Abstract
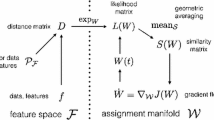
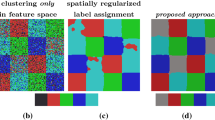
Recently, a smooth geometric approach to the image labeling problem was proposed [1] by following the Riemannian gradient flow of a given objective function on the so-called assignment manifold. The approach evaluates user-defined data term and additionally performs Riemannian averaging of the assignment vectors for spatial regularization. In this paper, we consider more elaborate graphical models, given by both data and pairwise regularization terms, and we show how they can be evaluated using the geometric approach. This leads to a novel inference algorithm on the assignment manifold, driven by local Wasserstein flows that are generated by pairwise model parameters. The algorithm is massively edge-parallel and converges to an integral labeling solution.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Åström, F., Petra, S., Schmitzer, B., Schnörr, C.: Image labeling by assignment. J. Math. Imaging Vis. 58(2), 211–238 (2017)
Bergmann, R., Fitschen, J.H., Persch, J., Steidl, G.: Iterative multiplicative filters for data labeling. Int. J. Comput. Vis. 1–19 (2017). http://dx.doi.org/10.1007/s11263-017-0995-9
Brualdi, R.: Combinatorial Matrix Classes. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge (2006)
Cuturi, M.: Sinkhorn Distances: Lightspeed Computation of Optimal Transport. In: Proceedings of the NIPS (2013)
Cuturi, M., Peyré, G.: A smoothed dual approach for variational wasserstein problems. SIAM J. Imag. Sci. 9(1), 320–343 (2016)
Danskin, J.: The theory of max min with applications. SIAM J. Appl. Math. 14, 641–664 (1966)
Kappes, J., Andres, B., Hamprecht, F., Schnörr, C., Nowozin, S., Batra, D., Kim, S., Kausler, B., Kröger, T., Lellmann, J., Komodakis, N., Savchynskyy, B., Rother, C.: A comparative study of modern inference techniques for structured discrete energy minimization problems. Int. J. Comput. Vis. 115(2), 155–184 (2015)
Kolouri, S., Park, S., Thorpe, M., Slepcev, D., Rohde, G.: Transport-based analysis, modeling, and learning from signal and data distributions (2016). preprint: https://arxiv.org/abs/1609.04767
Nesterov, Y.: Smooth minimization of non-smooth functions. Math. Program. Ser. A 103, 127–152 (2005)
Peyré, G.: Entropic approximation of wasserstein gradient flows. SIAM J. Imag. Sci. 8(4), 2323–2351 (2015)
Rockafellar, R.: On a special class of functions. J. Opt. Theor. Appl. 70(3), 619–621 (1991)
Schmidt, M.: UGM: Matlab code for undirected graphical models, January 2017
Schneider, M.: Matrix scaling, entropy minimization, and conjugate duality (II): the dual problem. Math. Program. 48, 103–124 (1990)
Wainwright, M., Jordan, M.: Graphical models, exponential families, and variational inference. Found. Trends Mach. Learn. 1(1–2), 1–305 (2008)
Weiss, Y.: Comparing the mean field method and belief propagation for approximate inference in MRFs. In: Advanced Mean Field Methods: Theory and Practice, pp. 229–240. MIT Press (2001)
Werner, T.: A linear programming approach to max-sum problem: a review. IEEE Trans. Patt. Anal. Mach. Intell. 29(7), 1165–1179 (2007)
Yedidia, J., Freeman, W., Weiss, Y.: Constructing free-energy approximations and generalized belief propagation algorithms. Trans. I. Theor. 51(7), 2282–2312 (2005)
Acknowledgments
We gratefully acknowledge support by the German Science Foundation, grant GRK 1653.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2017 Springer International Publishing AG
About this paper
Cite this paper
Åström, F., Hühnerbein, R., Savarino, F., Recknagel, J., Schnörr, C. (2017). MAP Image Labeling Using Wasserstein Messages and Geometric Assignment. In: Lauze, F., Dong, Y., Dahl, A. (eds) Scale Space and Variational Methods in Computer Vision. SSVM 2017. Lecture Notes in Computer Science(), vol 10302. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-58771-4_30
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-58771-4_30
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-319-58770-7
Online ISBN: 978-3-319-58771-4
eBook Packages: Computer ScienceComputer Science (R0)