Abstract
Compared to ordinary Portland cement (OPC) concrete, alkali activated compounds refer to inorganic materials that cement is not the main constituent in their mixes. In fact, alkali activated concretes have two main parts in their binder structure: source material and alkaline activator liquid. In this study, the binder consists of blast furnace slag as a source material and sodium silicate solution (wt. ratio: SiO2/Na2O = 2.33) and 6 M potassium hydroxide which are incorporated as alkaline activator liquids. Since there are several parameters that affect the properties of these concretes, 9 alkali activated concrete mix designs are utilized to investigate the influence of source material amount, solid part of alkaline activator, solid part of sodium silicate solution and the ratio of water to binder. Furthermore, one mix design for OPC concrete is performed to compare with alkali activated slag (AAS) concrete characteristics.
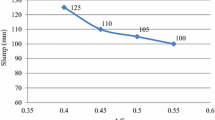
In this investigation, the fresh concrete properties are reported for these mix designs through slump loss test. Additionally, the compressive strength of the samples is measured at 1, 7, 28, 90 and 180 days ages. Moreover, because of the influence of chloride ion penetration that initiates corrosion of the reinforcement steel, chloride ion ingress is examined by diffusion tests based on NT Build 443. Besides, color change boundaries (CCB) in each specimen are measured to determine the penetration depth.
According to the results, mechanical properties and durability of AAS concretes are mostly influenced by the alkaline activator liquid contents and also it was observed that these characteristics development is decelerated specially by increasing the amount of activators.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Arya, C., Buenfeld, N.R., Newman, J.B.: Factors influencing chloride-binding in concrete. Cem. Concr. Res. 20(2), 291–300 (1990)
ASTM C143/C143M – 13: Standard Test Method for Slump of Hydraulic-Cement Concrete. ASTM International, West Conshohocken (2013)
ASTM C494/C494 M: Standard Specification for Chemical Admixtures for Concrete. ASTM International, West Conshohocken (2016)
ASTM C989/C989M-14: Standard Specification for Slag Cement for Use in Concrete and Mortars. ASTM International, West Conshohocken (2014)
Collins, F.G., Sanjayan, J.G.: Workability and mechanical properties of alkali activated slag concrete. Cem. Concr. Res. 29(3), 455–458 (1999)
Hakkinen, T.: Durability of alkali-activated slag concrete. Nord. Concr. Res. 6, 81–94 (1987)
Kazemian, A., Vayghan, A.G., Rajabipour, F.: Quantitative assessment of parameters that affect strength development in alkali activated fly ash binders. Constr. Build. Mater. 93, 869–876 (2015)
NT Build 443, Nord test method: Concrete, hardened: Accelerated chloride penetration (1995)
Sathonsaowaphak, A., Chindaprasirt, P., Pimraksa, K.: Workability and strength of lignite bottom ash geopolymer mortar. J. Hazard. Mater. 168(1), 44–50 (2009)
Saud, A.O.: Performance of alkali-activated slag concrete. The University of Sheffield, Sheffield (2002)
Wang, S.D., Pu, X.C., Scrivener, K.L., Pratt, P.L.: Alkali-activated slag cement and concrete: a review of properties and problems. Adv. Cem. Res. 7(27), 93–102 (1995)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2018 Springer International Publishing AG
About this paper
Cite this paper
Ramezanianpour, A.A., Bahman Zadeh, F., Zolfagharnasab, A., Ramezanianpour, A.M. (2018). Mechanical Properties and Chloride Ion Penetration of Alkali Activated Slag Concrete. In: Hordijk, D., Luković, M. (eds) High Tech Concrete: Where Technology and Engineering Meet. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-59471-2_252
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-59471-2_252
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-319-59470-5
Online ISBN: 978-3-319-59471-2
eBook Packages: EngineeringEngineering (R0)