Abstract
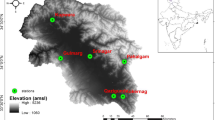
The modern and quite commonly used techniques for projection of climate change are the General Circulation Models or Global Climate Models (GCMs). However, these models predict climate at a much coarser spatial resolution. Often many studies involve the assessment of climate change impacts at smaller scales, viz., a catchment area of a river or even point scales, viz., a gauging station. In order to use the output of a GCM for conducting hydrological impact studies, downscaling is used. In the present study, the effect of climate change on meteorological parameters, viz., precipitation and temperature at four metrological stations, viz., Srinagar, Pahalgam, Qazigund, and Kupwara of Kashmir Valley, were examined. The data of mslpas (mean sea level pressure), tempas (mean temperature at 2 m), p500-as (500 hpa geopotential height), humas (specific humidity at 2 m), and p5_uas (500 hpa zonal velocity) obtained from Canadian third-generation Climate Model (CGCM3) were used as predictors along with National Center for Environmental Prediction/National Center for Atmospheric Research (NCEP/NCAR) reanalysis climatic data set. The locally observed temperature and precipitation were used as predictands. The methods of Multiple Linear Regression (MLR) and Statistical Downscaling Model (SDSM) were used as downscaling techniques. The large-scale GCM predictors were related to observed precipitation and temperature. It was found that the temperature of the Kashmir Valley is likely to increase in the coming decades while as the precipitation is going to decrease with each coming decade.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bardossy A, Plate EJ (1992) Space-time model for daily rainfall using atmospheric circulation patterns. Water Resour Res 28:1247–1259
Chaleeraktrakoon C, Punlum P (2010) Statistical analysis and downscaling for the minimum, average, and maximum daily-temperatures of the Chi and Mun River Basins. Thammasat Int J Sci Technol 15(4):64–81
Chow VT (1964) Handbook of applied hydrology. Tata Mc Graw-Hill, New York
Chu JT, Xia J, Xu C-Y, Singh VP (2010) Statistical downscaling of daily mean temperature, pan evaporation and precipitation for climate change scenarios in Haihe River, China. J Theor Appl Climatol 99(1–2):149–161
Coulibaly P, Dibike YB, Anctil F (2005) Downscaling precipitation and temperature with temporal neural networks. J Hydrometeorol
Ghosh S, Mujumdar PP (2008) Statistical downscaling of GCM simulations to streamflow using relevance vector machine. Adv Water Resour 31:132–146
Hewitson BC, Crane RG (1992) Large-scale atmospheric controls on local precipitation in tropical Mexico. Geophys Res Lett 19(18):1835–1838
IPCC (2007a) Climate change 2007: synthesis report. In: Pachauri RK, Reisinger A (eds) Contribution of Working Groups I, II and III to the fourth assessment report of the intergovernmental panel on climate change. Core Writing Team
IPCC (2007b) Climate change 2007: the physical science basis. In: Solomon S, Qin D, Manning M, Marquis M, Averyt K, Tignor MB, LeRoy Mil H (eds) Contribution of Working Group I to the fourth assessment report of the IPCC. Cambridge University Press
IPCC (2007c) Climate change 2007: impact adaptation and vulnerability. In: Parry ML, Canziani OF, Palutikof JP, van der Linden PJ, Hanson CE (eds) Contribution of Working Group II to the fourth assessment report of the IPCC. Cambridge University Press
Khan MS, Coulibaly P, Dibike Y (2006) Uncertainty analysis of statistical downscaling methods. J Hydrol 319:357–382
Murphy JM (1999) An evaluation of statistical and dynamical techniques for downscaling local climate. J Clim 12:2256–2284
Ojha CSP, Goyal MK, Adeloye AJ (2010) Downscaling of precipitation for lake catchment in the arid region in India using linear multiple regression and neural networks. Open Hydrol J 4:122–136
UNWTO (2007) Ministers summit on tourism and climate change. London Conference Pack
Wigley TML, Jones PD, Briffa KR, Smith G (1990) Obtaining sub-grid-scale information from coarse-resolution general circulation model output. J Geophys Res 95(D2):1943–1953
Wilby RL, Dawson CW (2007) Using SDSM Version 4.2—a decision support tool for the assessment of regional climate change impacts. User Manual, 90 p
Wilby RL, Dawson CW, Barrow EM (2002) SDSM—a decision support tool for the assessment of regional climate change impacts. Environ Model Softw 17:145–157
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2018 Springer International Publishing AG, part of Springer Nature
About this chapter
Cite this chapter
Ahanger, M.A., Lone, M.A. (2018). Effect of Climate Change Over Kashmir Valley. In: Sarma, A., Singh, V., Bhattacharjya, R., Kartha, S. (eds) Urban Ecology, Water Quality and Climate Change. Water Science and Technology Library, vol 84. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-74494-0_10
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-74494-0_10
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-319-74493-3
Online ISBN: 978-3-319-74494-0
eBook Packages: Earth and Environmental ScienceEarth and Environmental Science (R0)