep.2006.12.013.
Womack SR, Shaw DS, Weaver CM, Forbes EE. Bidirectional associations between cannabis use and depressive symptoms from adolescence through early adulthood among at-risk young men. J Stud Alcohol Drugs. 2016;77:287–97. https://doi.org/10.15288/jsad.2016.77.287.
Wu LT, Brady KT, Mannelli P, Killeen TK, NIDA AAPI Workgroup. Cannabis use disorders are comparatively prevalent among nonwhite racial/ethnic groups and adolescents: a national study. J Psychiatr Res. 2014;50:26–35. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jpsychires.2013.11.010.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2019 Springer Nature Switzerland AG
About this chapter
Cite this chapter
Tomko, R.L., Williamson, A.N., McRae-Clark, A.L., Gray, K.M. (2019). Cannabis Use Disorder as a Developmental Disorder. In: Montoya, I., Weiss, S. (eds) Cannabis Use Disorders. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-90365-1_18
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-90365-1_18
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-319-90364-4
Online ISBN: 978-3-319-90365-1
eBook Packages: MedicineMedicine (R0)