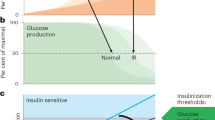
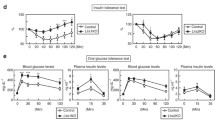
Abstract
Insulin promotes lipogenesis and suppresses hepatic gluconeogenesis. Paradoxically, the positive effect of insulin on lipid production in liver is maintained under conditions of insulin resistance, unlike its defective action on gluconeogenesis. In this chapter, we revisit this gluconeogenesis-selectivity notion by reviewing evidence that in fact, under normo-insulinemic conditions, insulin acutely reduces de novo lipogenesis in liver. This is mediated by the ability of insulin pulses in portal vein to phosphorylate the Carcino-Embryonic Antigen-related Cell Adhesion Molecule 1 (CEACAM1), an abundant protein in liver that promotes hepatic insulin clearance in a phosphorylation-dependent manner. In the presence of sustained hyperinsulinemia, pulsatility of insulin release diminishes together with its signaling, giving way to its chronic positive effect on lipogenic genes transcription. This would set the stage to redefine hepatic insulin resistance as a comprehensive process that includes defective insulin action in glucose as well as lipid production.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adams LA, Lymp JF, St Sauver J et al (2005) The natural history of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: a population-based cohort study. Gastroenterology 129:113–121
Ader M, Stefanovski D, Kim SP et al (2014) Hepatic insulin clearance is the primary determinant of insulin sensitivity in the normal dog. Obesity (Silver Spring) 22:1238–1245
Al-Share QY, Deangelis AM, Lester SG et al (2015) Forced hepatic overexpression of CEACAM1 curtails diet-induced insulin resistance. Diabetes 64:2780–2790
Arkan MC, Hevener AL, Greten FR et al (2005) IKK-beta links inflammation to obesity-induced insulin resistance. Nat Med 11:191–198
Baldeweg SE, Golay A, Natali A et al (2000) Insulin resistance, lipid and fatty acid concentrations in 867 healthy Europeans. European Group for the Study of Insulin Resistance (EGIR). Eur J Clin Invest 30:45–52
Bays H, Mandarino L, Defronzo RA (2004) Role of the adipocyte, free fatty acids, and ectopic fat in pathogenesis of type 2 diabetes mellitus: peroxisomal proliferator-activated receptor agonists provide a rational therapeutic approach. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 89:463–478, Review
Beauchemin N, Draber P, Dveksler G et al (1999) Redefined nomenclature for members of the carcinoembryonic antigen family. Exp Cell Res 252:243–249
Bergman RN (2000) Non-esterified fatty acids and the liver: why is insulin secreted into the portal vein? Diabetologia 43:946–952
Bergman RN, Ader M (2000) Free fatty acids and pathogenesis of type 2 diabetes mellitus. Trends Endocrinol Metab 11:351–356
Biddinger SB, Hernandez-Ono A, Rask-Madsen C et al (2008) Hepatic insulin resistance is sufficient to produce dyslipidemia and susceptibility to atherosclerosis. Cell Metab 7:125–134
Boden G, Cheung P, Stein TP et al (2002) FFA cause hepatic insulin resistance by inhibiting insulin suppression of glycogenolysis. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab 283:E12–E19
Brown MS, Goldstein JL (2008) Selective versus total insulin resistance: a pathogenic paradox. Cell Metab 7:95–96
Carpentier JL (1994) Insulin receptor internalization: molecular mechanisms and physiopathological implications. Diabetologia 37(Suppl 2):S117–S124
Chakravarthy MV, Pan Z, Zhu Y et al (2005) “New” hepatic fat activates PPARalpha to maintain glucose, lipid, and cholesterol homeostasis. Cell Metab 1:309–322
Charles MA, Eschwege E, Thibult N et al (1997) The role of non-esterified fatty acids in the deterioration of glucose tolerance in Caucasian subjects: results of the Paris Prospective Study. Diabetologia 40:1101–1106
Chavin KD, Yang S, Lin HZ et al (1999) Obesity induces expression of uncoupling protein-2 in hepatocytes and promotes liver ATP depletion. J Biol Chem 274:5692–5700
Corkey BE (2012) Banting lecture 2011: hyperinsulinemia: cause or consequence? Diabetes 61:4–13
Dankner R, Chetrit A, Shanik MH et al (2009) Basal-state hyperinsulinemia in healthy normoglycemic adults is predictive of type 2 diabetes over a 24-year follow-up: a preliminary report. Diabetes Care 32:1464–1466
Deangelis AM, Heinrich G, Dai T et al (2008) Carcinoembryonic antigen-related cell adhesion molecule 1: a link between insulin and lipid metabolism. Diabetes 57:2296–2303
Defronzo RA (1988) Lilly lecture 1987. The triumvirate: beta-cell, muscle, liver. A collusion responsible for NIDDM. A collusion responsible for NIDDM. Diabetes 37:667–687
Dubois MJ, Bergeron S, Kim HJ et al (2006) The SHP-1 protein tyrosine phosphatase negatively modulates glucose homeostasis. Nat Med 12:549–556
Eckel RH, Alberti KG, Grundy SM et al (2010) The metabolic syndrome. Lancet 375:181–183
Farrell GC (2009) The liver and the waistline: Fifty years of growth. J Gastroenterol Hepatol 24(Suppl 3):S105–S118
Farrell GC, Larter CZ (2006) Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: from steatosis to cirrhosis. Hepatology 43:S99–S112
Ferrante AW Jr (2007) Obesity-induced inflammation: a metabolic dialogue in the language of inflammation. J Intern Med 262:408–414
Formisano P, Najjar SM, Gross CN et al (1995) Receptor-mediated internalization of insulin. Potential role of pp 120/HA4, a substrate of the insulin receptor kinase. J Biol Chem 270:24073–24077
Freedland ES (2004) Role of a critical visceral adipose tissue threshold (CVATT) in metabolic syndrome: implications for controlling dietary carbohydrates: a review. Nutr Metab (Lond) 1:12
Gregor MF, Hotamisligil GS (2011) Inflammatory mechanisms in obesity. Annu Rev Immunol 29:415–445
Haeusler RA, Accili D (2008) The double life of Irs. Cell Metab 8:7–9
Hotamisligil GS, Shargill NS, Spiegelman BM (1993) Adipose expression of tumor necrosis factor-alpha: direct role in obesity-linked insulin resistance. Science 259:87–91
Jones CN, Abbasi F, Carantoni M et al (2000) Roles of insulin resistance and obesity in regulation of plasma insulin concentrations. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab 278:E501–E508
Kabir M, Catalano KJ, Ananthnarayan S et al (2005) Molecular evidence supporting the portal theory: a causative link between visceral adiposity and hepatic insulin resistance. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab 288:E454–E461
Kim YB, Kotani K, Ciaraldi TP et al (2003) Insulin-stimulated protein kinase C lambda/zeta activity is reduced in skeletal muscle of humans with obesity and type 2 diabetes: reversal with weight reduction. Diabetes 52:1935–1942
Kitamura Y, Accili D (2004) New insights into the integrated physiology of insulin action. Rev Endocr Metab Disord 5:143–149
Knowler WC, Barrett-Connor E, Fowler SE et al (2002) Reduction in the incidence of type 2 diabetes with lifestyle intervention or metformin. N Engl J Med 346:393–403
Lee W (2011) The CEACAM1 expression is decreased in the liver of severely obese patients with or without diabetes. Diagn Pathol 6:40
Lee CC, Haffner SM, Wagenknecht LE et al (2013) Insulin clearance and the incidence of type 2 diabetes in Hispanics and African Americans: the IRAS Family Study. Diabetes Care 36:901–907
Lester SG, Russo L, Ghanem SS et al. (2015) Hepatic CEACAM1 overexpression protects against diet-induced fibrosis and inflammation in white adipose tissue. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 6:116
Lewis GF, Carpentier A, Adeli K et al (2002) Disordered fat storage and mobilization in the pathogenesis of insulin resistance and type 2 diabetes. Endocr Rev 23:201–229
Lumeng CN, Saltiel AR (2011) Inflammatory links between obesity and metabolic disease. J Clin Invest 121:2111–2117
Marchesini G, Bugianesi E, Forlani G et al (2003) Nonalcoholic fatty liver, steatohepatitis, and the metabolic syndrome. Hepatology 37:917–923
Marra F, Gastaldelli A, Svegliati Baroni G et al (2008) Molecular basis and mechanisms of progression of non-alcoholic steatohepatitis. Trends Mol Med 14:72–81
Massillon D, Barzilai N, Hawkins M et al (1997) Induction of hepatic glucose-6-phosphatase gene expression by lipid infusion. Diabetes 46:153–157
Matveyenko AV, Liuwantara D, Gurlo T et al (2012) Pulsatile portal vein insulin delivery enhances hepatic insulin action and signaling. Diabetes 61:2269–2279
Mcgarry JD (1992) What if Minkowski had been ageusic? An alternative angle on diabetes. Science 258:766–770
Meistas MT, Margolis S, Kowarski AA (1983) Hyperinsulinemia of obesity is due to decreased clearance of insulin. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab 245:E155–E159
Mirsky IA, Broh-Kahn RH (1949) The inactivation of insulin by tissue extracts; the distribution and properties of insulin inactivating extracts. Arch Biochem 20:1–9
Mittelman SD, Van Citters GW, Kim SP et al (2000) Longitudinal compensation for fat-induced insulin resistance includes reduced insulin clearance and enhanced beta-cell response. Diabetes 49:2116–2125
Najjar SM (2002) Regulation of insulin action by CEACAM1. Trends Endocrinol Metab 13:240–245
Najjar SM, Russo L (2014) CEACAM1 loss links inflammation to insulin resistance in obesity and non-alcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH). Semin Immunopathol 36:55–71
Najjar SM, Accili D, Philippe N et al (1993) pp 120/ecto-ATPase, an endogenous substrate of the insulin receptor tyrosine kinase, is expressed as two variably spliced isoforms. J Biol Chem 268:1201–1206
Najjar SM, Philippe N, Suzuki Y et al (1995) Insulin-stimulated phosphorylation of recombinant pp 120/HA4, an endogenous substrate of the insulin receptor tyrosine kinase. Biochemistry 34:9341–9349
Najjar SM, Yang Y, Fernstrom MA et al (2005) Insulin acutely decreases hepatic fatty acid synthase activity. Cell Metab 2:43–53
Nguyen MT, Satoh H, Favelyukis S et al (2005) JNK and tumor necrosis factor-alpha mediate free fatty acid-induced insulin resistance in 3 T3-L1 adipocytes. J Biol Chem 280:35361–35371
Oakes ND, Cooney GJ, Camilleri S et al (1997) Mechanisms of liver and muscle insulin resistance induced by chronic high-fat feeding. Diabetes 46:1768–1774
Öbrink B (1997) CEA adhesion molecules: multifunctional proteins with signal-regulatory properties. Curr Opin Cell Biol 9:616–626
Odegaard JI, Chawla A (2013) Pleiotropic actions of insulin resistance and inflammation in metabolic homeostasis. Science 339:172–177
Osborn O, Olefsky JM (2012) The cellular and signaling networks linking the immune system and metabolism in disease. Nat Med 18:363–374
Ostman J, Arner P, Engfeldt P et al (1979) Regional differences in the control of lipolysis in human adipose tissue. Metabolism 28:1198–1205
Park SY, Cho YR, Kim HJ et al (2006) Mechanism of glucose intolerance in mice with dominant negative mutation of CEACAM1. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab 291:E517–E524
Pereira S, Park E, Mori Y et al (2014) FFA-induced hepatic insulin resistance in vivo is mediated by PKCδ, NADPH oxidase, and oxidative stress. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab 307:E34–E46
Perry RJ, Samuel VT, Petersen KF et al (2014) The role of hepatic lipids in hepatic insulin resistance and type 2 diabetes. Nature 510:84–91
Pivovarova O, Bernigau W, Bobbert T et al (2013) Hepatic insulin clearance is closely related to metabolic syndrome components. Diabetes Care 36:3779–3785
Pories WJ, Dohm GL (2012) Diabetes: have we got it all wrong? Hyperinsulinism as the culprit: surgery provides the evidence. Diabetes Care 35:2438–2442
Poy MN, Yang Y, Rezaei K et al (2002) CEACAM1 regulates insulin clearance in liver. Nat Genet 30:270–276
Rebrin K, Steil GM, Getty L et al (1995) Free fatty acid as a link in the regulation of hepatic glucose output by peripheral insulin. Diabetes 44:1038–1045
Saltiel AR (2012) Insulin resistance in the defense against obesity. Cell Metab 15:798–804
Shoelson SE, Lee J, Goldfine AB (2006) Inflammation and insulin resistance. J Clin Invest 116:1793–1801
Siddle K (2012) Molecular basis of signaling specificity of insulin and IGF receptors: neglected corners and recent advances. Front Endocrinol 3:34
Sidossis LS, Mittendorfer B, Walser E et al (1998) Hyperglycemia-induced inhibition of splanchnic fatty acid oxidation increases hepatic triacylglycerol secretion. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab 275:E798–E805
Sladek R, Rocheleau G, Rung J et al (2007) A genome-wide association study identifies novel risk loci for type 2 diabetes. Nature 445:881–885
Takahashi Y, Fukusato T (2010) Pediatric nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: overview with emphasis on histology. World J Gastroenterol 16:5280–5285
Unger RH, Zhou YT (2001) Lipotoxicity of beta-cells in obesity and in other causes of fatty acid spillover. Diabetes 50(Suppl 1):S118–S121
Ward GM, Walters JM, Aitken PM et al (1990) Effects of prolonged pulsatile hyperinsulinemia in humans. Enhancement of insulin sensitivity. Diabetes 39:501–507
White MF (2003) Insulin signaling in health and disease. Science 302:1710–1711
Williamson JR, Kreisberg RA, Felts PW (1966) Mechanism for the stimulation of gluconeogenesis by fatty acids in perfused rat liver. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 56:247–254
Wong RH, Chang I, Hudak CS et al (2009) A role of DNA-PK for the metabolic gene regulation in response to insulin. Cell 136:1056–1072
Zebhauser R, Kammerer R, Eisenried A et al (2005) Identification of a novel group of evolutionarily conserved members within the rapidly diverging murine Cea family. Genomics 86:566–580
Zeggini E, Weedon MN, Lindgren CM et al (2007) Replication of genome-wide association signals in UK samples reveals risk loci for type 2 diabetes. Science 316:1336–1341
Acknowledgements
The author thanks all the past and current trainees, and collaborators who participated in the studies of the effect of CEACAM1. This work was supported by grants from the NIH R01 DK054254, R01 DK083850, R01 HL112248 and 5P01 HL036573 to SMN.
Disclosures: None.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2016 Springer International Publishing Switzerland
About this chapter
Cite this chapter
Najjar, S.M. (2016). The Lipogenic Effect of Insulin Revisited. In: Ntambi, J. (eds) Hepatic De Novo Lipogenesis and Regulation of Metabolism. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-25065-6_14
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-25065-6_14
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-319-25063-2
Online ISBN: 978-3-319-25065-6
eBook Packages: Biomedical and Life SciencesBiomedical and Life Sciences (R0)