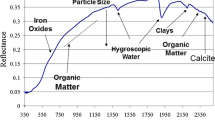
Abstract
Since the early ages of soil surveys, air photographs have been intensively used by soil surveyors for depicting the soil variations across landscapes. The variations of soil surfaces, specifically color and ratio of vegetation cover, that were revealed by this early remote sensing product were a great help for interpolating the scarce soil observations and for delineating the soil class boundaries. This was further transposed in digital soil mapping (McBratney et al. 2003), thanks to the large availability of remote sensing images provided by the emerging spatial data infrastructures. Up to now, digital soil mappers have mainly used remote sensing images as spatial data inputs for representing the landscape variables that are related with soil, such as vegetation and parent material (the soil covariates). Boettinger et al. (2008) reviewed the main indicators that could be retrieved for estimating these soil covariates, using multispectral data acquired in the visible near-infrared and short-wave infrared (VIS, 400–700 nm; NIR, 700–1100 nm; SWIR, 1100–2500 nm) spectral domain. After a spatial overlay with the sparse sets of observed and measured sites collected in a given area, the indicators derived from remote sensing have been used as independent variables in regression-like models or as external drift in geostatistic models (McBratney et al. 2003, Chap. 12 of this book).
“If you were born without wings, do nothing to prevent them from growing”.
Coco Chanel
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ackerson JP, Demattê JAM, Morgan CLS (2015) Predicting clay content on field-moist intact tropical soils using a dried, ground VisNIR library with external parameter orthogonalization. Geoderma 259–260:196–204
Bartholomeus H, Epema G, Schaepman M (2007) Determining iron content in Mediterranean soils in partly vegetated areas, using spectral reflectance and imaging spectroscopy. Int J Appl Earth Obs Geoinf 9:194–203
Bartholomeus H, Schaepman ME, Kooistra L, Stevens A, Hoogmoed WB, Spaargaren OSP (2008) Spectral reflectance based indices for soil organic carbon quantification. Geoderma 145(1–2):28–36
Bartholomeus H, Kooistra L, Stevens A, Van Leeuwen M, Van Wesemael B, Ben-Dor E, Tychon B (2011) Soil organic carbon mapping of partially vegetated agricultural fields with imaging spectroscopy. Int J Appl Earth Obs Geoinf 13:81–88
Baume O, Skøien JO, Heuvelink GBM, Pebesma EJ (2011) A geostatistical approach to data harmonization – application to radioactivity exposure data. Int J Appl Earth Obs Geoinf 13(3):409–419
Baumgardner MF, Kristof SJ, Johannsen CJ, Zachary AL (1970) Effects of organic matter on the multispectral properties of soils. Proc Indian Acad Sci 79:413–422
Baumgardner MF, Silva LF, Biehl LL, Stoner ER (1985) Reflectance properties of soils. Adv Agron 38:l–44
Ben-Dor E, Banin A (1995) Near infrared analysis (NIRA) as a simultaneous method to evaluate spectral featureless constituents in soils. Soil Sci 159:259–269
Ben-Dor E, Inbar Y, Chen Y (1997) The reflectance spectra of organic matter in the visible near-infrared and short wave infrared region (400–2500) during a controlled decomposition process. Remote Sens Environ 61:1–15
Ben-Dor E, Irons JA, Epema A (1998) Soil spectroscopy. In: Rencz A (ed) Manual of remote sensing, 3rd edn. Wiley, New-York, pp 111–189
Ben-Dor E, Patkin K, Banin A, Karnieli A (2002) Mapping of several soil properties using DAIS-7915 hyperspectral scanner data – a case study over clayey soils in Israel. Int J Remote Sens 23:1043–1062
Ben-Dor E, Levin N, Singer A, Karnieli A, Braun O, Kidron GJ (2006) Quantitative mapping of the soil rubification process on sand dunes using an airborne hyperspectral sensor. Geoderma 131:1–21
Ben-Dor E, Taylor RG, Hill J, Demattê JAM, Whiting ML, Chabrillat S, Sommer S (2008) Imaging spectrometry for soil applications. Adv Agron Acad Press 97:321–392
Ben-Dor E, Chabrillat S, Demattê JAM, Taylor GR, Hill J, Whiting ML, Sommer S (2009) Using imaging spectroscopy to study soil properties. Remote Sens Environ 113(1):S38–S55. 2009
Bishop TFA, McBratney AB, Laslett GM (1999) Modelling soil attribute depth functions with equal-area quadratic smoothing splines. Geoderma 91:27–45
Boettinger J, Ramsey RD, Bodily JM, (2008) Landsat spectral data for digital soil mapping. In: Hartemink A, McBratney AB Mendonca Santos L (eds), Digital soil mapping with limited data. pp. 193–199
Bowers SA, Hanks AJ (1965) Reflection of radiant energy from soil. Soil Sci 100:130–138
Bricklemyer RS, Brown DJ (2010) On-the-go VisNIR: potential and limitations for mapping soil clay and organic carbon. Comput Electron Agric 70(1):209–216
Briottet X, Marion R, Carrere V, Jacquemoud S, Bourguignon A, Chami M, Chanussot J, Chevrel S, Deliot P, Dumont M, Foucher PY, Minghelli-Roman A, Sheeren D, Weber C, Prastault P, Hosford S, Lefevre MJ (2013) HYPXIM: HYPXIM: a second generation high spatial resolution hyperspectral satellite for dual applications, Fifth Workshop on Hyperspectral Image and Signal Processing: Evolution in Remote Sensing (WHISPERS)., June 2013. Gainesville, Florida
Chabrillat S, Goetz AFH, Krosley S, Olsen HW (2002) Use of hyperspectral images in the identification and mapping of expansive clay soils and the role of spatial resolution. Remote Sens Environ 82:431–445
Ciampalini R, Lagacherie P, Monestiez P, Walker E, Gomez C (2012) Co-kriging of soil properties with Vis-NIR hyperspectral covariates in the Cap Bon region (Tunisia). In: Minasny, Malone, McBratney (eds), Digital soil assessments and beyond. CRC Press 2012, pp. 393–398
Ciampalini R, Lagacherie P, Gomez C, Grunberger O, Hamrouni H, Mekki I, Richard A (2013) Detecting and correcting biases of measured soil profiles data. A case study in the Cap Bon Region (Tunisia). Geoderma 192:68–76
Escadafal R, Huete A (1991) Etude des propriétés spectrales des sols arides appliquée à l’amélioration des indices végétation obtenus par télédétection. C R Acad Sci Paris Série II 312:1385–1391
Gaffey SJ (1987) Spectral reflectance of carbonate minerals in the visible and near infrared (0.35–2.55 pm): calcite, aragonite and dolomite. J Geophys Res Solid Earth 71:151–162
Ge Y, Morgan CLS, Ackerson JP (2014) VisNIR spectra of dried ground soils predict properties of soils scanned moist and intact. Geoderma 213:61–69
Gomez C, Viscarra Rossel RA, McBratney AB (2008a) Soil organic carbon prediction by hyperspectral remote sensing and field vis-NIR spectroscopy: an Australian case study. Geoderma 146(3–4):403–411
Gomez C, Lagacherie P, Coulouma G (2008b) Continuum removal versus PLSR method for clay and calcium carbonate content estimation from laboratory and airborne hyperspectral measurements. Geoderma 148(2):141–148
Gomez C, Lagacherie P Bacha S (2012a) Using an Vis-NIR hyperspectral image to map topsoil properties over bare soil surfaces in the Cap Bon region (Tunisia). In: Minasny, Malone & McBratney (eds), Digital soil assessments and beyond. CRC Press 2012, pp. 387–392
Gomez C, Coulouma G, Lagacherie P (2012b) Regional predictions of eight common soil properties and their spatial structures from hyperspectral Vis–NIR data. Geoderma 189–190:176–185
Gomez C, Drost APA, Roger J (2015) Remote sensing of environment analysis of the uncertainties affecting predictions of clay contents from VNIR/SWIR hyperspectral data. Remote Sens Environ 156:58–70
Gomez C, Gholizadeh A, Borůvka L, Lagacherie P (2016) Using legacy data for predicting soil surface clay content from VNIR/SWIR hyperspectral airborne images. Geoderma 276:84–92
Grunwald S (2009) Multi-criteria characterization of recent digital soil mapping and modeling approaches. Geoderma 152:195–207
Guanter L, Kaufmann H, Segl K, Förster S, Rogass C, Chabrillat S, Küster T, Hollstein A, Rossner G, Chlebek C, Straif C, Fischer S, Schrader S, Storch T, Heiden U, Müller A, Bachmann M, Mühle H, Müller R, Habermeyer M, Ohndorf A, Hill J, Buddenbaum H, Hostert P, van der Linden S, Leitao PJ, Rabe A, Doerffer R, Krasemann H, Xi H, Mauser W, Hank T, Locherer M, Rast M, Staenz K, Sang B (2015) The EnMAP Spaceborne imaging spectroscopy mission for earth observation. Remote Sens 7(7):8830–8857
Haubrock S, Chabrillat S, Lemmnitz C, Kaufmann H (2008) Surface soil moisture quantification models from reflectance data under field conditions. Int J Remote Sens 29:3–29
Hunt GR, Salisbury JW, Lenhoff CJ (1971) Visible and near-infrared spectra of minerals and rocks: III. Oxides hydroxides. Mod Geol 2:195–205
Journel AG (1986) Constrained interpolation and qualitative information – the soft kriging approach. Math Geol 18:269
Kennard RW, Stone LA (1969) Computer aided design of experiments. Technometrics 11(1):137–148
Kokaly RF, Clark RN (1999) Spectroscopic determination of leaf biochemistry using band-depth analysis of absorption features and stepwise multiple linear regression. Remote Sens Environ 67:267–287
Lagacherie P, Baret F, Feret JB, Madeira NJ, Robbez-Masson JM (2008) Estimation of soil clay and calcium carbonate using laboratory, field and airborne hyperspectral measurements. Remote Sens Environ 112(3):825–835
Lagacherie P, Bailly JS, Monestiez P, Gomez C (2012) Using scattered soil sensing field surveys to map soil properties over a region. An example with airborne hyperspectral imagery. Eur J Soil Sci 63:110–119
Lagacherie P, Sneep A-R, Gomez C, Bacha S, Coulouma G, Hamrouni MH, Mekki I (2013) Combining Vis–NIR hyperspectral imagery and legacy measured soil profiles to map subsurface soil properties in a Mediterranean area (Cap-Bon, Tunisia). Geoderma 209–210:168–176
Levin N, Tsoar H, Maia LP, Sales VC, Herrmann H (2007) Dune whitening and inter-dune freshwater ponds in NE Brazil. Catena 70(1):1–15
Madeira J, Bedidi A, Pouget J, Cervelle B, Flay N (1997) Spectrometric indices (visible) of hematite and goethite contents in lateritic soils. Application to a TM image for soil mapping of Brasilia area. Int J Remote Sens 18(13):2835–2852
McBratney AB, Mendonca Santos ML, Minasny B (2003) On digital soil mapping. Geoderma 117:3–52
Minasny B, McBratney AB, Pichon L, Sun W, Short MG (2009) Evaluating near infrared spectroscopy for field prediction of soil properties. Soil Res 47(7):664–673
Minasny B, McBratney AB, Bellon-Maurel V, Roger JM, Gobrecht A, Ferrand L, Joalland S (2011) Removing the effect of soil moisture from NIR diffuse reflectance spectra for the prediction of soil organic carbon. Geoderma 167–168:118–124
Morris RV, Lauer HV, Lawson CA, Gibson EK Jr, Nace GA, Stewart C (1985) Spectral and other physicochemical properties of submicron powders of Hematite (α-Fe 2 O 3 ), Maghematite (γ-Fe 2 O 3 ), Magnetite (Fe 3 O 4 ), Goethite (α-FeOOH), and Lepidocrocite (γ-FeOOH). J Geophys Res 90:3126–3144
Nanni MR, Demattê JAM (2006) Spectral reflectance methodology in comparison to traditional soil analysis. Soil Sci Soc Am J 70(2):393–407
Nocita M, Stevens A, Noon C, Van Wesemael B (2013) Prediction of soil organic carbon for different levels of soil moisture using Vis-NIR spectroscopy. Geoderma 199:37–42
Ouerghemmi W, Gomez C, Naceur S, Lagacherie P (2011) Applying blind source separation on hyperspectral data for clay content estimation over partially vegetated surfaces. Geoderma 163(3–4):227–237
Ouerghemmi W, Gomez C, Nacer S, Lagacherie P (2016) Semi-blind source separation for estimation of clay content over semi-vegetated areas, from VNIR/SWIR hyperspectral airborne data. Remote Sens Environ 181:251–263
Pouget M, Madeira J, Le Floc’h E, Kamal S (1991) Caractéristiques spectrales des surfaces sableuses de la région cotière nord-ouest de l’Egypte: application aux données satellitaires SPOT. In Proc. 2e’me Journées Télédétection. In: Caractérisation et Suivi des Milieux Terrestres en Régions Arides et Tropicales. ORSTOM, Bondy, pp. 27–38
Roger JM, Chauchard F, Bellon-Maurel V (2003) EPO–PLS external parameter orthogonalisation of PLS application to temperature-independent measurement of sugar content of intact fruits. Chemom Intell Lab Syst 66(2):191–204
Schwanghart W, Jarmer T (2011) Linking spatial patterns of soil organic carbon to topography – a case study from south-eastern Spain. Geomorphology 126:252–263
Selige T, Bohner J, Schmidhalter U (2006) High resolution topsoil mapping using hyperspectral image and field data in multivariate regression modeling procedures. Geoderma 136(1–2):235–244
Snee RD (1977) Validation of regression models: methods and examples. Technometrics 19(4):415–428
Stevens A, Wesemael B, Bartholomeus B, Rosillon D, Tychon B, Ben-Dor E (2008) Laboratory, field and airborne spectroscopy for monitoring organic carbon content in agricultural soils. Geoderma 144(1–2):395–404
Stoner ER, Baumgardner MF (1981) Characteristic variations in reflectance of surface soils. Soil Sci Soc Am J 45:1161–1165
Sun W, Minasny B, McBratney AB (2012) Analysis and prediction of soil properties using local regression-kriging. Geoderma 171–172:16–23
Van Der Meer F (2004) Analysis of spectral absorption features in hyperspectral imagery. Int J Appl Earth Obs Geoinf 5(1):55–68
Viscarra Rossel RA, Walvoort DJJ, McBratney AB, Janik LJ, Skjemstad JO (2006) Visible, near infrared, mid infrared or combined diffuse reflectance spectroscopy for simultaneous assessment of various soil properties. Geoderma 131:59–75
Wackernagel H (1995) Multivariate geostatistics. Springer Verlag edition
Wold S, Sjostrom M, Eriksson L (2001) PLS-regression: a basic tool of chemometrics. Chemom Intell Lab Syst 58:109–130
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2018 Springer International Publishing AG, part of Springer Nature
About this chapter
Cite this chapter
Lagacherie, P., Gomez, C. (2018). Vis-NIR-SWIR Remote Sensing Products as New Soil Data for Digital Soil Mapping. In: McBratney, A., Minasny, B., Stockmann, U. (eds) Pedometrics. Progress in Soil Science. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-63439-5_13
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-63439-5_13
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-319-63437-1
Online ISBN: 978-3-319-63439-5
eBook Packages: Earth and Environmental ScienceEarth and Environmental Science (R0)