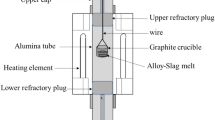
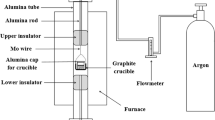
Abstract
The effect of silicon on removal of phosphorus from high phosphorus Si–Mn alloy was investigated at 1673 K by CaO-based slag. It was found that the dephosphorization efficiency increases significantly as increasing the silicon content, which is due to the reaction between silicon and CaO at slag/alloy interface. The relation between silicon content with oxygen activity and phosphorus activity coefficient of Si–Mn melt was determined respectively as follows:
The carbon content in Si–Mn melt decreases continuously with the increasing silicon content, meanwhile, the decreasing rate of carbon content becomes rapid when the mole fraction of silicon is about 0.32. Si addition is beneficial for both dephosphorization process and low carbon Si–Mn alloy production.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
L.J. Zhu, W.U. Di, X.M. Zhao, Effect of silicon content on thermodynamics of austenite decomposition in C–Si–Mn TRIP Steels. J. Iron. Steel Res. Int. 13(3), 57–60 (2006)
S.I. Rudyuk et al., Effect of sulfur and phosphorus on the properties of steel 18B. Met. Sci. Heat Treat. 16(12), 1056–1059 (1974)
X.S. Wen, H.Y. Li, Y.D. Sun, Application of reduction dephosphorization on low or extra low carbon ferromanganese-silicon. Ferroalloys 42(2), 1–3 (2011)
S.P. Liu, P. Tang, Review of dephosphorization processes for ferromanganese. Ferroalloys 34(4), 5–6 (2003)
D.M. Ni, W. Cheng, S.K. Wei, Study on dephosphorization of silicomanganese ferroalloy under reducing atmosphere with metallic calcium. Iron Steel 24(9), 49–53 (1989)
T. Ogasawara et al., The activity of calcium in calcium-calcium halide fluxes. ISIJ Int. 36(Suppl), S30–S33 (1996)
N. Masumitsu, K. Ito, R.J. Fruehan, Thermodynamics of Ca–CaF2 and Ca–CaCI2 systems for the dephosphorization of steel. Metall. Trans. B 19(4), 643–648 (1988)
S. Tabuchi, N. Sano, Thermodynamics of phosphate and phosphide in CaO–CaF2 melts. Metall. Mater. Trans. B 15(2), 351–356 (1984)
J.H. Shin, J.H. Park, Thermodynamics of reducing refining of phosphorus from Si–Mn alloy using CaO–CaF2 slag. Metall. Mater. Trans. B 43(6), 1–4 (2012)
S.L. Zeng, J. Liu, H. Li, Experiments on outside furnace dephosphorization for ferromanganese-silicon. Ferroalloys 35(1), 1–5 (2004)
S.L. Zeng et al., Optimization of technics on precipitation and dephosphorization for ferromanganese-silicon. Ferroalloys 40(6), 1–5 (2009)
E. Aida, D. Min, N. Sano, Phosphorus distribution between Mn–Si melts and CaO–SiO2–MnO–CaF2 Slags, Tetsu-to-Hagane(J. Iron Steel Inst. Jpn.) 74(10), 1931–1938 (1988)
K.Y. Hong et al., Reassessment of solution properties of liquid Mn–Si alloy. ISIJ Int. 53(3), 544–546 (2013)
R. Gee, T. Rosenqvist, Scand. J. Metall. 5, 57–62 (1976)
D.R. Swinbourne, W.J. Rankin, R.H. Eric, The effect of alumina in slag on manganese and silicon distributions in silicomanganese smelting. Metal. Mater. Trans. B 26(1), 59–65 (1995)
S. Ueda, K. Morita, N. Sano, Thermodynamics of phosphorus in molten Si–Fe and Si–Mn alloys. Metall. Mater. Trans. B 28(6), 1151–1155 (1997)
E.T. Turkdogan, R.A. Hancock, Trans. Inst. Min. Metall. 67, 573–600 (1957)
R. Ni, Z. Ma, S. Wei, Thermodynamics of Mn–Fe–C and Mn–Si–C System. Steel Res. 61, 113–116 (1990)
J.P. Shin, Y.E. Lee, Assessment of Mn–Fe–Si–C melt in unified interaction parameter formalism. Metall. Mater. Trans. B 47(1), 216–227 (2016)
M.K. Paek et al., Thermodynamic interactions among carbon, silicon and iron in carbon saturated manganese melts. Korean J. Met. Mater. 50(1), 45–51 (2012)
K. Tang, S.E. Olsen, Computer simulation of equilibrium relations in manganese ferroalloy production. Metall. Mater. Trans. B 7(37), 599–606 (2006)
S.H. Ahn et al., Thermodynamic assessment of liquid Fe–Si–C system by unified interaction parameter model. ISIJ Int. 54(4), 750–755 (2014)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2017 The Minerals, Metals & Materials Society
About this paper
Cite this paper
Zhou, Z., Zhu, Z., Ding, Y., Zhou, S. (2017). Effect of Silicon on Removal of Phosphorus from High Phosphorus Si–Mn Alloy by CaO-Based Slag. In: Hwang, JY., et al. 8th International Symposium on High-Temperature Metallurgical Processing. The Minerals, Metals & Materials Series. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-51340-9_55
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-51340-9_55
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-319-51339-3
Online ISBN: 978-3-319-51340-9
eBook Packages: Chemistry and Materials ScienceChemistry and Material Science (R0)