Abstract
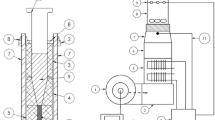
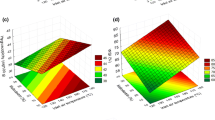
The clean utilization of the residue containing chloride, CuCl residue, produced from zinc hydrometallurgy is very important for the recycle of valuable metals. And drying is the main process in recycling. In this study, response surface methodology was used to optimize operating conditions of the drying of CuCl residue in a convection oven and desirability function used as the methodology for the optimization. Optimization factors were air temperature (80–100°C), material thickness (10–25mm) and process time (80–120min) while investigated responses was final moisture content. The optimum conditions were found to be the temperature of 95.48°C with the material thickness of 13.47mm for the process time of 89.48 min. Under optimum conditions, the predicted moisture content of CuCl residue was 4.11% while the experimental date was 4.13%. The experimental value after process optimization was found to agree satisfactory with the predicted value. After drying, XRD was used to analyze the main phases of CuCl residue. The CuCl residue is made up of CuCl,Cu2O, ZnS and other compounds.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Preview
Unable to display preview. Download preview PDF.
Similar content being viewed by others
Reference
M.K. Jha, V. Kumar and R.J. Singh, “Review of hydrometallurgical recovery of zinc from industrial wastes,” Resources, Conservation and Recycling, 33 (2001), 1–22.
S. Lu, Y. Xia and C. Huang, “Removing chlorine of CuCl residue from zinc hydrometallurgy by microwave roasting,” Journal of Central South University, 21 (2014), 1290–1295
S. Lu, Y. Wei, S. Ju, J. Peng, C. Huang, G. Wu, L. Zhang, “The Contrastive Studies of Microwave and Conventional Roasting CuCl Residue from Zinc Hydrometallurgy, “ Characterization of Minerals, Metals, and Materials, (2013), 529–540.
O.V. Ekechukwu, “Review of solar-energy drying systems I: an overview of drying principles and theory,” Energy Conversion and Management, 40 (1999), 593–613.
C. Liyana-Pathirana, F. Shahidi, “Optimization of extraction of phenolic compounds from wheat using response surface methodology,” Food Chemistry, 93 (2005), 47–56.
X.L. Bai, T.L. Yue and Y.H. Yuan, “Optimization of microwave — assisted extraction of polyphenols from apple pomace using response surface methodology and HPLC analysis,” Journal of Separation Science, 33 (2010), 3751–3758.
A. Aleboyeh, N. Daneshvar and M.B. Kasiri, “Optimization of C.I. Acid Red 14 azo dye removal by electrocoagulation batch process with response surface methodology,” Chemical Engineering and Processing, 47 (2008), 827–832.
A. R. Amani-Ghadim, S. Aber and A. Olad, “Optimization of electrocoagulation process for removal of an azo dye using response surface methodology and investigation on the occurrence of destructive side reactions,” Chemical Engineering and Processing, 64 (2013), 68–78.
S. Lu, S. Sun and J. Lv, “Optimization of Microwave Roasting for Dechlorination of CuCl Residue from Zinc Hydrometallurgy,” Journal of Microwave Power and Electromagnetic Energy, 48 (2014), 1290
G. Chen, J. Chen and C. Srinivasakannan, “Application of response surface methodology for optimization of the synthesis of synthetic rutile from titania slag,” Applied Surface Science, 258 (2012), 3068–3073.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2015 TMS (The Minerals, Metals & Materials Society)
About this chapter
Cite this chapter
Zhanyong, G., Shaohua, J., Ting, L., Jinhui, P., Libo, Z., Feng, J. (2015). Optimization on Drying of CuCl Residue by Hot-Air Using Response Surface Methodology. In: Battle, T.P., et al. Drying, Roasting, and Calcining of Minerals. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-48245-3_9
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-48245-3_9
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-319-48600-0
Online ISBN: 978-3-319-48245-3
eBook Packages: Chemistry and Materials ScienceChemistry and Material Science (R0)