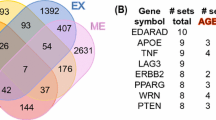
Abstract
Volumes of high-throughput assays been made publicly available. These massive repositories of biological data provide a wealth of information that can harnessed to investigate pressing questions regarding aging and disease. However, there is a distinct imbalance between available data generation techniques and data analysis methodology development. Similar to the four “V’s” of big data, biological data has volume, velocity, heterogeneity, and is prone to error, and as a result methods for analysis of this “biomedical big data” have developed at a slower rate. One promising solution to this multi-dimensional issue are network models, which have emerged as effective tools for analysis as they are capable of representing biological relationships en masse. Here we examine the need for development of standards and workflows in the usage of the correlation network model, where nodes and edges represent correlation between expression pattern in genes. One structure identified as biologically relevant in a correlation network, the gateway node, represents genes that change in co-expression between two different states. In this research, we manipulate parameters used to identify the gateway nodes within a given dataset to determine the consistency of results among network building and clustering approaches. This proof-of-concept is extremely important to investigate as there is a growing pool of methods used for various steps in our network analysis workflow, causing a lack of robustness, consistency, and reproducibility. This research compares the original gateway nodes analysis approach with manipulation in (1) network creation and (2) clustering analysis to test the consistency of structural results in the correlation network. To truly be able to trust these approaches, it must be addressed that even minor changes in approach can have sweeping effects on results. The results of this study allow the authors to call for stronger studies in benchmarking and reproducibility in biomedical “big” data analyses.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Benson, M., Breitling, R.: Network theory to understand microarray studies of complex diseases. Curr. Mol. Med. 6(6), 695–701 (2006)
Reverter, A., Chan, E.K.: Combining partial correlation and an information theory approach to the reversed engineering of gene co-expression networks. Bioinformatics 24(21), 2491–2497 (2008). doi:10.1093/bioinformatics/btn482
Horvath, S., Dong, J.: Geometric interpretation of gene coexpression network analysis. PLoS Comput. Biol. 4(8), e1000117 (2008). doi:10.1371/journal.pcbi.1000117
Dempsey, K.M., Ali, H.H.: Identifying aging-related genes in mouse hippocampus using gateway nodes. BMC Syst. Biol. 8, 62 (2014). doi:10.1186/1752-0509-8-62
Barabasi, A.L., Albert, R.: Emergence of scaling in random networks. Science 286(5439), 509–512 (1999). doi:7898. [pii]
Jeong, H., Mason, S.P., Barabasi, A.L., Oltvai, Z.N.: Lethality and centrality in protein networks. Nature 411(6833), 41–42 (2001). doi:10.1038/35075138
Barabasi, A.L., Oltvai, Z.N.: Network biology: understanding the cell’s functional organization. Nat. Rev. Genet. 5(2), 101–113 (2004). doi:10.1038/nrg1272
Albert, R.: Scale-free networks in cell biology. J. Cell Sci. 118(Pt 21), 4947–4957 (2005). doi:118/21/4947. [pii]
Bader, G.D., Hogue, C.W.: An automated method for finding molecular complexes in large protein interaction networks. BMC Bioinform. 4, 2 (2003)
Michaut, M., Baryshnikova, A., Costanzo, M., et al.: Protein complexes are central in the yeast genetic landscape. PLoS Comput. Biol. 7(2), e1001092 (2011). doi:10.1371/journal.pcbi.1001092
Dempsey, K., Thapa, I., Bastola, D., Ali, H.: Functional identification in correlation networks using gene ontology edge annotation. Int. J. Comput. Biol. Drug Des. 5(3–4), 222–244 (2012). doi:10.1504/IJCBDD.2012.049206
Dempsey, K., Ali, H.: On the robustness of the biological correlation network model. In: International Conference on Bioinformatics Models, Methods and Algorithms (BIOINFORMATICS 2014), pp. 186–195 (2014)
Dempsey, K., Ali, H.: On the discovery of cellular subsystems in gene correlation networks using measures of centrality. Curr. Bioinform. 8(3), 305–314 (2013)
Dempsey, K., Bhowmick, S., Ali, H.: Function-preserving filters for sampling in biological networks. Procedia Comput. Sci. 9, 587–595 (2012). doi:10.1016/j.procs.2012.04.063
Dempsey, K., Duraisamy, K., Bhowmick, S., Ali, H.: The development of parallel adaptive sampling algorithms for analyzing biological networks. In: 2013 IEEE International Symposium on Parallel and Distributed Processing, Workshops and PhD Forum, pp. 725–734. doi:10.1109/IPDPSW.2012.90 (2012)
Dempsey, K., Thapa, I., Cortes, C., Eriksen, Z., Bastola, D.K., Ali, H.: On mining biological signals using correlation networks. In: 2013 IEEE 13th International Conference on Data Mining Workshops, pp. 327–334. doi:10.1109/ICDMW.201 (2013)
Khazanchi, R., Dempsey, K., Thapa, I., Ali, H.: On identifying and analyzing significant nodes in protein-protein interaction networks. In: 2013 IEEE 13th International Conference on Data Mining Workshops, pp. 343–348. doi:10.1109/ICD (2013)
Barrett, T., Wilhite, S.E., Ledoux, P., et al.: NCBI GEO: archive for functional genomics data sets–update. Nucleic Acids Res. 41(Database issue), D991–D9915 (2013). doi:10.1093/nar/gks1193
Backes, C., Keller, A., Kuentzer, J., et al.: GeneTrail–advanced gene set enrichment analysis. Nucleic Acids Res. 35(Web Server issue), W186–W192 (2007). doi:10.1093/nar/gks1193
Jiang, P., Singh, M.: SPICi: a fast clustering algorithm for large biological networks. Bioinformatics 26(8), 1105–1111 (2010). doi:10.1093/bioinformatics/btq078
Ashburner, M., Ball, C.A., Blake, J.A., et al.: Gene ontology: tool for the unification of biology. the gene ontology consortium. Nat. Genet. 25(1), 25–29 (2000). doi:10.1038/75556
Aoki, K.F., Kanehisa, M.: Using the KEGG database resource. Curr. Protoc. Bioinform. Chapter 1: Unit 1.12. 10.1002/0471250953.bi0112s11 (2005)
Kriete, A., Mayo, K.L.: Atypical pathways of NF-kappaB activation and aging. Exp. Gerontol. 44(4), 250–255 (2009). doi:10.1016/j.exger.2008.12.005
Deane, R., Du Yan, S., Submamaryan, R.K., et al.: RAGE mediates amyloid-beta peptide transport across the blood-brain barrier and accumulation in brain. Nat. Med. 9(7), 907–913 (2003). doi:10.1038/nm890
Leclerc, E., Sturchler, E., Vetter, S.W., Heizmann, C.W.: Crosstalk between calcium, amyloid beta and the receptor for advanced glycation endproducts in alzheimer’s disease. Rev. Neurosci. 20(2), 95–110 (2009)
Arancio, O., Zhang, H.P., Chen, X., et al.: RAGE potentiates abeta-induced perturbation of neuronal function in transgenic mice. EMBO J. 23(20), 4096–4105 (2004). doi:10.1038/sj.emboj.7600415
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2015 Springer International Publishing Switzerland
About this paper
Cite this paper
Cooper, K.M., Bonasera, S., Ali, H. (2015). Evaluating the Robustness of Correlation Network Analysis in the Aging Mouse Hypothalamus. In: Fred, A., Gamboa, H., Elias, D. (eds) Biomedical Engineering Systems and Technologies. BIOSTEC 2015. Communications in Computer and Information Science, vol 574. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-27707-3_14
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-27707-3_14
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-319-27706-6
Online ISBN: 978-3-319-27707-3
eBook Packages: Computer ScienceComputer Science (R0)