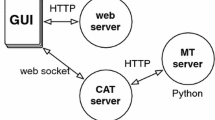
Abstract
Post-editing is the most popular approach to improve accuracy and speed of human translators by applying the machine translation (MT) technology. During the translation process, human translators generate the translation by correcting MT outputs in the post-editing scenario. To avoid repeating the same MT errors, in this paper, we propose an efficient framework to update MT in real-time by learning from user feedback. This framework includes: (1) an anchor-based word alignment model, being specially designed to get correct alignments for unknown words and new translations of known words, for extracting the latest translation knowledge from user feedback; (2) an online translation model, being based on random forests (RFs), updating translation knowledge in real-time for later predictions and having a strong adaptability with temporal noise as well as context changes. The extensive experiments demonstrate that our proposed framework significantly improves translation quality as the number of feedback sentences increasing, and the translation quality is comparable to that of the off-line baseline system with all training data.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bertoldi, N., Simianer, P., Cettolo, M., Wäschle, K., Federico, M., Riezler, S.: Online adaptation to post-edits for phrase-based statistical machine translation. Mach. Transl. 28(3–4), 309–339 (2014)
Blain, F., Schwenk, H., Senellart, J.: Incremental adaptation using translation information and post-editing analysis. In: International Workshop on Spoken Language Translation, pp. 234–241 (2012)
Bosch, A., Zisserman, A., Munoz, X.: Representing shape with a spatial pyramid kernel. In: Proceedings of the 6th ACM International Conference on Image and Video Retrieval, pp. 401–408 (2007)
Breiman, L.: Random forests. Mach. Learn. 45(1), 5–32 (2001)
Brown, P.F., Pietra, V.J.D., Pietra, S.A.D., Mercer, R.L.: The mathematics of statistical machine translation: parameter estimation. Comput. Linguist. 19(2), 263–311 (1993)
Carl, M., Dragsted, B., Elming, J., Hardt, D., Jakobsen, A.L.: The process of post-editing: a pilot study. In: Proceedings of the 8th International NLPSC Workshop. Special Theme: Human-Machine Interaction in Translation, vol. 41, pp. 131–142 (2011)
Cesa-Bianchi, N., Lugosi, G.: Prediction, Learning, and Games. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge (2006)
Denkowski, M., Dyer, C., Lavie, A.: Learning from post-editing: online model adaptation for statistical machine translation. In: Proceedings of ACL 2014 (2014)
Farajian, A.M., Bertoldi, N., Federico, M.: Online word alignment for online adaptive machine translation. In: Proceeding of EACL 2014 Workshop on Humans and Computer-Assisted Translation, pp. 84–92 (2014)
Geurts, P., Ernst, D., Wehenkel, L.: Extremely randomized trees. Mach. Learn. 63(1), 3–42 (2006)
Hardt, D., Elming, J.: Incremental re-training for post-editing SMT. In: 9th Conference of the Association for Machine Translation in the Americas (AMTA) (2002)
He, Z., Liu, Q., Lin, S.: Improving statistical machine translation using lexicalized rule selection. In: Proceddings of COLING 2008, pp. 321–328 (2008)
Huang, G., Zhang, J., Zhou, Y., Zong, C.: A new input method for human translators: integrating machine translation effectively and imperceptibly. In: Proceedings of the IJCAI 2015 (2015)
Koehn, P.: Statistical significance tests for machine translation evaluation. In: Proceedings of EMNLP 2004 (2004)
Koehn, P.: Computer-added trasnlation. Machine Translation Marathon (2012)
Koehn, P., Och, F.J., Marcu, D.: Statistical phrase-based translation. In: Proceedings of HLT-NAACL 2003, pp. 48–54 (2003)
Li, L.J., Fei-Fei, L.: Optimol: automatic online picture collection via incremental model learning. Int. J. Comput. Vis. 88(2), 147–168 (2010)
Liu, Q., He, Z., Liu, Y., Lin, S.: Maximum entropy based rule selection model for syntax-based statistical machine translation. In: Proceedings of EMNLP 2008, pp. 89–97 (2008)
Mccarley, J.S., Ittycheriah, A., Roukos, S., Xiang, B., Xu, J.M.: A correction model for word alignments. In: Proceedings of EMNLP 2011, pp. 889–898 (2011)
Nepveu, L., Lapalme, G., Langlais, P., Foster, G.F.: Adaptive language and translation models for interactive machine translation. In: Proceedings of EMNLP 2004, pp. 190–197 (2004)
Och, F.J., Ney, H.: Improved statistical alignment models. In: Proceedings of ACL 2000, pp. 440–447 (2000)
Och, F.J., Ney, H.: A systematic comparison of various statistical alignment models. Comput. Linguist. 29(1), 19–51 (2003)
Ortiz-Martínez, D., García-Varea, I., Casacuberta, F.: Online learning for interactive statistical machine translation. In: Proceedings of NAACL 2010, pp. 546–554 (2010)
Oza, N.C.: Online bagging and boosting. In: IEEE International Conference on Systems, Man and Cybernetics, vol. 3, pp. 2340–2345 (2005)
Saffari, A., Leistner, C., Santner, J., Godec, M., Bischof, H.: On-line random forests. In: IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision Workshops (2009)
Simard, M., Foster, G.: PEPr: post-edit propagation using phrase-based statistical machine translation. In: Proceedings of the XIV Machine Translation Summit 2013, pp. 191–198 (2013)
Snover, M., JDorr, B., Schwartz, R., Micciulla, L., Makhoul, J.: A study of translation edit rate with targeted human annotation. In: Conference of the Association for Machine Translation in the Americas (2006)
Stolcke, A., et al.: SRILM - an extensible language modeling toolkit. In: Proceedings of the International Conference on Spoken Language Processing, vol. 2, pp. 901–904 (2002)
Utgoff, P.E., Berkman, N.C., Clouse, J.A.: Decision tree induction based on efficient tree restructuring. Mach. Learn. 29(1), 5–44 (1997)
Vogel, S., Ney, H., Tillmann, C.: HMM-based word alignment in statistical translation. In: Proceedings of the 16th Conference on Computational Linguistics, vol. 2, pp. 836–841 (1996)
Xiong, D., Liu, Q., Lin, S.: Maximum entropy based phrase reordering model for statistical machine translation. In: Proceedings of COLING-ACL 2006 (2006)
Xu, P., Jelinek, F.: Random forests in language modeling. In: Proceedings of EMNLP 2004, vol. 4, pp. 325–332 (2004)
Zaidan, O.F.: Z-MERT: a fully configurable open source tool for minimum error rate training of machine translation systems. Prague Bull. Math. Linguist. 91, 79–88 (2009)
Zhang, Y., Vogel, S., Waibel, A.: Integrated phrase segmentation and alignment model for statistical machine translation. In: Proceedings of NLP-KE 2003 (2003)
Zhao, B., Vogel, S.: Adaptive parallel sentences mining from web bilingual news collection. In: Proceedings of IEEE International Conference on Data Mining 2002, pp. 745 (2002)
Zhechev, V.: Machine translation infrastructure and post-editing performance at autodesk. In: AMTA 2012 Workshop on Post-Editing Technology and Practice (WPTP 2012), pp. 87–96 (2012)
Acknowledgements
The research work has been funded by the Natural Science Foundation of China under Grant No. 61303181.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2016 Springer International Publishing AG
About this paper
Cite this paper
Huang, G., Zhang, J., Zhou, Y., Zong, C. (2016). Learning from User Feedback for Machine Translation in Real-Time. In: Lin, CY., Xue, N., Zhao, D., Huang, X., Feng, Y. (eds) Natural Language Understanding and Intelligent Applications. ICCPOL NLPCC 2016 2016. Lecture Notes in Computer Science(), vol 10102. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-50496-4_53
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-50496-4_53
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-319-50495-7
Online ISBN: 978-3-319-50496-4
eBook Packages: Computer ScienceComputer Science (R0)