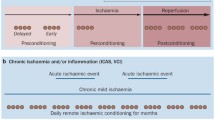
Abstract
Ischemic preconditioning is the most potent protectant against ischemic injury. Remote ischemic conditioning (RIC), a further development of ischemic preconditioning, is safe, feasible, and highly translational and represents one of the most promising strategies for neuroprotection and vasculoprotection during acute ischemic stroke. RIC grew out of the field of cardioprotection but there is now strong preclinical evidence and emerging clinical evidence of its activity and efficacy in acute ischemic stroke. While the mechanisms of protection are not completely known, RIC triggers endogenous protective mechanism and increases cerebral blood flow. RIC is ideal as a prehospital therapy and has potential as an adjunctive therapy to mechanical thrombectomy. Its ease of use makes RIC an attractive therapy to be used in community hospitals and during helicopter transport.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Mozaffarian D, Benjamin EJ, Go AS, Arnett DK, Blaha MJ, Cushman M et al (2015) Heart disease and stroke statistics—2015 update: a report from the American Heart Association. Circulation 131(4):e29–e322
Moretti A, Ferrari F, Villa RF (2015) Neuroprotection for ischaemic stroke: current status and challenges. Pharmacol Ther 146:23–34
Park JM, Hess DC (2015) Breaking out from the neuroprotective logjam: combined treatment with remote ischemic conditioning and minocycline in the prehospital setting. Neural Regen Res 10(4):537
Iadecola C, Anrather J (2011) Stroke research at a crossroad: asking the brain for directions. Nat Neurosci 14(11):1363–1368
Saver JL, Goyal M, Bonafe A, Diener H-C, Levy EI, Pereira VM et al (2015) Stent-retriever thrombectomy after intravenous t-PA vs. t-PA alone in stroke. N Engl J Med 372(24):2285–2295
Goyal M, Menon BK, van Zwam WH, Dippel DW, Mitchell PJ, Demchuk AM et al (2016) Endovascular thrombectomy after large-vessel ischaemic stroke: a meta-analysis of individual patient data from five randomised trials. Lancet 387(10029):1723–1731
Campbell BC, Mitchell PJ, Kleinig TJ, Dewey HM, Churilov L, Yassi N et al (2015) Endovascular therapy for ischemic stroke with perfusion-imaging selection. N Engl J Med 372(11):1009–1018
Jovin TG, Chamorro A, Cobo E, de Miquel MA, Molina CA, Rovira A et al (2015) Thrombectomy within 8 hours after symptom onset in ischemic stroke. N Engl J Med 372(24):2296–2306
Hougaard K, Hjort N, Zeidler D, Sørensen L, Nørgaard A, Thomsen R et al (2013) Remote ischemic perconditioning in thrombolysed stroke patients: randomized study of activating endogenous neuroprotection–design and MRI measurements. Int J Stroke 8(2):141–146
Albers GW, Goldstein LB, Hess DC, Wechsler LR, Furie KL, Gorelick PB et al (2011) Stroke Treatment Academic Industry Roundtable (STAIR) recommendations for maximizing the use of intravenous thrombolytics and expanding treatment options with intra-arterial and neuroprotective therapies. Stroke 42(9):2645–2650
Hess DC, Blauenfeldt RA, Andersen G, Hougaard KD, Hoda MN, Ding Y et al (2015) Remote ischaemic conditioning [mdash] a new paradigm of self-protection in the brain. Nat Rev Neurol 11(12):698–710
Janoff A (1964) Alterations in lysosomes (intracellular enzymes) during shock; effects of preconditioning (tolerance) and protective drugs. Int Anesthesiol Clin 2:251–269
Ring J, Gutermuth J (2011) 100 years of hyposensitization: history of allergen-specific immunotherapy (ASIT). Allergy 66(6):713–724
Valle G, Carmignani M, Stanislao M, Facciorusso A, Volpe AR (2012) Mithridates VI Eupator of Pontus and mithridatism. Allergy 67(1):138–139; author reply 9–40
Valle G, Stanislao M, Facciorusso A, Carmignani M, Volpe AR (2009) Mithridates VI Eupator, father of the empirical toxicology. Clin Toxicol 47(5):433
Waddell WJ (2010) History of dose response. J Toxicol Sci 35(1):1–8
Nietzsche F (2008) [1895] Twilight of the idols: or how to philosophize. Oxford University Press, Oxford
Hahn CD, Manlhiot C, Schmidt MR, Nielsen TT, Redington AN (2011) Remote ischemic per-conditioning: a novel therapy for acute stroke? Stroke 42(10):2960–2962
Zhang Y, Liu X, Yan F, Min L, Ji X, Luo Y (2012) Protective effects of remote ischemic preconditioning in rat hindlimb on ischemia-reperfusion injury. Neural Regen Res 7(8):583–587
Failure of extracranial-intracranial arterial bypass to reduce the risk of ischemic stroke. Results of an international randomized trial. The EC/IC Bypass Study Group (1985) N Engl J Med 313(19):1191–1200
Murry CE, Jennings RB, Reimer KA (1986) Preconditioning with ischemia: a delay of lethal cell injury in ischemic myocardium. Circulation 74(5):1124–1136
Li Y, Whittaker P, Kloner RA (1992) The transient nature of the effect of ischemic preconditioning on myocardial infarct size and ventricular arrhythmia. Am Heart J 123(2):346–353
Przyklenk K, Bauer B, Ovize M, Kloner RA, Whittaker P (1993) Regional ischemic ‘preconditioning’ protects remote virgin myocardium from subsequent sustained coronary occlusion. Circulation 87(3):893–899
Birnbaum Y, Hale SL, Kloner RA (1997) Ischemic preconditioning at a distance reduction of myocardial infarct size by partial reduction of blood supply combined with rapid stimulation of the gastrocnemius muscle in the rabbit. Circulation 96(5):1641–1646
Oxman T, Arad M, Klein R, Avazov N, Rabinowitz B (1997) Limb ischemia preconditions the heart against reperfusion tachyarrhythmia. Am J Physiol 273(4):H1707–H1712
Kharbanda R, Mortensen U, White P, Kristiansen S, Schmidt M, Hoschtitzky J et al (2002) Transient limb ischemia induces remote ischemic preconditioning in vivo. Circulation 106(23):2881–2883
Schmidt MR, Smerup M, Konstantinov IE, Shimizu M, Li J, Cheung M et al (2007) Intermittent peripheral tissue ischemia during coronary ischemia reduces myocardial infarction through a KATP-dependent mechanism: first demonstration of remote ischemic perconditioning. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol 292(4):H1883–H1890
Candilio L, Malik A, Hausenloy DJ (2013) Protection of organs other than the heart by remote ischemic conditioning. J Cardiovasc Med 14(3):193–205
Yuan H-J, Zhu X-H, Luo Q, Wu Y-N, Kang Y, Jiao J-J et al (2012) Noninvasive delayed limb ischemic preconditioning in rats increases antioxidant activities in cerebral tissue during severe ischemia-reperfusion injury. J Surg Res 174(1):176–183
Ren C, Gao X, Steinberg GK, Zhao H (2008) Limb remote-preconditioning protects against focal ischemia in rats and contradicts the dogma of therapeutic time windows for preconditioning. Neuroscience 151(4):1099–1103
Aimo A, Borrelli C, Giannoni A, Pastormerlo LE, Barison A, Mirizzi G et al (2015) Cardioprotection by remote ischemic conditioning: mechanisms and clinical evidences. World J Cardiol 7(10):621
Le Page S, Bejan-Angoulvant T, Angoulvant D, Prunier F (2015) Remote ischemic conditioning and cardioprotection: a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized clinical trials. Basic Res Cardiol 110(2):1–17
Hausenloy DJ, Yellon DM (2011) The therapeutic potential of ischemic conditioning: an update. Nat Rev Cardiol 8(11):619–629
Hoda MN, Siddiqui S, Herberg S, Periyasamy-Thandavan S, Bhatia K, Hafez SS et al (2012) Remote ischemic perconditioning is effective alone and in combination with intravenous tissue-type plasminogen activator in murine model of embolic stroke. Stroke 43(10):2794–2799
Zhao H (2009) Ischemic postconditioning as a novel avenue to protect against brain injury after stroke. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 29(5):873–885
Ren C, Wang P, Wang B, Li N, Li W, Zhang C et al (2015) Limb remote ischemic per-conditioning in combination with post-conditioning reduces brain damage and promotes neuroglobin expression in the rat brain after ischemic stroke. Restor Neurol Neurosci 33(3):369–379
Yu Z, Liu N, Liu J, Yang K, Wang X (2012) Neuroglobin, a novel target for endogenous neuroprotection against stroke and neurodegenerative disorders. Int J Mol Sci 13(6):6995–7014
Veighey K, MacAllister RJ (2012) Clinical applications of remote ischemic preconditioning. Cardiol Res Pract 2012:620681
Hausenloy DJ, Yellon DM (2008) Remote ischemic preconditioning: underlying mechanisms and clinical application. Cardiovasc Res 79(3):377–386
Hess DC (2013) Remote limb preconditioning and postconditioning: will it translate into a promising treatment for acute stroke? Stroke 44(4):1191–1197
Yetgin T, Manintveld OC, Groen F, Tas B, Kappetein AP, van Geuns R-J et al (2012) The emerging application of remote ischemic conditioning in the clinical arena. Cardiol Rev 20(6):279–287
Lim SY, Hausenloy DJ (2012) Remote ischemic conditioning: from bench to bedside. Front Physiol 3:27
Gho BC, Schoemaker RG, van den Doel MA, Duncker DJ, Verdouw PD (1996) Myocardial protection by brief ischemia in noncardiac tissue. Circulation 94(9):2193–2200
Mastitskaya S, Marina N, Gourine A, Gilbey MP, Spyer KM, Teschemacher AG et al (2012) Cardioprotection evoked by remote ischaemic preconditioning is critically dependent on the activity of vagal pre-ganglionic neurones. Cardiovasc Res 95(4):487–494
Jones WK, Fan GC, Liao S, Zhang JM, Wang Y, Weintraub NL et al (2009) Peripheral nociception associated with surgical incision elicits remote nonischemic cardioprotection via neurogenic activation of protein kinase C signaling. Circulation 120(11 Suppl):S1–S9
Redington KL, Disenhouse T, Strantzas SC, Gladstone R, Wei C, Tropak MB et al (2012) Remote cardioprotection by direct peripheral nerve stimulation and topical capsaicin is mediated by circulating humoral factors. Basic Res Cardiol 107(2):241
Shimizu M, Tropak M, Diaz RJ, Suto F, Surendra H, Kuzmin E et al (2009) Transient limb ischaemia remotely preconditions through a humoral mechanism acting directly on the myocardium: evidence suggesting cross-species protection. Clin Sci (Lond) 117(5):191–200
Davidson SM, Selvaraj P, He D, Boi-Doku C, Yellon RL, Vicencio JM et al (2013) Remote ischaemic preconditioning involves signalling through the SDF-1alpha/CXCR4 signalling axis. Basic Res Cardiol 108(5):377
Li J, Rohailla S, Gelber N, Rutka J, Sabah N, Gladstone RA et al (2014) MicroRNA-144 is a circulating effector of remote ischemic preconditioning. Basic Res Cardiol 109(5):423
Cai ZP, Parajuli N, Zheng X, Becker L (2012) Remote ischemic preconditioning confers late protection against myocardial ischemia-reperfusion injury in mice by upregulating interleukin-10. Basic Res Cardiol 107(4):277
Rassaf T, Totzeck M, Hendgen-Cotta UB, Shiva S, Heusch G, Kelm M (2014) Circulating nitrite contributes to cardioprotection by remote ischemic preconditioning. Circ Res 114(10):1601–1610
Hess DC, Hoda MN, Khan MB (2016) Humoral mediators of remote ischemic conditioning: important role of eNOS/NO/nitrite. Brain Edema XVI. Springer, Basel, pp 45–48
Abu-Amara M, Yang SY, Quaglia A, Rowley P, De Mel A, Tapuria N et al (2011) Nitric oxide is an essential mediator of the protective effects of remote ischaemic preconditioning in a mouse model of liver ischaemia/reperfusion injury. Clin Sci 121(6):257–266
Abu‐Amara M, Yang SY, Quaglia A, Rowley P, Fuller B, Seifalian A et al (2011) Role of endothelial nitric oxide synthase in remote ischemic preconditioning of the mouse liver. Liver Transpl 17(5):610–619
Jensen RV, Støttrup NB, Kristiansen SB, Bøtker HE (2012) Release of a humoral circulating cardioprotective factor by remote ischemic preconditioning is dependent on preserved neural pathways in diabetic patients. Basic Res Cardiol 107(5):1–9
Konstantinov IE, Arab S, Kharbanda RK, Li J, Cheung MM, Cherepanov V et al (2004) The remote ischemic preconditioning stimulus modifies inflammatory gene expression in humans. Physiol Genomics 19(1):143–150
Wei M, Xin P, Li S, Tao J, Li Y, Li J et al (2011) Repeated remote ischemic postconditioning protects against adverse left ventricular remodeling and improves survival in a rat model of myocardial infarction. Circ Res 108(10):1220–1225
Yellon DM, Hausenloy DJ (2007) Myocardial reperfusion injury. N Engl J Med 357(11):1121–1135
Kloner RA, Schwartz LL (2011) State of the science of cardioprotection: challenges and opportunities—proceedings of the 2010 NHLBI workshop on cardioprotection. J Cardiovasc Pharmacol Ther 16(3–4):223–232
Botker HE, Kharbanda R, Schmidt MR, Bottcher M, Kaltoft AK, Terkelsen CJ et al (2010) Remote ischaemic conditioning before hospital admission, as a complement to angioplasty, and effect on myocardial salvage in patients with acute myocardial infarction: a randomised trial. Lancet 375(9716):727–734
White SK, Frohlich GM, Sado DM, Maestrini V, Fontana M, Treibel TA, et al (2015) Remote ischemic conditioning reduces myocardial infarct size and edema in patients with ST-segment elevation myocardial infarction. JACC Cardiovasc Interv 8(1 Pt B):178–188
Prunier F, Angoulvant D, Saint Etienne C, Vermes E, Gilard M, Piot C et al (2014) The RIPOST-MI study, assessing remote ischemic perconditioning alone or in combination with local ischemic postconditioning in ST-segment elevation myocardial infarction. Basic Res Cardiol 109(2):400
Sloth AD, Schmidt MR, Munk K, Kharbanda RK, Redington AN, Schmidt M et al (2014) Improved long-term clinical outcomes in patients with ST-elevation myocardial infarction undergoing remote ischaemic conditioning as an adjunct to primary percutaneous coronary intervention. Eur Heart J 35(3):168–175
Davies WR, Brown AJ, Watson W, McCormick LM, West NE, Dutka DP et al (2013) Remote ischemic preconditioning improves outcome at 6 years after elective percutaneous coronary intervention: the CRISP stent trial long-term follow-up. Circ Cardiovasc Interv 6(3):246–251
Hausenloy DJ, Kharbanda R, Rahbek Schmidt M, Moller UK, Ravkilde J, Okkels Jensen L et al (2015) Effect of remote ischaemic conditioning on clinical outcomes in patients presenting with an ST-segment elevation myocardial infarction undergoing primary percutaneous coronary intervention. Eur Heart J 36(29):1846–1848
Yellon DM, Ackbarkhan AK, Balgobin V, Bulluck H, Deelchand A, Dhuny MR et al (2015) Remote ischemic conditioning reduces myocardial infarct size in STEMI patients treated by thrombolysis. J Am Coll Cardiol 65(25):2764–2765
Hess DC, Hoda MN, Bhatia K (2013) Remote limb preconditioning and postconditioning: will it translate into a promising treatment for acute stroke? Stroke 44(4):1191–1197
Hoda MN, Bhatia K, Hafez SS, Johnson MH, Siddiqui S, Ergul A et al (2014) Remote ischemic perconditioning is effective after embolic stroke in ovariectomized female mice. Transl Stroke Res 5(4):484–490
Hoda MN, Fagan SC, Khan MB, Vaibhav K, Chaudhary A, Wang P et al (2014) A 2 × 2 factorial design for the combination therapy of minocycline and remote ischemic perconditioning: efficacy in a preclinical trial in murine thromboembolic stroke model. Exp Transl Stroke Med 6:10
Khan MB, Hoda MN, Vaibhav K, Giri S, Wang P, Waller JL et al (2015) Remote ischemic postconditioning: harnessing endogenous protection in a murine model of vascular cognitive impairment. Transl Stroke Res 6(1):69–77
Hoda MN, Bhatia K, Hafez SS, Johnson MH, Siddiqui S, Ergul A, et al (2014) Remote ischemic perconditioning is effective after embolic stroke in ovariectomized female mice. Transl Stroke Res 5(4):484–490
Hoyte LC, Papadakis M, Barber PA, Buchan AM (2006) Improved regional cerebral blood flow is important for the protection seen in a mouse model of late phase ischemic preconditioning. Brain Res 1121(1):231–237
Zhao L, Nowak TS (2006) CBF changes associated with focal ischemic preconditioning in the spontaneously hypertensive rat. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 26(9):1128–1140
Meng R, Asmaro K, Meng L, Liu Y, Ma C, Xi C et al (2012) Upper limb ischemic preconditioning prevents recurrent stroke in intracranial arterial stenosis. Neurology 79(18):1853–1861
Hougaard KD, Hjort N, Zeidler D, Sørensen L, Nørgaard A, Hansen TM et al (2014) Remote ischemic perconditioning as an adjunct therapy to thrombolysis in patients with acute ischemic stroke a randomized trial. Stroke 45(1):159–167
Saver JL, Starkman S, Eckstein M, Stratton SJ, Pratt FD, Hamilton S et al (2015) Prehospital use of magnesium sulfate as neuroprotection in acute stroke. N Engl J Med 372(6):528–536
Koch S, Katsnelson M, Dong C, Perez-Pinzon M (2011) Remote ischemic limb preconditioning after subarachnoid hemorrhage a phase Ib study of safety and feasibility. Stroke 42(5):1387–1391
Gonzalez NR, Connolly M, Dusick JR, Bhakta H, Vespa P (2014) Phase I clinical trial for the feasibility and safety of remote ischemic conditioning for aneurysmal subarachnoid hemorrhage. Neurosurgery 75(5):590
Meng R, Ding Y, Asmaro K, Brogan D, Meng L, Sui M, et al (2015) Ischemic conditioning is safe and effective for octo- and nonagenarians in stroke prevention and treatment. Neurotherapeutics 12(3):667–677
Martin-Gill C, Wayne M, Guyette FX, Olafiranye O, Toma C (2016) Feasibility of remote ischemic peri-conditioning during air medical transport of STEMI patients. Prehosp Emerg Care 20(1):82–89
Ren C, Yan Z, Wei D, Gao X, Chen X, Zhao H (2009) Limb remote ischemic postconditioning protects against focal ischemia in rats. Brain Res 1288:88–94
Wei D, Ren C, Chen X, Zhao H (2012) The chronic protective effects of limb remote preconditioning and the underlying mechanisms involved in inflammatory factors in rat stroke. PLoS One 7(2):e30892
Malhotra S, Naggar I, Stewart M, Rosenbaum DM (2011) Neurogenic pathway mediated remote preconditioning protects the brain from transient focal ischemic injury. Brain Res 1386:184–190
Ren C, Gao M, Dornbos D 3rd, Ding Y, Zeng X, Luo Y et al (2011) Remote ischemic post-conditioning reduced brain damage in experimental ischemia/reperfusion injury. Neurol Res 33(5):514–519
Sun J, Tong L, Luan Q, Deng J, Li Y, Li Z et al (2012) Protective effect of delayed remote limb ischemic postconditioning: role of mitochondrial K(ATP) channels in a rat model of focal cerebral ischemic reperfusion injury. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 32(5):851–859
Hu S, Dong H, Zhang H, Wang S, Hou L, Chen S et al (2012) Noninvasive limb remote ischemic preconditioning contributes neuroprotective effects via activation of adenosine A1 receptor and redox status after transient focal cerebral ischemia in rats. Brain Res 1459:81–90
Liu X, Zhao S, Liu F, Kang J, Xiao A, Li F et al (2014) Remote ischemic postconditioning alleviates cerebral ischemic injury by attenuating endoplasmic reticulum stress-mediated apoptosis. Transl Stroke Res 5(6):692–700
Hu X, Lu Y, Zhang Y, Li Y, Jiang L (2013) Remote ischemic preconditioning improves spatial learning and memory ability after focal cerebral ischemia-reperfusion in rats. Perfusion 28(6):546–551
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2017 Springer International Publishing Switzerland
About this chapter
Cite this chapter
Ezepue, C.J., Hess, D.C. (2017). Remote Ischemic Conditioning: A Highly Translatable Therapy for Acute Stroke. In: Lapchak, P., Zhang, J. (eds) Neuroprotective Therapy for Stroke and Ischemic Disease. Springer Series in Translational Stroke Research. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-45345-3_18
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-45345-3_18
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-319-45344-6
Online ISBN: 978-3-319-45345-3
eBook Packages: MedicineMedicine (R0)