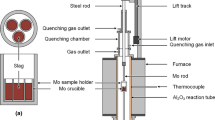
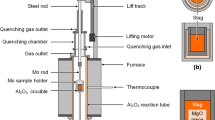
Abstract
Directly charging limestone into slag in BOF is a newly emerging technique which broke through the traditional BOF slagging principle. It is necessary to study the decomposition behavior of limestone in converter slag during BOF steelmaking. FeO x , SiO2, MnO x and pre-melting slags were mixed with limestone according to different quality proportion to simulate the environment of limestone in converter slag. TG-DTA results indicated that slag with individual component, including FeO x , SiO2 and MnO x , all had obvious effects on reducing the decomposition temperature of limestone. Pre-melting slags with multiple components had further reducing effects than individual component. XRD results showed converter slag component would react with decomposition product of CaCO3 and generate solid solution or oxide, reducing the activity of CaO and the decomposition temperature of CaCO3.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
C.J. Lewis, Acceleration of the Dissolution of Lime in the BOF Progress. American Patent, 3,574,575, 13 Mar 1971
H. Li, Y. Qu, A Method of Using Limestone Instead of Lime for Slagging in BOF Steelmaking. CN Patent, CN101,525,678, 20 Oct 2009
H. Li, Y. Qu, Discussion on limestone addition instead of lime for energy saving and emission reduction in BOF steelmaking. China Metall. 20, 59–63 (2010)
D.X. Dong, J. Feng, W. Nian, Experimental study on using limestone instead of lime for slagging in 60t converter. China Metall. 23, 58–62 (2013)
T.F. Deng, P. Nortier, M. Ek, S.C. Du, Limestone dissolution in converter slag at 1873 K. Metall. Mater. Trans. B. 44, 98–105 (2013)
N. Maruoka, A. Ishikawa, H. Shibata et al., Dissolution rate of various limes into steelmaking slag. High Temp. Mater. Process. (London) 32, 15–24 (2013)
H. Li, L.F. Guo, Y.Q. Li et al., Industrial experiments of using limestone instead of lime for slagging during LD-steelmaking Process. Adv. Mater. Res. 233–235, 2644–2647 (2011)
W.C. Song, H. Li, L.F. Guo et al., Analysis on energy-saving and CO2 emissions reduction in BOF steelmaking by substituting limestone for lime to slag. Int. Conf. Mater. Renewable Energy Environ. 1, 991–994 (2011)
H. Li, J. Feng, Y.Q. Li et al., Thermodynamic analysis of limestone decomposition and CO2 oxidation effect in the early stage of BOF steelmaking. J. Uni. Sci. Technol. Beijing, S 1, 83–87 (2011)
J. Feng, H. Li, C.X. Li et al., Research on using limestone for slagging during BOF steelmaking process. Adv. Mater. Res. 690–693, 237–245 (2013)
Z.Q. Li, H. Li, L.F. Guo et al., Preliminary research on the behavior of limestone charged into converter in the process of making slag. Steelmaking 27, 33–36 (2011)
Acknowledgements
The financial support of the National Key Technology Support Program (2012BAC27B02) is gratefully acknowledged.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2017 The Minerals, Metals & Materials Society
About this paper
Cite this paper
Lu, H., Li, C., Mao, W., Li, H. (2017). Influence of Converter Slag on Decomposition Behavior of Limestone During BOF Steelmaking Process. In: Hwang, JY., et al. 8th International Symposium on High-Temperature Metallurgical Processing. The Minerals, Metals & Materials Series. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-51340-9_69
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-51340-9_69
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-319-51339-3
Online ISBN: 978-3-319-51340-9
eBook Packages: Chemistry and Materials ScienceChemistry and Material Science (R0)