Abstract
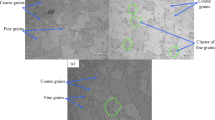
The microstructural aspects of shock induced plasticity and consequent failure in metals were studied using AZ31B and AMX602 magnesium alloys which were mechanically processed via Equal Channel Angular Extrusion (ECAE) and Spinning Water Atomization Process (SWAP) respectively. Results show that microstructure and microstructure evolution can strongly influence the mechanical response and consequent failure of these materials. Failure in both ECAE processed AZ31B-4E and AZ31B-4B/C magnesium alloy was dominated by debonding of the matrix magnesium from large Al-Mn-rich intermetallic inclusions and/or cracking of inclusions after the passage of shock stresses ranging from 1.5 to 4.5 GPa. However, the failure characteristic in the SWAP AMX602 magnesium alloy was distinctly different from that of the AZ31B magnesium alloy for the similar shock stress range. Numerous isolated cracks were observed around the spall plane possibly emanating from nucleation sites other than the Al2Ca intermetallic inclusions in AMX602. The spall surfaces of the AMX602 samples were striated possibly due to corrosion of the SWAP powder prior to green-compaction. Mixed-mode failure was observed in all three materials possibly due to homogeneous and heterogeneous nucleation, growth, and coalescence of nanovoids and microvoids respectively.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Tenckhoff, E.: Review of deformation mechanisms, texture, and mechanical anisotropy in zirconium and Zirconium Base alloys. Astm Special Tech- Nical Publication. 2(4), 1–26 (2006)
Mises, R.V.: Mechanik der plastischen formnderung von kristallen. ZAMM (Journal of Applied Mathematics and Mechanics/Zeitschrift fr Angewandte Mathematik und Mechanik). 8(3), 161–185 (1928)
Klimanek, P., Poetzsch, A.: Mater. Sci. Eng. A. 324, 145–150 (2002)
Kelley, E.W., Hosford Jr., W.F.: Trans. AIME. 242, 5–13 (1968)
Wonsiewicz, B.C., Backofen, W.A.: Trans. AIME. 239, 1422–1431 (1967)
Renganathan, P., Winey, J.M., Gupta, Y.M.: J. Appl. Phys. 121, 035901 (2017)
Schmidt, R.M., Davies, F.W., Lempriere, B.M., Holsapple, K.A.: J. Phys. Chem. Solids. 39, 375 (1978)
McQueen, R.G., Marsh, S.P., Taylor, J.W., Fritz, J.N., Carter, W.J.: In: Kinslow, R. (ed.) High Velocity Impact Phenomena, pp. 293–417. Academic, New York (1970)
Marsh, S.P.: LASL Shock Hugoniot Data. University of California Press, Berkeley (1980)
Kanel, G.I., Razorenov, S.V., Bogatch, A., Utkin, A.V., Grady, D.E.: Int J Impact Eng. 20, 467 (1997)
Hazell, P.J., Appleby-Thomas, G.J., Wielewski, E., Stennett, C., Siviour, C.: Acta Mater. 60, 6042–6050 (2012)
Farbaniec, L., Williams, C.L., Kecskes, L., Ramesh, K.T., Becker, R.: Int. J. Impact Eng. 98, 34–41 (2016)
Barber, R.E., Dudo, T., Yasskin, P.B., Hartwig, K.T.: Scr. Mater. 51(5), 373–377 (2004)
Kondoh, K., El-Sayed, A.H., Imai, H., Umeda, J.: ARL-CR-647 US Army Research Laboratory (2010)
Williams, C.L., Chen, C.Q., Ramesh, K.T., Dandekar, D.P.: J. Appl. Phys. 114, 093502 (2013)
Williams, C.L., Chen, C.Q., Ramesh, K.T., Dandekar, D.P.: J. MSEA. 618, 596–604 (2014)
Farbaniec, L., Williams, C.L., Kecskes, L., Becker, R., Ramesh, K.T.: Unpublished (2017)
Kanel, G.I.: J. Appl. Mech. Tech. Phys. 42(2), 358 (2001)
Acknowledgements
The authors gratefully acknowledge Mr. Jermaine Bradley and Mr. Micah Gallagher for their valuable support in sample fabrication and recovery experiments. Thanks to Dr. Laszlo Kecskes and Mr. Tyrone Jones for providing the AZ31B and AMX602 plates from which plate impact samples were fabricated.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2018 The Society for Experimental Mechanics, Inc.
About this paper
Cite this paper
Williams, C.L., Ligda, J., Farbaniec, L., Krywopusk, N. (2018). On the Microstructural Aspects of Shock Induced Failure in Magnesium Alloys. In: Kimberley, J., Lamberson, L., Mates, S. (eds) Dynamic Behavior of Materials, Volume 1. Conference Proceedings of the Society for Experimental Mechanics Series. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-62956-8_20
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-62956-8_20
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-319-62955-1
Online ISBN: 978-3-319-62956-8
eBook Packages: EngineeringEngineering (R0)