Abstract
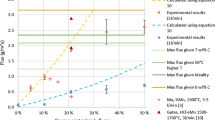
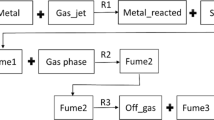
During the casting of ferromanganese alloys, a considerable amount of dark fumes, consisting primarily of manganese oxides, are generated when the Mn vapour oxidises in the atmosphere. Previous studies indicate that these fumes can be reduced by increasing the humidity above the melt. However, the reduction mechanism is not fully understood. In an attempt to understand the reduction mechanism, the influence of a humidity change on the fuming rate was studied. Laboratory scale experiments were conducted where an impinging jet blew air with a varying humidity onto the melt where dust was captured to determine relative mass fluxes. When the wet air experiments’ fume fluxes were compared to the dry air experiment, it was found that the increase in humidity resulted in a significant fume reduction (between 33 and 79%), confirming industrial observations. Dust composition from the experiments as well as dust reduction mechanisms are presented and discussed.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
E. Turkdogan et al., Enhancement of diffusion-limited rates of vaporization of metals. J. Phys. Chem. 67(8), 1647–1654 (1963)
S.E. Olsen et al., Production of Manganese Ferroalloys (Tapir Akademisk Forlag, Trondheim, Norway, 2007)
Y.E. Lee, L. Kolbeinsen, Kinetics of oxygen refining process for ferromanganese alloys. ISIJ Int. 45(9), 1282–1290 (2005)
K. Yamamoto et al., Decarburization of molten ferro-manganese in combined blowing converter. Fourth Japan-Nordic countries symposium on science and technology of process metallurgy, Tokyo, 1986
I. Kero et al., Fume formation from liquid ferromanganese, in Sustainable Industrial Processing Summit, Antalya, Turkey (2015)
M.K. Næss et al., Experimental study of rate of silica formation from active oxidation of liquid silicon, in Infraxon XIII, Almaty, Kazakhstan, Infraxon XIII (2013)
S.J. Gates et al., The use of fine water sprays to suppress fume emissions when casting ferromanganese. Clean Air J. 25(2), 26–35 (2015)
N. de Nevers, Air Pollution Control Engineering, 2nd edn. (McGraw-Hill International Editions, Singapore, 2010), pp. 299–307
S.J. Gates et al. Mechanisms to supress fume emissions by using water sprays when casting FeMn (Report 11048-4-06-2-06, Resonant Environmental Technologies, 2016)
L.R. Genskow et al. Psychrometry, evaporative cooling and solids drying, in Perry’s Chemical Engineers’ Handbook, ed. by W. Green (McGra-Hill Companies Inc., United States of America, 2008), pp. 3–6
J.P. Holman, Experimental Methods for Engineers, 8th edn. (McGraw-Hill/Connect Learn Succeed, New York, NY, 2012)
Acknowledgements
The authors acknowledge the financial support of the DeMaskUs project through the Norwegian Research Council grant no 245216.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2017 The Minerals, Metals & Materials Society
About this chapter
Cite this chapter
Gates, S.J., Kornelius, G., Kero, I., Tranell, G.M. (2017). The Influence of Water Vapour on the Fuming Rate in a Ferromanganese System. In: Liu, X., et al. Energy Materials 2017. The Minerals, Metals & Materials Series. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-52333-0_7
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-52333-0_7
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Online ISBN: 978-3-319-52333-0
eBook Packages: Chemistry and Materials ScienceChemistry and Material Science (R0)