Abstract
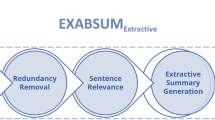
Sentence-based extractive summarization aims at automatically generating shorter versions of texts by extracting from them the minimal set of sentences that are necessary and sufficient to cover their content. Providing effective solutions to this task would allow the users to save time in selecting the most appropriate documents to read for satisfying their information needs or for supporting their decision-making tasks. This paper proposes 2 contributions: (i) it defines a novel approach, based on abstract argumentation, to select the sentences in a text that are to be included in the summary; (ii) it proposes a new strategy for similarity assessment among sentences, adopting a different similarity measure than those traditionally exploited in the literature. The effectiveness of the proposed approach was confirmed by experimental results obtained on the English subset of the benchmark MultiLing2015 dataset.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Banerjee, S., Mitra, P., Sugiyama, K.: Multi-document abstractive summarization using ILP based multi-sentence compression. In: IJCAI 2015 (2015)
Carbonell, J., Goldstein, J.: The use of MMR, diversity-based reranking for reordering documents and producing summaries. In: ACM SIGIR, pp. 335–336. ACM (1998)
Cayrol, C., Lagasquie-Schiex, M.C.: On the acceptability of arguments in bipolar argumentation frameworks. In: Godo, L. (ed.) ECSQARU 2005. LNCS (LNAI), vol. 3571, pp. 378–389. Springer, Heidelberg (2005). https://doi.org/10.1007/11518655_33
Davis, S.T., et al.: OCCAMS—an optimal combinatorial covering algorithm for multi-document summarization. In: ICDMW, pp. 454–463. IEEE (2012)
De Marneffe, M., Manning, C.D.: The Stanford typed dependencies representation. In: Coling 2008, pp. 1–8. ACL (2008)
Dung, P.M.: On the acceptability of arguments and its fundamental role in nonmonotonic reasoning, logic programming and n-person games. Artif. Intell. 77(2), 321–357 (1995)
Dunne, P.E., et al.: Weighted argument systems: basic definitions, algorithms, and complexity results. Artif. Intell. 175(2), 457–486 (2011)
Ferilli, S., Biba, M., Di Mauro, N., Basile, T.M.A., Esposito, F.: Plugging taxonomic similarity in first-order logic horn clauses comparison. In: Serra, R., Cucchiara, R. (eds.) AI*IA 2009. LNCS, vol. 5883, pp. 131–140. Springer, Heidelberg (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-642-10291-2_14
Ferreira, R., et al.: Assessing sentence scoring techniques for extractive text summarization. Expert Syst. Appl. 40(14), 5755–5764 (2013)
Ferreira, R., et al.: A new sentence similarity assessment measure based on a three-layer sentence representation. In: DocEng, pp. 25–34. ACM (2014)
Giannakopoulos, G., et al.: Multiling 2015: multilingual summarization of single and multi-documents, on-line fora, and call-center conversations. In: SIGDIAL, pp. 270–274 (2015)
Gupta, P., et al.: Summarizing text by ranking text units according to shallow linguistic features. In: ICACT, pp. 1620–1625. IEEE (2011)
Lin, C.: Rouge: a package for automatic evaluation of summaries. In: ACL-04 Workshop, vol. 8 (2004)
Lloret, E., Palomar, M.: Text summarisation in progress: a literature review. Artif. Intell. Rev. 37(1), 1–41 (2012)
Manning, C.D., et al.: The Stanford CoreNLP natural language processing toolkit. In: ACL (System Demonstrations), pp. 55–60 (2014)
Mihalcea, R., Tarau, P.: TextRank: bringing order into texts. In: Association for Computational Linguistics (2004)
Miller, G.: WordNet: a lexical database for English. Commun. ACM 38(11), 39–41 (1995)
Nenkova, A., McKeown, K.: A survey of text summarization techniques. In: Aggarwal, C., Zhai, C. (eds.) Mining Text Data, pp. 43–76. Springer, Boston (2012)
Rotella, F., Leuzzi, F., Ferilli, S.: Learning and exploiting concept networks with ConNeKTion. Appl. Intell. 42(1), 87–111 (2015)
Shardan, R., Kulkarni, U.: Implementation and evaluation of evolutionary connectionist approaches to automated text summarization (2010)
Umam, K., et al.: Coverage, diversity, and coherence optimization for multi-document summarization. Jurnal Ilmu Komputer dan Informasi 8(1), 1–10 (2015)
Vasilescu, F., Langlais, P., Lapalme, G.: Evaluating variants of the lesk approach for disambiguating words. In: Lrec (2004)
Acknowledgments
This work was partially funded by the Italian PON 2007-2013 project PON02_00563_3489339 ‘Puglia@Service’.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2017 Springer International Publishing AG
About this paper
Cite this paper
Ferilli, S., Pazienza, A., Angelastro, S., Suglia, A. (2017). A Similarity-Based Abstract Argumentation Approach to Extractive Text Summarization. In: Esposito, F., Basili, R., Ferilli, S., Lisi, F. (eds) AI*IA 2017 Advances in Artificial Intelligence. AI*IA 2017. Lecture Notes in Computer Science(), vol 10640. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-70169-1_7
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-70169-1_7
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-319-70168-4
Online ISBN: 978-3-319-70169-1
eBook Packages: Computer ScienceComputer Science (R0)