Abstract
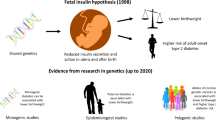
The hypothesis of fetal over-nutrition or fuel-mediated teratogenesis proposed in the 1950s by Pedersen postulates that intrauterine exposure to hyperglycemia causes permanent changes in the fetus of a woman with diabetes in pregnancy, leading to malformations, macrosomia, and an increased risk of developing obesity and type 2 diabetes later in life. More recent data confirm that exposure to diabetes in utero has effects on offspring body size that are distinct from, or act in concert with, genetic susceptibility to obesity and the postnatal environment. There is also evidence that exposure to maternal diabetes represents the extreme of a distribution of altered maternal fuels to which the fetus is exposed in pregnancies complicated by obesity. If maternal obesity during pregnancy drives fuel-mediated teratogenesis, the public health consequences are enormous. Efforts that reduce obesity in women of reproductive age and prevent excessive weight gain during pregnancy may not only decrease the risk of gestational diabetes in the mother, but will likely also reduce the risk of excess fetal growth, future obesity, and type 2 diabetes in the offspring.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ogden CL, Carroll MD, Kit BK, Flegal KM. Prevalence of childhood and adult obesity in the United States, 2011-2012. JAMA. 2014;311:806–14.
Wang Y, Beydoun MA. The obesity epidemic in the United States--gender, age, socioeconomic, racial/ethnic, and geographic characteristics: a systematic review and meta-regression analysis. Epidemiol Rev. 2007;29:6–28.
Flegal KM, Troiano RP. Changes in the distribution of body mass index of adults and children in the US population. Int J Obes Relat Metab Disord. 2000;24:807–18.
Beydoun MA, Wang Y. Socio-demographic disparities in distribution shifts over time in various adiposity measures among American children and adolescents: what changes in prevalence rates could not reveal. Int J Pediatr Obes. 2011;6:21–35.
Freedman DS, Dietz WH, Srinivasan SR, Berenson GS. The relation of overweight to cardiovascular risk factors among children and adolescents: the Bogalusa Heart Study. Pediatrics. 1999;103:1175–82.
Reilly JJ, Kelly J. Long-term impact of overweight and obesity in childhood and adolescence on morbidity and premature mortality in adulthood: systematic review. Int J Obes. 2011;35:891–8.
Ben-Shlomo Y, Kuh D. A life course approach to chronic disease epidemiology: conceptual models, empirical challenges and interdisciplinary perspectives. Int J Epidemiol. 2002;31:285–93.
Barker DJ. In utero programming of chronic disease. Clin Sci (Lond). 1998;95:115–28.
Barker DJ, Fall CH. Fetal and infant origins of cardiovascular disease. Arch Dis Child. 1993;68:797–9.
Barker DJ, Gluckman PD, Godfrey KM, Harding JE, Owens JA, Robinson JS. Fetal nutrition and cardiovascular disease in adult life. Lancet. 1993;341:938–41.
Freinkel N. Banting Lecture 1980. Of pregnancy and progeny. Diabetes. 1980;29:1023–35.
Pettitt DJ, Baird HR, Aleck KA, Bennett PH, Knowler WC. Excessive obesity in offspring of Pima Indian women with diabetes during pregnancy. N Engl J Med. 1983;308:242–5.
He XJ, Qin FY, Hu CL, Zhu M, Tian CQ, Li L. Is gestational diabetes mellitus an independent risk factor for macrosomia: a meta-analysis? Arch Gynecol Obstet. 2015;291:729–35.
Zhang X, Decker A, Platt RW, Kramer MS. How big is too big? The perinatal consequences of fetal macrosomia. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 2008;198:517 e511–6.
Catalano PM, Thomas A, Huston-Presley L, Amini SB. Increased fetal adiposity: a very sensitive marker of abnormal in utero development. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 2003;189:1698–704.
Logan KM, Gale C, Hyde MJ, Santhakumaran S, Modi N. Diabetes in pregnancy and infant adiposity: systematic review and meta-analysis. Arch Dis Child Fetal Neonatal Ed. 2017;102(1):F65–72.
Crume TL, Shapiro AL, Brinton JT, Glueck DH, Martinez M, Kohn M, Harrod C, Friedman JE, Dabelea D. Maternal fuels and metabolic measures during pregnancy and neonatal body composition: the Healthy Start Study. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2015;100:1672–80.
Petitt DJ, Bennett PH, Knowler WC, Baird HR, Aleck KA. Gestational diabetes mellitus and impaired glucose tolerance during pregnancy. Long-term effects on obesity and glucose tolerance in the offspring. Diabetes. 1985;34(Suppl 2):119–22.
Pettitt DJ, Nelson RG, Saad MF, Bennett PH, Knowler WC. Diabetes and obesity in the offspring of Pima Indian women with diabetes during pregnancy. Diabetes Care. 1993;16:310–4.
Pettitt DJ, Knowler WC, Bennett PH, Aleck KA, Baird HR. Obesity in offspring of diabetic Pima Indian women despite normal birth weight. Diabetes Care. 1987;10:76–80.
Silverman BL, Rizzo T, Green OC, Cho NH, Winter RJ, Ogata ES, Richards GE, Metzger BE. Long-term prospective evaluation of offspring of diabetic mothers. Diabetes. 1991;40(Suppl 2):121–5.
Crume TL, Ogden L, Daniels S, Hamman RF, Norris JM, Dabelea D. The impact of in utero exposure to diabetes on childhood body mass index growth trajectories: the EPOCH study. J Pediatr. 2011;158:941–6.
Crume TL, Ogden L, West NA, Vehik KS, Scherzinger A, Daniels S, McDuffie R, Bischoff K, Hamman RF, Norris JM, Dabelea D. Association of exposure to diabetes in utero with adiposity and fat distribution in a multiethnic population of youth: the Exploring Perinatal Outcomes among Children (EPOCH) Study. Diabetologia. 2011;54:87–92.
Crume TL, Ogden LG, Mayer-Davis EJ, Hamman RF, Norris JM, Bischoff KJ, McDuffie R, Dabelea D. The impact of neonatal breast-feeding on growth trajectories of youth exposed and unexposed to diabetes in utero: the EPOCH study. Int J Obes. 2012;36:529–34.
Wright CS, Rifas-Shiman SL, Rich-Edwards JW, Taveras EM, Gillman MW, Oken E. Intrauterine exposure to gestational diabetes, child adiposity, and blood pressure. Am J Hypertens. 2009;22:215–20.
Krishnaveni GV, Veena SR, Hill JC, Kehoe S, Karat SC, Fall CH. Intrauterine exposure to maternal diabetes is associated with higher adiposity and insulin resistance and clustering of cardiovascular risk markers in Indian children. Diabetes Care. 2010;33:402–4.
Kubo A, Ferrara A, Windham GC, Greenspan LC, Deardorff J, Hiatt RA, Quesenberry CP Jr, Laurent C, Mirabedi AS, Kushi LH. Maternal hyperglycemia during pregnancy predicts adiposity of the offspring. Diabetes Care. 2014;37:2996–3002.
Lawlor DA, Fraser A, Lindsay RS, Ness A, Dabelea D, Catalano P, Davey Smith G, Sattar N, Nelson SM. Association of existing diabetes, gestational diabetes and glycosuria in pregnancy with macrosomia and offspring body mass index, waist and fat mass in later childhood: findings from a prospective pregnancy cohort. Diabetologia. 2010;53:89–97.
Gillman MW, Rifas-Shiman S, Berkey CS, Field AE, Colditz GA. Maternal gestational diabetes, birth weight, and adolescent obesity. Pediatrics. 2003;111:e221–6.
Whitaker RC, Pepe MS, Seidel KD, Wright JA, Knopp RH. Gestational diabetes and the risk of offspring obesity. Pediatrics. 1998;101:E9.
Dabelea D, Pettitt DJ. Intrauterine diabetic environment confers risks for type 2 diabetes mellitus and obesity in the offspring, in addition to genetic susceptibility. J Pediatr Endocrinol Metab. 2001;14:1085–91.
Dabelea D, Mayer-Davis EJ, Lamichhane AP, D’Agostino RB Jr, Liese AD, Vehik KS, Narayan KM, Zeitler P, Hamman RF. Association of intrauterine exposure to maternal diabetes and obesity with type 2 diabetes in youth: the SEARCH Case-Control Study. Diabetes Care. 2008;31:1422–6.
Maftei O, Whitrow MJ, Davies MJ, Giles LC, Owens JA, Moore VM. Maternal body size prior to pregnancy, gestational diabetes and weight gain: associations with insulin resistance in children at 9-10 years. Diabet Med. 2015;32:174–80.
Chandler-Laney PC, Bush NC, Granger WM, Rouse DJ, Mancuso MS, Gower BA. Overweight status and intrauterine exposure to gestational diabetes are associated with children’s metabolic health. Pediatr Obes. 2012;7:44–52.
Holder T, Giannini C, Santoro N, Pierpont B, Shaw M, Duran E, Caprio S, Weiss R. A low disposition index in adolescent offspring of mothers with gestational diabetes: a risk marker for the development of impaired glucose tolerance in youth. Diabetologia. 2014;57:2413–20.
Davis JN, Gunderson EP, Gyllenhammer LE, Goran MI. Impact of gestational diabetes mellitus on pubertal changes in adiposity and metabolic profiles in Latino offspring. J Pediatr. 2013;162:741–5.
Holemans K, Gerber RT, Meurrens K, De Clerck F, Poston L, Van Assche FA. Streptozotocin diabetes in the pregnant rat induces cardiovascular dysfunction in adult offspring. Diabetologia. 1999;42:81–9.
Chen YW, Chenier I, Tran S, Scotcher M, Chang SY, Zhang SL. Maternal diabetes programs hypertension and kidney injury in offspring. Pediatr Nephrol. 2010;25:1319–29.
Rostand SG, Cliver SP, Goldenberg RL. Racial disparities in the association of foetal growth retardation to childhood blood pressure. Nephrol Dial Transplant. 2005;20:1592–7.
Bunt JC, Tataranni PA, Salbe AD. Intrauterine exposure to diabetes is a determinant of hemoglobin A(1)c and systolic blood pressure in pima Indian children. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2005;90:3225–9.
Cho NH, Silverman BL, Rizzo TA, Metzger BE. Correlations between the intrauterine metabolic environment and blood pressure in adolescent offspring of diabetic mothers. J Pediatr. 2000;136:587–92.
Manderson JG, Mullan B, Patterson CC, Hadden DR, Traub AI, McCance DR. Cardiovascular and metabolic abnormalities in the offspring of diabetic pregnancy. Diabetologia. 2002;45:991–6.
Boney CM, Verma A, Tucker R, Vohr BR. Metabolic syndrome in childhood: association with birth weight, maternal obesity, and gestational diabetes mellitus. Pediatrics. 2005;115:e290–6.
Plagemann A, Harder T, Kohlhoff R, Rohde W, Dorner G. Glucose tolerance and insulin secretion in children of mothers with pregestational IDDM or gestational diabetes. Diabetologia. 1997;40:1094–100.
Clausen TD, Mathiesen ER, Hansen T, Pedersen O, Jensen DM, Lauenborg J, Schmidt L, Damm P. Overweight and the metabolic syndrome in adult offspring of women with diet-treated gestational diabetes mellitus or type 1 diabetes. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2009;94:2464–70.
Wroblewska-Seniuk K, Wender-Ozegowska E, Szczapa J. Long-term effects of diabetes during pregnancy on the offspring. Pediatr Diabetes. 2009;10:432–40.
Boerschmann H, Pfluger M, Henneberger L, Ziegler AG, Hummel S. Prevalence and predictors of overweight and insulin resistance in offspring of mothers with gestational diabetes mellitus. Diabetes Care. 2010;33:1845–9.
Silverman BL, Metzger BE, Cho NH, Loeb CA. Impaired glucose tolerance in adolescent offspring of diabetic mothers. Relationship to fetal hyperinsulinism. Diabetes Care. 1995;18:611–7.
Sobngwi E, Boudou P, Mauvais-Jarvis F, Leblanc H, Velho G, Vexiau P, Porcher R, Hadjadj S, Pratley R, Tataranni PA, Calvo F, Gautier JF. Effect of a diabetic environment in utero on predisposition to type 2 diabetes. Lancet. 2003;361:1861–5.
Franks PW, Looker HC, Kobes S, Touger L, Tataranni PA, Hanson RL, Knowler WC. Gestational glucose tolerance and risk of type 2 diabetes in young Pima Indian offspring. Diabetes. 2006;55:460–5.
Shapiro AL, Schmiege SJ, Brinton JT, Glueck D, Crume TL, Friedman JE, Dabelea D. Testing the fuel-mediated hypothesis: maternal insulin resistance and glucose mediate the association between maternal and neonatal adiposity, the Healthy Start study. Diabetologia. 2015;58:937–41.
Catalano PM, Drago NM, Amini SB. Factors affecting fetal growth and body composition. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 1995;172:1459–63.
Sacks DA. Fetal macrosomia and gestational diabetes: what’s the problem? Obstet Gynecol. 1993;81:775–81.
Wen SW, Goldenberg RL, Cutter GR, Hoffman HJ, Cliver SP, Davis RO, DuBard MB. Smoking, maternal age, fetal growth, and gestational age at delivery. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 1990;162:53–8.
Meis PJ, Michielutte R, Peters TJ, Wells HB, Sands RE, Coles EC, Johns KA. Factors associated with term low birth weight in Cardiff, Wales. Paediatr Perinat Epidemiol. 1997;11:287–97.
Goldenberg RL, Cliver SP. Small for gestational age and intrauterine growth restriction: definitions and standards. Clin Obstet Gynecol. 1997;40:704–14.
Perry IJ, Lumey LH. Fetal growth and development: the role of nutrition and other factors. In: Kuh D, Ben-Shlomo Y, editors. A life course approach to chronic disease epidemiology. Oxford: Oxford University Press; 2004. p. 345–71.
Luke B. Nutritional influences on fetal growth. Clin Obstet Gynecol. 1994;37:538–49.
Abrams BF, Berman CA. Nutrition during pregnancy and lactation. Prim Care. 1993;20:585–97.
Starling AP, Brinton JT, Glueck DH, Shapiro AL, Harrod CS, Lynch AM, Siega-Riz AM, Dabelea D. Associations of maternal BMI and gestational weight gain with neonatal adiposity in the Healthy Start study. Am J Clin Nutr. 2015;101:302–9.
Group HSCR. Hyperglycaemia and Adverse Pregnancy Outcome (HAPO) Study: associations with maternal body mass index. BJOG. 2010;117:575–84.
Vohr BR, McGarvey ST, Coll CG. Effects of maternal gestational diabetes and adiposity on neonatal adiposity and blood pressure. Diabetes Care. 1995;18:467–75.
Vohr BR, McGarvey ST. Growth patterns of large-for-gestational-age and appropriate-for-gestational-age infants of gestational diabetic mothers and control mothers at age 1 year. Diabetes Care. 1997;20:1066–72.
Rankinen T, Zuberi A, Chagnon YC, Weisnagel SJ, Argyropoulos G, Walts B, Perusse L, Bouchard C. The human obesity gene map: the 2005 update. Obesity (Silver Spring). 2006;14:529–644.
White P. Childhood diabetes. Its course, and influence on the second and third generations. Diabetes. 1960;9:345–55.
Pettitt DJ, Knowler WC. Long-term effects of the intrauterine environment, birth weight, and breast-feeding in Pima Indians. Diabetes Care. 1998;21(Suppl 2):B138–41.
Perucca-Lostanlen D, Narbonne H, Hernandez JB, Staccini P, Saunieres A, Paquis-Flucklinger V, Vialettes B, Desnuelle C. Mitochondrial DNA variations in patients with maternally inherited diabetes and deafness syndrome. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2000;277:771–5.
Dabelea D, Hanson RL, Lindsay RS, Pettitt DJ, Imperatore G, Gabir MM, Roumain J, Bennett PH, Knowler WC. Intrauterine exposure to diabetes conveys risks for type 2 diabetes and obesity: a study of discordant sibships. Diabetes. 2000;49:2208–11.
Catalano PM, Kirwan JP, Haugel-de Mouzon S, King J. Gestational diabetes and insulin resistance: role in short- and long-term implications for mother and fetus. J Nutr. 2003;133:1674S–83S.
Shankar K, Harrell A, Liu X, Gilchrist JM, Ronis MJ, Badger TM. Maternal obesity at conception programs obesity in the offspring. Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol. 2008;294:R528–38.
Kieffer TJ, Habener JF. The adipoinsular axis: effects of leptin on pancreatic beta-cells. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab. 2000;278:E1–E14.
Seufert J, Kieffer TJ, Habener JF. Leptin inhibits insulin gene transcription and reverses hyperinsulinemia in leptin-deficient ob/ob mice. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1999;96:674–9.
Seufert J, Kieffer TJ, Leech CA, Holz GG, Moritz W, Ricordi C, Habener JF. Leptin suppression of insulin secretion and gene expression in human pancreatic islets: implications for the development of adipogenic diabetes mellitus. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1999;84:670–6.
Simmons D, Breier BH. Fetal overnutrition in polynesian pregnancies and in gestational diabetes may lead to dysregulation of the adipoinsular axis in offspring. Diabetes Care. 2002;25:1539–44.
Mantzoros CS, Rifas-Shiman SL, Williams CJ, Fargnoli JL, Kelesidis T, Gillman MW. Cord blood leptin and adiponectin as predictors of adiposity in children at 3 years of age: a prospective cohort study. Pediatrics. 2009;123:682–9.
Muhlhausler BS, Adam CL, Findlay PA, Duffield JA, McMillen IC. Increased maternal nutrition alters development of the appetite-regulating network in the brain. FASEB J. 2006;20:1257–9.
Persson B, Westgren M, Celsi G, Nord E, Ortqvist E. Leptin concentrations in cord blood in normal newborn infants and offspring of diabetic mothers. Horm Metab Res. 1999;31:467–71.
Wolf HJ, Ebenbichler CF, Huter O, Bodner J, Lechleitner M, Foger B, Patsch JR, Desoye G. Fetal leptin and insulin levels only correlate inlarge-for-gestational age infants. Eur J Endocrinol. 2000;142:623–9.
Kieffer TJ, Heller RS, Habener JF. Leptin receptors expressed on pancreatic beta-cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1996;224:522–7.
Plagemann A. ‘Fetal programming’ and ‘functional teratogenesis’: on epigenetic mechanisms and prevention of perinatally acquired lasting health risks. J Perinat Med. 2004;32:297–305.
Franke K, Harder T, Aerts L, Melchior K, Fahrenkrog S, Rodekamp E, Ziska T, Van Assche FA, Dudenhausen JW, Plagemann A. ‘Programming’ of orexigenic and anorexigenic hypothalamic neurons in offspring of treated and untreated diabetic mother rats. Brain Res. 2005;1031:276–83.
Gauguier D, Bihoreau MT, Ktorza A, Berthault MF, Picon L. Inheritance of diabetes mellitus as consequence of gestational hyperglycemia in rats. Diabetes. 1990;39:734–9.
Aerts L, Sodoyez-Goffaux F, Sodoyez JC, Malaisse WJ, Van Assche FA. The diabetic intrauterine milieu has a long-lasting effect on insulin secretion by B cells and on insulin uptake by target tissues. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 1988;159:1287–92.
Hultquist GT, Olding LB. Pancreatic-islet fibrosis in young infants of diabetic mothers. Lancet. 1975;2:1015–6.
Gautier JF, Wilson C, Weyer C, Mott D, Knowler WC, Cavaghan M, Polonsky KS, Bogardus C, Pratley RE. Low acute insulin secretory responses in adult offspring of people with early onset type 2 diabetes. Diabetes. 2001;50:1828–33.
Shao WJ, Tao LY, Gao C, Xie JY, Zhao RQ. Alterations in methylation and expression levels of imprinted genes H19 and Igf2 in the fetuses of diabetic mice. Comp Med. 2008;58:341–6.
Ding GL, Wang FF, Shu J, Tian S, Jiang Y, Zhang D, Wang N, Luo Q, Zhang Y, Jin F, Leung PC, Sheng JZ, Huang HF. Transgenerational glucose intolerance with Igf2/H19 epigenetic alterations in mouse islet induced by intrauterine hyperglycemia. Diabetes. 2012;61:1133–42.
Ma RC, Tutino GE, Lillycrop KA, Hanson MA, Tam WH. Maternal diabetes, gestational diabetes and the role of epigenetics in their long term effects on offspring. Prog Biophys Mol Biol. 2015;118:55–68.
Landon MB, Spong CY, Thom E, Carpenter MW, Ramin SM, Casey B, Wapner RJ, Varner MW, Rouse DJ, Thorp JM Jr, Sciscione A, Catalano P, Harper M, Saade G, Lain KY, Sorokin Y, Peaceman AM, Tolosa JE, Anderson GB, Eunice Kennedy Shriver National Institute of Child H, Human Development Maternal-Fetal Medicine Units N. A multicenter, randomized trial of treatment for mild gestational diabetes. N Engl J Med. 2009;361:1339–48.
Gillman MW, Oakey H, Baghurst PA, Volkmer RE, Robinson JS, Crowther CA. Effect of treatment of gestational diabetes mellitus on obesity in the next generation. Diabetes Care. 2010;33:964–8.
Landon MB, Rice MM, Varner MW, Casey BM, Reddy UM, Wapner RJ, Rouse DJ, Biggio JR Jr, Thorp JM, Chien EK, Saade G, Peaceman AM, Blackwell SC, VanDorsten JP, Eunice Kennedy Shriver National Institute of Child H, Human Development Maternal-Fetal Medicine Units N. Mild gestational diabetes mellitus and long-term child health. Diabetes Care. 2015;38:445–52.
Poston L, Bell R, Croker H, Flynn AC, Godfrey KM, Goff L, Hayes L, Khazaezadeh N, Nelson SM, Oteng-Ntim E, Pasupathy D, Patel N, Robson SC, Sandall J, Sanders TA, Sattar N, Seed PT, Wardle J, Whitworth MK, Briley AL, Consortium UT. Effect of a behavioural intervention in obese pregnant women (the UPBEAT study): a multicentre, randomised controlled trial. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 2015;3:767–77.
Dodd JM, Cramp C, Sui Z, Yelland LN, Deussen AR, Grivell RM, Moran LJ, Crowther CA, Turnbull D, McPhee AJ, Wittert G, Owens JA, Robinson JS, Group LRT. The effects of antenatal dietary and lifestyle advice for women who are overweight or obese on maternal diet and physical activity: the LIMIT randomised trial. BMC Med. 2014;12:161.
Song C, Li J, Leng J, Ma RC, Yang X. Lifestyle intervention can reduce the risk of gestational diabetes: a meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Obes Rev. 2016;17:960–9.
Pettitt DJ, Knowler WC. Diabetes and obesity in the Pima Indians: a cross-generational vicious cycle. J Obesity Weight Regul. 1988:61–5.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2018 Springer International Publishing AG
About this chapter
Cite this chapter
Dabelea, D., Sauder, K.A. (2018). Intrauterine Exposure to Maternal Diabetes and Childhood Obesity. In: Freemark, M. (eds) Pediatric Obesity. Contemporary Endocrinology. Humana Press, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-68192-4_13
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-68192-4_13
Published:
Publisher Name: Humana Press, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-319-68191-7
Online ISBN: 978-3-319-68192-4
eBook Packages: MedicineMedicine (R0)