Abstract
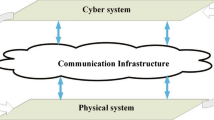
Communication networks are an essential part of any cyber-physical system (CPS) as they interconnect the CPS subsystems and components. In this chapter, we first introduce CPSs and the major role of networked control in such systems. Then, data communication networks are outlined in general and the different types of communication networks for CPSs are presented. The chapter goes on to describe some of the deficiencies of data networks and their influences on control loops. Thereafter, we highlight the need for improved communication reliability to realize CPSs and describe the existing general approaches to improve it. The potential benefits and the challenges to use the Internet are discussed after that. This is followed by considering a prominent communication standard for CPSs in the domain of smart grids. Then, the importance of pattern-based development is indicated and a description of common communication patterns for CPSs is provided. Finally, we conclude this chapter.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ahmadi H, Abdelzaher T (2009) An adaptive-reliability cyber-physical transport protocol for spatio-temporal data. In: 2009 30th IEEE real-time systems symposium. IEEE, pp 238–247
Ahmed SH, Kim G, Kim D (2013) Cyber physical system: architecture, applications and research challenges. In: 2013 IFIP wireless days (WD). IEEE, pp 1–5
Aho J, Buckspan A, Laks J et al (2012) A tutorial of wind turbine control for supporting grid frequency through active power control. In: 2012 American control conference (ACC). IEEE, pp 3120–3131
Alexander C (1979) The timeless way of building, vol 8. Oxford University Press, Oxford
Al-Kuwaiti M, Kyriakopoulos N, Hussein S (2009) A comparative analysis of network dependability, fault-tolerance, reliability, security, and survivability. IEEE Commun Surv Tutor 11:106–124. doi:10.1109/SURV.2009.090208
Babazadeh D, Chenine M, Nordström L (2013) Survey on the factors required in design of communication architecture for future DC grids. In: 2nd IFAC workshop on convergence of information technologies and control methods with power systems, ICPS 2013, Cluj-Napoca, Romania, pp. 58–63, 22 May–24 May 2013
Boswarthick D, Elloumi O, Hersent O (2012) M2M communications: a systems approach. Wiley, New York
Brambilla M, Guglielmetti G, Tziviskou C (2005) Asynchronous web services communication patterns in business protocols. In: Ngu AHH, Kitsuregawa M, Neuhold EJ, Chung J-Y, Sheng QZ (eds) Web information systems engineering—WISE 2005. Springer, Heidelberg, pp 435–442
Budka K, Deshpande J, Thottan M (2014) Communication networks for smart grids. Springer, London
Buschmann F, Meunier R, Rohnert H (1996) A system of patterns: pattern-oriented software architecture. Wiley, New York
Curtis K (2005) A DNP3 protocol primer. DNP User Group, pp. 1–8
Demir K, Germanus D, Suri N (2014) Robust and real-time communication on heterogeneous networks for smart distribution grid. In: 2014 IEEE international conference on smart grid communications (SmartGridComm). IEEE, pp 386–391
Dye M, McDonald R, Rufi A (2007) Network fundamentals, CCNA exploration companion guide. Cisco Press, USA
Elwalid A, Jin C, Low S, Widjaja I (2001) MATE: MPLS adaptive traffic engineering. In: Proceedings IEEE INFOCOM 2001, conference on computer communications. Twentieth annual joint conference of the IEEE computer and communications society (Cat. No. 01CH37213). IEEE, pp 1300–1309
ETR003 ETSI (1994) Network aspects (NA), general aspects of quality of service (QoS) and network performance (NP). Technical report
Fall K (2003) A delay-tolerant network architecture for challenged internets. In: Proceedings of the 2003 conference on applications, technologies, architectures, and protocols for computer communications—SIGCOMM 2003. ACM Press, New York, p 27
Faza A, Sedigh S, McMillin B (2010) Integrated cyber-physical fault injection for reliability analysis of the smart grid. In: Schoitsch E (ed) Proceedings of computer safety, reliability, and security: 29th international conference, SAFECOMP 2010, Vienna, Austria, 14–17 September 2010. Lecture notes in computer science, vol 6351. Springer, Berlin, pp 277–290
Galloway B, Hancke GP (2013) Introduction to industrial control networks. IEEE Commun Surv Tutorials 15:860–880. doi:10.1109/SURV.2012.071812.00124
Gamma E, Helm R, Johnson R, Vlissides J (1994) Design patterns: elements of reusable object-oriented software. Pearson Education, India
Haddadi H, Bonaventure O (eds) (2013) Recent advances in networking. ACM SIGCOMM, Brazil
Hauser CH, Bakken DE, Bose A (2005) A failure to communicate: next generation communication requirements, technologies, and architecture for the electric power grid. IEEE Power Energy Mag 3:47–55. doi:10.1109/MPAE.2005.1405870
Henneke D, Elattar M, Jasperneite J (2015) Communication patterns for cyber-physical systems. In: 2015 IEEE 20th conference on emerging technologies and factory automation (ETFA). IEEE, pp 1–4
Hespanha J, Naghshtabrizi P, Xu Y (2007) A survey of recent results in networked control systems. Proc IEEE 95:138
Hopps C (2000) Analysis of an equal-cost multi-path algorithm. IETF RFC 2992
Hu Y, Donnelly M, Helmer T, et al (2010) NASPInet specification—an important step toward its implementation. In: 2010 43rd Hawaii international conference on system sciences. IEEE, pp 1–9
IEEE (2012) IEEE standard for electric power systems communications—distributed network protocol (DNP3). IEEE Std 1815–2010
ITU (2014) The tactile internet. http://www.itu.int/en/ITU-T/techwatch/Pages/tactile-internet.aspx. Accessed 12 May 2016
ITU-T (1994) Terms and definitions related to quality of service and network performance including dependability. Recommendation E 800
ITU-T (2003) Network performance objectives for IP-based services. ITU-T Recommendation
Kamrani E (2012) Real-time internet-based teleoperation. Intell Control Autom 03:356–375. doi:10.4236/ica.2012.34041
Kamrani E, Momeni H, Sharafat A (2005) Modeling internet delay dynamics for teleoperation. In: Proceedings of 2005 IEEE conference on control applications, CCA 2005. IEEE, pp 1528–1533
Keshav S (1997) Engineering approach to computer networking: ATM networks, the internet, and the telephone network. Addison-Wesley Longman Publishing Co., Inc., USA
Khan R, Khan J (2013) A comprehensive review of the application characteristics and traffic requirements of a smart grid communications network. Comput Netw 57:825–845
Kirrmann H, Hansson M, Muri P (2007) IEC 62439 PRP: bumpless recovery for highly available, hard real-time industrial networks. In: 2007 IEEE conference on emerging technologies and factory automation (EFTA 2007). IEEE, pp 1396–1399
Kurose J, Ross K (2013) Computer networking: a top-down approach: international edition. Pearson Higher Education, USA
Lee EA (2006) Cyber-physical systems-are computing foundations adequate. In: Position paper for NSF workshop on cyber-physical systems: research motivation, techniques and roadmap. Citeseer
Lee EA (2008) Cyber physical systems: design challenges. In: 2008 11th IEEE international symposium on object and component-oriented real-time distributed computing (ISORC). IEEE, pp 363–369
Li H, Dimitrovski A, Bin SJ et al (2014) Communication infrastructure design in cyber physical systems with applications in smart grids: a hybrid system framework. IEEE Commun Surv Tutor 16:1689–1708. doi:10.1109/SURV.2014.052914.00130
Lin S-C, Gu L, Chen K-C (2015) Statistical dissemination control in large machine-to-machine communication networks. IEEE Trans Wirel Commun 14:1897–1910. doi:10.1109/TWC.2014.2376952
Liotine M (2003) Mission-critical network planning. Artech House, USA
Marashi K, Sarvestani SS (2014) Towards comprehensive modeling of reliability for smart grids: requirements and challenges. In: 2014 IEEE 15th international symposium high-assurance systems engineering (HASE), pp 105–112. doi:10.1109/HASE.2014.23
McCabe JD (1998) Practical computer network analysis and design. Morgan Kaufmann Publishers Inc., USA
NGMN Alliance (2015) NGMN 5G white paper. http://ngmn.org/uploads/media/NGMN_5G_White_Paper_V1_0.pdf. Accessed 12 May 2016
Open Networking Foundation (2012) Software-defined networking: the new norm for networks. ONF white paper
Popovic M, Mohiuddin M, Tomozei D-C, Le Boudec J-Y (2015) iPRP: parallel redundancy protocol for IP networks. In: 2015 IEEE world conference on factory communication systems (WFCS). IEEE, pp 1–4
Radatz J, Geraci A, Katki F (1990) IEEE standard glossary of software engineering terminology. IEEE Std 610121990:3
Rentschler M, Heine H (2013) The parallel redundancy protocol for industrial IP networks. In: 2013 IEEE international conference on industrial technology (ICIT). IEEE, pp 1404–1409
Schoch E, Kargl F, Weber M (2008) Communication patterns in VANETs. IEEE Commun Mag 46:119–125. doi:10.1109/MCOM.2008.4689254
Singh C, Sprintson A (2010) Reliability assurance of cyber-physical power systems. In: IEEE PES general meeting. IEEE, pp 1–6
Snow AP (2001) Network reliability: the concurrent challenges of innovation, competition, and complexity. IEEE Trans Reliab 50:38–40. doi:10.1109/24.935015
The 3rd Generation Partnership Project (3GPP) (1999) 3GPP release 99. http://www.3gpp.org/. Accessed 10 May 2016
The 3rd Generation Partnership Project (3GPP) (2008) Long-term evolution (LTE). http://www.3gpp.org/specifications/releases/72-release-8. Accessed 10 May 2016
The technology network: intelligent technical systems Ostwestfalen-Lippe it’s OWL (2014) Towards industrial 4.0: solutions from the leading-edge cluster it’s OWL. http://www.its-owl.de/fileadmin/PDF/Industrie_4.0/Auf_dem_Weg_zu_Industrie_4.0_-_Loesungen_aus_dem_Spitzencluster_its_OWL_RGB.pdf. Accessed 12 May 2016
Tipsuwan Y, Chow M (2003) Control methodologies in networked control systems. Control Eng Pract 11:1099–1111
Tozal ME, Al-Shaer E, Sarac K, Thuraisingham B (2011) On secure and resilient telesurgery communications over unreliable networks. In: 2011 IEEE conference on computer communications workshops (INFOCOM WKSHPS). IEEE, pp 714–719
US. DOE (2010) Communications requirements of smart grid technologies. US Department Energy, Technical report 2010
Weiner M, Jorgovanovic M, Sahai A, Nikolie B (2014) Design of a low-latency, high-reliability wireless communication system for control applications. In: 2014 IEEE international conference on communications (ICC). IEEE, pp 3829–3835
Wilamowski B, Irwin J (2011) Industrial communication systems. CRC Press, Boca Raton
Wu F, Kao Y, Tseng Y (2011) From wireless sensor networks towards cyber physical systems. Pervasive Mob Comput 7:397–413
Wu X, Dong Y, Ge Y, Zhao H (2013) A high reliable communication technology in electric vehicle charging station. In: 2013 IEEE seventh international conference on software security and reliability companion. IEEE, pp 198–203
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2017 Springer International Publishing Switzerland
About this chapter
Cite this chapter
Elattar, M., Wendt, V., Jasperneite, J. (2017). Communications for Cyber-Physical Systems. In: Jeschke, S., Brecher, C., Song, H., Rawat, D. (eds) Industrial Internet of Things. Springer Series in Wireless Technology. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-42559-7_13
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-42559-7_13
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-319-42558-0
Online ISBN: 978-3-319-42559-7
eBook Packages: EngineeringEngineering (R0)