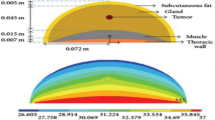
Abstract
The incidence of breast cancer has rapidly increased over the past few decades in India and the mortality rate is more than other countries across the entire world. These facts have motivated the development of new technologies or modification of the existing technologies for the identification of breast cancer before it metastasizes to the neighboring tissues. Breast thermography is a promising front-line breast screening method, which is noncontact, cheap, quick, economic, and painless. The use of thermal imaging for the identification of breast abnormality is based on the principle that the temperature distribution in precancerous tissue and its surrounding area are always higher than that in normal breast tissue. However, the accurate interpretation and classification of the breast thermograms for proper diagnostic decision-making is a major problem. Proper segmentation of hottest region from the segmented breast region plays a key part in the diagnosis of breast cancer that calls for the application of hybrid intelligent methods in the segmentation of hottest region. The shape and size of the hottest regions are used to determine the degree of malignancy of the tumor and classify its type. Hybrid intelligent systems have been successfully applied in the classification of breast thermal images over the last few years. In this chapter, we have proposed a sequential hybrid intelligent technique for the segmentation of the hottest region and also shown the significance of hybrid intelligence systems over the conventional methods for the segmentation of hottest region. A detailed review related to the segmentation of breast region and the segmentation of hottest region is included in this chapter. In addition, this chapter also contains the detailed overview of the principles, reliability, and predictive ability of the breast thermogram in early diagnosis of breast cancer.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
International Agency for Research on Cancer (IARC) and World Health Organization (WHO). GLOBOCAN 2012: Estimated cancer incidence, mortality and prevalence worldwide in 2012 (2014). http://globocan.iarc.fr/Pages/fact-sheets-cancer.aspx
http://www.breastcancerindia.net/statistics/trends.html. Accessed 10 Jan 2016
Gautherie, M.: Thermopathology of breast cancer: measurement and analysis of in vivo temperature and blood flow. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 335, 383–415 (1999)
Tan, T.Z., Quek, C., Ng, G.S., Ng, E.Y.K.: A novel cognitive interpretation of breast cancer thermography with complementary learning fuzzy neural memory structure. Expert Syst. Appl. 33, 652–666 (2007)
Amula, W.C.: A review of breast thermography. Int. Acad. Clin. Thermol. (2003). http://www.iact-org.org/articles/articles-review-btherm.html
Borchartt, T.B., Conci, A., Lima, R.C.F., Resmini, R., Sanchez, A.: Breast thermography from an image processing viewpoint: a survey. Signal Process. 93, 2785–2803 (2013)
EtehadTavakol, M., Sadri, S., Ng, E.Y.K.: Application of K- and fuzzy c-means for color segmentation of thermal infrared breast images. J. Med. Syst. 34, 35–42 (2010)
Milosevic, M., Jankovic, D., Peulic, A.: Thermography based breast cancer detection using texture features and minimum variance quantization. EXCLI J. 13, 1204–1215 (2014)
Pramanik, S., Bhattacharjee, D., Nasipuri, M.: Wavelet based thermogram analysis for breast cancer detection. In: Proceedings of IEEE International Symposium on Advanced Computing and Communication, Silchar, India, pp. 205–212 (2015)
de Oliveira, J.P.S., Conci, A., Perez, M.G., Andaluz, V.H.: Segmentation of infrared images: a new technology for early detection of breast diseases. In: Proceedings of IEEE International Conference on Industrial Technology, Seville, pp. 1765–1771 (2015)
https://ktlarkin.files.wordpress.com/2009/12/breast-anatomy2.gif?w=479. Accessed 21 Feb 2016
Sobin, L.H., Wittekind, C.H.: TNM classification of malignant tumours, 4th edn. Paris, Springer 100, (1988)
http://www.cancer.org/cancer/breastcancer/detailedguide/breast-cancer-risk-factors. Accessed 10 Jan 2016
http://ww5.komen.org/BreastCancer/Statistics.html. Accessed 10th January 2016
http://ww5.komen.org/BreastCancer/FamilyHistoryofBreastOvarianorProstateCancer.html. Accessed 10 Jan 2016
http://ww5.komen.org/KomenPerspectives/Breast-Density-and-Breast-Cancer-Risk.html. Accessed 10 Jan 2016
http://www.breastcancer.org/risk/factors. Accessed 10th Jan 2016
Collaborative Group on Hormonal Factors in Breast Cancer: Breast cancer and breast feeding: collaborative reanalysis of individual data from 47 epidemiological studies in 30 countries, including 50,302 women with breast cancer and 96,973 women without the disease. Lancet 20, 187–95 (2002)
Thermology. http://www.thermology.com/history.htm. Accessed 24 Jan 2016
Gautherine, M., Gros, C.: Contribution of infrared thermography to early diagnosis, pretheraputic prognosis and post-irradiation follow-up of breast carcinomas. Med. Mundi 21, 135–149 (1976)
Gautherie, M., Gros, C.M.: Breast thermography and cancer risk prediction. Cancer 45(1), 51–56 (1980)
Kennedy, D., Lee, T., Seely, D.: A comparative review of thermography as a breast screening technique. Integr. Cancer Ther. 8(1), 9–16 (2009)
Gogoi, U.R., Bhowmik, M.K., Bhattacharjee, D., Ghosh, A.K., Majumder, G.: A study and analysis of hybrid intelligent techniques for breast cancer detection using breast thermograms. In: Hybrid Soft Computing Approaches, pp. 329–359 (2015)
Amalu, W.C., Hobbins, W.B., Head, J.F., Elliot, R.L.: Infrared imaging of the breast: a review. In: Diakides Nicholas, A., Bronzino Joseph, D. (eds.) Medical Infrared Imaging, pp. 9-1–9-22. Taylor and Francis, Boca Raton (2007)
Gershen-Cohen, J., Haberman, J., Brueschke, E.E.: Medical thermography: a summary of current status. Radiol. Clin. North Am. 3, 403–431 (1965)
Hoffman, R.: Thermography in the detection of breast malignancy. Am. J. Obstet. Gynecol. 98, 681–686 (1967)
Amalric, R., Giraud, D., Altschule, C., Spitalier, J.M.: Value and interest of dynamic telethermography in detection of breast cance. Acta Thermogr. 1, 89–96 (1976)
Hobbins, W.B.: Abnormal thermogram - significance in breast cancer. Interam. J. Rad. 12, 337 (1987)
Spitalier, H., Giraud, D., Altschuler, C., Amalric, F., Spitalier, J.M., Brandone, H., Ayme, Y., Gardiol, A.: Does infrared thermography truly have a role in present-day breast cancer management? In: Biomedical Thermology (Proceedings of an International Symposium), pp. 269–278. Alan R. Liss, Inc., New York City (1982)
Nyirjesy, I., Ayme, T.: Clinical evaluation, mammography, and thermography in the diagnosis of breast carcinoma. Thermology 1, 170–173 (1986)
Parisky, Y.R., Sardi, A., Hamm, R., Hughes, K., Esserman, L., Rust, S., Callahan, K.: Efficacy of computerized infrared imaging analysis to evaluate mammographically suspicious lesions. Am. J. Roentgenol. 180, 263–269 (2003)
Borchartt, T.B., Resmini, R., Conci, A., Martins, A., Silva, A.C., Diniz, E.M., Paiva, A., Lima, R.C.F.: Thermal feature analysis to aid on breast disease diagnosis. In: Proceedings of 21st Brazilian Congress of Mechanical Engineering-COBEM2011, Natal, Brazil, pp. 1–8 (2011)
Gautherie, M., Kotewicz, A., Gueblez, P.: Accurate and objective evaluation of breast thermograms: Basic principles and new advances with special reference to an improved computer assisted scoring system. In: Thermal assessment of Breast Health, pp. 72–97. MTP Press Limited (1983)
Gautherie, M.: New protocol for the evaluation of breast thermograms. In: Thermological Methods, VCH mbH, pp. 227–235 (1985)
Amalu, W.C., Hobbins, W.B., Head, J.F., Elliot, R.L.: Infrared Imaging of the Breast - An Overview, Medical Devices and Systems, pp. 25.1–25.20. CRC Press, Boca Raton (2006)
http://www.adelphatherm.com/#!untitled/c1dyz. Accessed 1 Jan 2016
Ng, E.Y.K.: A review of thermography as promising non-invasive detection modality for breast tumor. Int. J. Thermal Sci. 48(5), 849–859 (2009)
Ring, E.F.J.: Quantitative thermal imaging. Clin. Phys. Physiol. Meas. 11, 87–95 (1990)
Thermography Guidelines (TG), Standards and Protocols in Clinical Thermographic Imaging, September 2002. http://www.iact-org.org/professionals/thermog-guidelines.html. Accessed Feb 2016
Qi, H., Head, J.F.: Asymmetry analysis using automatic segmentation and classification for breast cancer detection in thermograms. In: Proceedings of the 23rd Annual International Conference of the IEEE EMBS, 3, Turkey, pp. 2866-2869 (2001)
Arena, F., Barone, C., Di Cicco, T.: Use of digital infrared imaging in enhanced breast cancer detection and monitoring of the clinical response to treatment. In: Proceedings of the 25th Annual International Conference on Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society (EMBS), vol. 2, pp. 1129-1132 (2003)
Arora, N., Martins, D., Ruggerio, D., Tousimis, E., Swistel, A.J., Osborne, M.P., Simmons, R.M.: Effectiveness of a non-invasive digital infrared thermal imaging system in the detection of breast cancer. Am. J. Surg. 196(4), 523–526 (2008)
Tang, X., Ding, H., Yuan, Y., Wang, Q.: Morphological measurement of localized temperature increase amplitudes in breast infrared thermograms and its clinical application. Biomed. Signal Process. Control 3(1), 312–318 (2008)
Ng, E.Y.K., Kee, E.C.: Integrative computer-aided diagnostic with breast thermogram. J. Mech. Med. Biol. 7(1), 1–10 (2007)
Agostini, V., Knaflitz, M., Molinari, F.: Motion artifact reduction in breast dynamic infrared imaging. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 56(3), 903–906 (2009)
Wishart, G.C., Campisi, M., Boswell, M., Chapman, D., Shackleton, V., Iddles, S., Hallett, A., Britton, P.D.: The accuracy of digital infrared imaging for breast cancer detection in women undergoing breast biopsy. Eur. J Cancer Surg. 36, 535–540 (2010)
Acharya, U.R., Ng, E.Y.K., Tan, J.H., Sree, S.V.: Thermography based breast cancer detection using texture features and support vector machine. J. Med. Syst. 36(3), 1503–1510 (2010)
Nurhayati, O.D., Susanto, A., Widodo, T.S., Tjokronagoro, M.: Principal component analysis combined with first order statistical method for breast thermal images classification. Int. J. Comput. Sci. Technol. 2(2), 12–18 (2011)
Kontos, M., Wilson, R., Fentiman, I.: Digital infrared thermal imaging (DITI) of breast lesions: sensitivity and specificity of detection of primary breast cancers. Clin. Radiol. 66(2011), 536–539 (2011)
Zadeh, H.G., Haddadnia, J., Hashemian, M., Hassanpour, K.: Diagnosis of breast cancer using a combination of genetic algorithm and artificial neural network in medical infrared thermal imaging. Iran J. Med. Phys. 9(4), 265–274 (2012)
PROENG. Image processing and image analyses applied to mastology (2012). http://visual.ic.uff.br/en/proeng/. Accessed 31 Jan 2016
Silva, L.F., Saade, D.C.M., Sequeiros-Olivera, G.O., Silva, A.C., Paiva, A.C., Bravo, R.S., Conci, A.: A new database for breast research with infrared image. J. Med. Imaging Health Inf. 4(1), 92–100(9) (2014)
Tejerina, A.: Aula de Habilidadesy Simulacion em Patologia de la Mama’ (in Spanish). ADEMAS Comunicacion Grafica, Madrid, Spain (2009)
Delgado, F.G., Luna, J.G.V.: Feasibility of new-generation infrared screening for breast cancer in rural communities. US Obstet. Gynecol. Touch Briefings 5, 52–56 (2010)
Antonini, S., Kolaric, D., Nola, I.A., Herceg, Z., Ramljak, V., Kulis, T., Holjevac, J.K., Ferencic, Z.: Thermography surveillance after breast conserving surgery-three cases. In: 53rd International Symposium ELMAR, Croatia, pp. 317–319 (2011)
Kolaric, D., Herceg, Z., Nola, I.A., Ramljak, V., Kulis, T., Holjevac, J.K., Deutsch, J.A., Antonini, S.: Thermography-a feasible method for screening breast cancer. Coll. Antropol. 37(2), 583–588 (2013)
Motta, L.S., Conci, A., Lima, R.C.F., Diniz, E.M.: Automatic segmentation on thermograms in order to aid diagnosis and 2D modeling. In: Proceedings of 10th Workshop em Informatica Medica, Belo Horizonte, MG, Brazil, vol. 1, pp. 1610-1619 (2010). http://www.visual.ic.uff.br/proeng Accessed 19 March 2015
Bharathi, G.B., Francis, S.V., Sasikala, M., Sandeep, J.D.: Feature analysis for abnormality detection in breast thermogram sequences subject to cold stress. In: Proceedings of the National Conference on Man Machine Interaction (NCMMI), 15-2 (2014)
Beware of Poor Breast Thermograms, ILSI Thermography Service. http://www.doctormedesign.com/HTMLcontent/Beware/of/Poor/Thermograms.htm
Etehadtavakol, M., Ng, E.Y.K.: Breast thermography as a potential non-contact method in the early detection of cancer: a review. J. Mech. Med. Biol. 2(13), 1330001.1–1330001.20 (2013)
Ville Marie Medical Center. http://www.villemariemed.com. Accessed 31 Jan 2016
Koay, J., Herry, C., Frize, M.: Analysis of breast thermography with an artificial neural network. Eng. Med. Biol. Soc. IEMBS 1(1), 1159–1162 (2004)
BioBD. Bancode Dadosde Pesquisa Biomedica (2012). http://150.161.110.168/termo. Accessed 23 Jan 2016
Araujo, M.C., Lima, R.C.F., Santos, F.: Desenvolvimento de um banco de dados como ferramenta auxiliary na deteccao precoce de cancer de mama’30 Iberian-Latin-American Congress on Computational Methods in Engineering, vol. 1, pp. 1–15. Armacao dos Buzios, RJ, Brazil (2009)
Conci, A., Lima, R.C.F., Fontes, C.A.P., Motta, L.S., Resmini, R.: A new method for automatic segmentation of the region of interest of thermographic breast image. Thermol. Int. 20(4), 134–135 (2010)
Conci, A., Lima, R.C.F., Fontes, C.A.P., Borchartt, T.B., Resmini, R.: A new method to aid to the breast diagnosis using fractal geometry. Thermol. Int. 20(4), 135–136 (2010)
Borchartt, T.B., Resmini, R., Motta, L.S., Clua, E.W.G., Conci, A., Viana, M.J.A., Santos, L.C., Lima, R.C.F., Sanchez, A.: Combining approaches for early diagnosis of breast diseases using thermal imaging’. Int. J. Innov. Comput. Appl. 3(4), 163–183 (2012)
Gerasimova, E., Audit, B., Roux, S.G., Khalil, A., Gileva, O., Argoul, F., Naimark, O., Arneodo, A.: Wavelet-based multifractal analysis of dynamic infrared thermograms to assist in early breast cancer diagnosis. Front. Physiol. 5(176), 1–11 (2014)
Gileva, O.S., Freynd, G.G., Orlov, O.A., Libik, T.V., Gerasimova, E.I., Plekhov, O.A.: Interdisciplinary approaches to early diagnosis and screening of tumors and precancerous diseases (for example, breast cancer). RFBR J. 74–75, 93–99 (2012)
Qi, H., Kuruganti, P.T., Snyder, W.E.: Detecting breast cancer from thermal infrared images by asymmetry analysis. Biomedical Engineering Handbook 27(1–27), 14 (2006)
Jin-Yu, Z., Yan, C., Xian-Xiang, H.: IR thermal image segmentation based on enhanced genetic algorithms and two- dimensional classes square error. In: Second International Conference on Information and Computation Science, vol. 2(1), pp. 309–312 (2009)
Kapoor, P., Prasad, S.V.A.V.: Image processing for early diagnosis of breast cancer using infrared images. In: 2nd International Conference on Computer and Automation Engineering, vol. 3(1), pp. 564–566 (2010)
Zadeh, H.G., Kazerouni, I.A., Haddadnia, J.: Distinguish breast cancer based on thermal features in infrared images. Canadian J. Image Process. Comput. Vis. 2(6), 54–58 (2011)
Golestani, N., EtehadTavakol, M., Ng, E.Y.K.: Level set method for segmentation of infrared breast thermograms. EXCLI J. 13, 241–251 (2014)
Ji, Z., Liu, J., Cao, G., Sun, Q., Chen, Q.: Robust spatially constrained fuzzy c-means algorithm for brain MR image segmentation. Pattern Recogn. 47(7), 2454–2466 (2014)
Torbati, N., Ayatollahi, A., Kermani, A.: An efficient neural network based method for medical image segmentation. Comput. Biol. Med. 44, 76–87 (2014)
Krawczyk, B., Schaefer, G., Woźniak, M.: A hybrid cost-sensitive ensemble for imbalanced breast thermogram classification. Artif. Intell. Med. 65(3), 219–227 (2015)
Li, H., Burgess, A.E.: Evaluation of signal detection performance with pseudo-color display and lumpy backgrounds. In: Kundel, H.L. (ed.) SPIE, Medical Imaging: Image Perception, Newport Beach, vol. 3036, pp. 143–149 (1997)
Bezdek, J.C., Keller, J., Krisnapuram, R., Pal, N.R.: Fuzzy models and algorithms for pattern recognition and image processing. Kluwer, Norwell (1999)
Davies, D.L., Bouldin, D.W.: A cluster separation measure. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. PAMI–1(2), 224–227 (1979)
Acknowledgments
Authors are thankful to DBT, Govt. of India for funding a project with Grant no. BT/533/NE/TBP/2014. Sourav Pramanik is also thankful to Department of Electronics and Information Technology (DeitY), Govt. of India, for providing him PhD-Fellowship under Visvesvaraya PhD scheme.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2016 Springer International Publishing AG
About this chapter
Cite this chapter
Pramanik, S., Bhowmik, M.K., Bhattacharjee, D., Nasipuri, M. (2016). Hybrid Intelligent Techniques for Segmentation of Breast Thermograms. In: Bhattacharyya, S., Dutta, P., De, S., Klepac, G. (eds) Hybrid Soft Computing for Image Segmentation. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-47223-2_11
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-47223-2_11
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-319-47222-5
Online ISBN: 978-3-319-47223-2
eBook Packages: Computer ScienceComputer Science (R0)