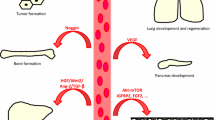
Abstract
The pulmonary vasculature remains the poor cousin of lung development. Evidence has challenged old notions that the development of blood vessels in the lung passively follows that of the airways. Rather, lung blood vessels actively promote alveolar growth during development and contribute to the maintenance of alveolar structures throughout postnatal life. These observations may be relevant for lung diseases characterized by arrested alveolar growth or loss of alveoli. This review summarizes the role of angiogenic growth factors during normal alveolar development, injury, and repair and identifies gaps in our understanding of lung vasculogenesis and angiogenesis.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Liebow AA (1959) Pulmonary emphysema with special reference to vascular changes. Am Rev Respir Dis 80:67–93
Burri PH, Dbaly J, Weibel ER (1974) The postnatal growth of the rat lung. I. Morphometry. Anat Rec 178:711–730
Burri PH, Moschopulos M (1992) Structural analysis of fetal rat lung development. Anat Rec 234:399–418
Parera MC, van Dooren M, van Kempen M, de Krijger R, Grosveld F, Tibboel D, Rottier R (2005) Distal angiogenesis: a new concept for lung vascular morphogenesis. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol 288:L141–L149
deMello DE, Sawyer D, Galvin N, Reid LM (1997) Early fetal development of lung vasculature. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol 16:568–581
Anderson-Berry A, O’Brien EA, Bleyl SB, Lawson A, Gundersen N, Ryssman D et al (2005) Vasculogenesis drives pulmonary vascular growth in the developing chick embryo. Dev Dyn 233:145–153
Yamamoto Y, Baldwin HS, Prince LS (2012) Endothelial differentiation by multipotent fetal mouse lung mesenchymal cells. Stem Cells Dev 21:1455–1465
Hall SM, Hislop AA, Pierce CM, Haworth SG (2000) Prenatal origins of human intrapulmonary arteries: formation and smooth muscle maturation. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol 23:194–203
Peng T, Morrisey EE (2013) Development of the pulmonary vasculature: current understanding and concepts for the future. Pulm Circ 3:176–178
Burri P (1999) Lung development and pulmonary angiogenesis. In: Gaultier C, Bourbon JR, Post M (eds) Lung Development. Oxford University Press, New York, pp 122–151
Djonov V, Schmid M, Tschanz SA, Burri PH (2000) Intussusceptive angiogenesis: its role embryonic vascular network formation. Circ Res 86:286–292
Ackermann M, Houdek JP, Gibney BC, Ysasi A, Wagner W, Belle J et al (2014) Sprouting and intussusceptive angiogenesis in postpneumonectomy lung growth: mechanisms of alveolar neovascularization. Angiogenesis 17:541–551
Neufeld G, Cohen T, Gengrinovitch S, Poltorak Z (1999) Vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) and its receptors. Faseb J 13:9–22
Ferrara N, Carver-Moore K, Chen H, Dowd M, Lu L, O’Shea KS et al (1996) Heterozygous embryonic lethality induced by targeted inactivation of the VEGF gene. Nature 380:439–442
Carmeliet P, Ferreira V, Breier G, Pollefeyt S, Kieckens L, Gertsenstein M et al (1996) Abnormal blood vessel development and lethality in embryos lacking a single VEGF allele. Nature 380:435–439
Fong GH, Rossant J, Gertsenstein M, Breitman ML (1995) Role of the Flt-1 receptor tyrosine kinase in regulating the assembly of vascular endothelium. Nature 376:66–70
Shalaby F, Rossant J, Yamaguchi TP, Gertsenstein M, Wu XF, Breitman ML, Schuh AC (1995) Failure of blood-island formation and vasculogenesis in Flk-1-deficient mice. Nature 376:62–66
Gerber HP, Hillan KJ, Ryan AM, Kowalski J, Keller GA, Rangell L et al (1999) VEGF is required for growth and survival in neonatal mice. Development 126:1149–1159
Healy AM, Morgenthau L, Zhu X, Farber HW, Cardoso WV (2000) VEGF is deposited in the subepithelial matrix at the leading edge of branching airways and stimulates neovascularization in the murine embryonic lung. Dev Dyn 219:341–352
Gebb SA, Shannon JM (2000) Tissue interactions mediate early events in pulmonary vasculogenesis. Dev Dyn 217:159–169
Kalinichenko VV, Lim L, Stolz DB, Shin B, Rausa FM, Clark J et al (2001) Defects in pulmonary vasculature and perinatal lung hemorrhage in mice heterozygous null for the Forkhead Box f1 transcription factor. Dev Biol 235:489–506
Ng YS, Rohan R, Sunday ME, Demello DE, D’Amore PA (2001) Differential expression of VEGF isoforms in mouse during development and in the adult. Dev Dyn 220:112–121
Galambos C, Ng YS, Ali A, Noguchi A, Lovejoy S, D’Amore PA, DeMello DE (2002) Defective pulmonary development in the absence of heparin-binding vascular endothelial growth factor isoforms. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol 27:194–203
Jakkula M, Le Cras TD, Gebb S, Hirth KP, Tuder RM, Voelkel NF, Abman SH (2000) Inhibition of angiogenesis decreases alveolarization in the developing rat lung. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol 279:L600–L607
Thebaud B, Ladha F, Michelakis ED, Sawicka M, Thurston G, Eaton F et al (2005) Vascular endothelial growth factor gene therapy increases survival, promotes lung angiogenesis, and prevents alveolar damage in hyperoxia-induced lung injury: evidence that angiogenesis participates in alveolarization. Circulation 112:2477–2486
Zhao L, Wang K, Ferrara N, Vu TH (2005) Vascular endothelial growth factor co-ordinates proper development of lung epithelium and vasculature. Mech Dev 122:877–886
Kasahara Y, Tuder RM, Taraseviciene-Stewart L, Le Cras TD, Abman S, Hirth PK et al (2000) Inhibition of VEGF receptors causes lung cell apoptosis and emphysema. J Clin Invest 106:1311–1319
Akeson AL, Cameron JE, Le Cras TD, Whitsett JA, Greenberg JM (2005) Vascular endothelial growth factor-A induces prenatal neovascularization and alters bronchial development in mice. Pediatr Res 57:82–88
Le Cras TD, Spitzmiller RE, Albertine KH, Greenberg JM, Whitsett JA, Akeson AL (2004) VEGF causes pulmonary hemorrhage, hemosiderosis, and air space enlargement in neonatal mice. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol 287:L134–L142
Yamamoto H, Yun EJ, Gerber HP, Ferrara N, Whitsett JA, Vu TH (2007) Epithelial-vascular cross talk mediated by VEGF-A and HGF signaling directs primary septae formation during distal lung morphogenesis. Dev Biol 308:44–53
Abman S, Kinsella J, Mercier J (1999) Nitric oxide and endothelin in the developing pulmonary circulation: physiologic and clinical implications. In: Gaultier C, Bourbon JR, Post M (eds) Lung Development. Oxford University Press, New York, pp 196–202
Balasubramaniam V, Maxey AM, Morgan DB, Markham NE, Abman SH (2006) Inhaled NO restores lung structure in eNOS-deficient mice recovering from neonatal hypoxia. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol 291:L119–L127
Han RN, Babaei S, Robb M, Lee T, Ridsdale R, Ackerley C et al (2004) Defective lung vascular development and fatal respiratory distress in endothelial NO synthase-deficient mice: a model of alveolar capillary dysplasia? Circ Res 94:1115–1123
Balasubramaniam V, Tang JR, Maxey A, Plopper CG, Abman SH (2003) Mild hypoxia impairs alveolarization in the endothelial nitric oxide synthase (eNOS) deficient mouse. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol 284:L964–L971
Semenza GL, Wang GL (1992) A nuclear factor induced by hypoxia via de novo protein synthesis binds to the human erythropoietin gene enhancer at a site required for transcriptional activation. Mol Cell Biol 12:5447–5454
Semenza GL (2012) Hypoxia-inducible factors in physiology and medicine. Cell 148:399–408
Bruick RK, McKnight SL (2001) A conserved family of prolyl-4-hydroxylases that modify HIF. Science 294:1337–1340
Majmundar AJ, Wong WJ, Simon MC (2010) Hypoxia-inducible factors and the response to hypoxic stress. Mol Cell 40:294–309
Maxwell PH, Wiesener MS, Chang GW, Clifford SC, Vaux EC, Cockman ME et al (1999) The tumour suppressor protein VHL targets hypoxia-inducible factors for oxygen-dependent proteolysis. Nature 399:271–275
Shimoda LA, Semenza GL (2011) HIF and the lung role of hypoxia-inducible factors in pulmonary development and disease. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 183:152–156
Groenman F, Rutter M, Caniggia I, Tibboel D, Post M (2007) Hypoxia-inducible factors in the first trimester human lung. J Histochem Cytochem 55:355–363
Rajatapiti P, van der Horst IW, de Rooij JD, Tran MG, Maxwell PH, Tibboel D et al (2008) Expression of hypoxia-inducible factors in normal human lung development. Pediatr Dev Pathol 11:193–199
van Tuyl M, Liu J, Wang J, Kuliszewski M, Tibboel D, Post M (2005) Role of oxygen and vascular development in epithelial branching morphogenesis of the developing mouse lung. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol 288:L167–L178
Bridges JP, Lin S, Ikegami M, Shannon JM (2012) Conditional hypoxia inducible factor-1alpha induction in embryonic pulmonary epithelium impairs maturation and augments lymphangiogenesis. Dev Biol 362:24–41
Iyer NV, Kotch LE, Agani F, Leung SW, Laughner E, Wenger RH et al (1998) Cellular and developmental control of O2 homeostasis by hypoxia- inducible factor 1 alpha. Genes Dev 12:149–162
Ryan HE, Lo J, Johnson RS (1998) HIF-1 alpha is required for solid tumor formation and embryonic vascularization. EMBO J 17:3005–3015
Compernolle V, Brusselmans K, Acker T, Hoet P, Tjwa M, Beck H et al (2002) Loss of HIF-2alpha and inhibition of VEGF impair fetal lung maturation, whereas treatment with VEGF prevents fatal respiratory distress in premature mice. Nat Med 8:702–710
Saini Y, Harkema JR, LaPres JJ (2008) HIF1alpha is essential for normal intrauterine differentiation of alveolar epithelium and surfactant production in the newborn lung of mice. J Biol Chem 283:33650–33657
Hosford GE, Olson DM (2003) Effects of hyperoxia on VEGF, its receptors, and HIF-2alpha in the newborn rat lung. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol 285:L161–L168
Vadivel A, Alphonse RS, Etches N, van Haaften T, Collins JJ, O’Reilly M et al (2014) Hypoxia-inducible factors promote alveolar development and regeneration. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol 50:96–105
DeLisser HM, Helmke BP, Cao G, Egan PM, Taichman D, Fehrenbach M et al (2006) Loss of PECAM-1 function impairs alveolarization. J Biol Chem 281:8724–8731
D’Angio CT, Ryan RM (2014) Animal models of bronchopulmonary dysplasia. The preterm and term rabbit models. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol 307:L959–L969
Berger J, Bhandari V (2014) Animal models of bronchopulmonary dysplasia. The term mouse models. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol 307:L936–L947
O’Reilly M, Thebaud B (2014) Animal models of bronchopulmonary dysplasia. The term rat models. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol 307:L948–L958
Yoder BA, Coalson JJ (2014) Animal models of bronchopulmonary dysplasia. The preterm baboon models. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol 307:L970–L977
Tomashefski JF Jr, Oppermann HC, Vawter GF, Reid LM (1984) Bronchopulmonary dysplasia: a morphometric study with emphasis on the pulmonary vasculature. Pediatr Pathol 2:469–487
De Paepe ME, Mao Q, Powell J, Rubin SE, DeKoninck P, Appel N et al (2006) Growth of pulmonary microvasculature in ventilated preterm infants. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 173:204–211
Randell SH, Mercer RR, Young SL (1990) Neonatal hyperoxia alters the pulmonary alveolar and capillary structure of 40-day-old rats. Am J Pathol 136:1259–1266
Roberts RJ, Weesner KM, Bucher JR (1983) Oxygen-induced alterations in lung vascular development in the newborn rat. Pediatr Res 17:368–375
Wilson WL, Mullen M, Olley PM, Rabinovitch M (1985) Hyperoxia-induced pulmonary vascular and lung abnormalities in young rats and potential for recovery. Pediatr Res 19:1059–1067
Shaffer SG, O’Neill D, Bradt SK, Thibeault DW (1987) Chronic vascular pulmonary dysplasia associated with neonatal hyperoxia exposure in the rat. Pediatr Res 21:14–20
Han RN, Buch S, Tseu I, Young J, Christie NA, Frndova H et al (1996) Changes in structure, mechanics, and insulin-like growth factor-related gene expression in the lungs of newborn rats exposed to air or 60% oxygen. Pediatr Res 39:921–929
Maniscalco WM, Watkins RH, D’Angio CT, Ryan RM (1997) Hyperoxic injury decreases alveolar epithelial cell expression of vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) in neonatal rabbit lung. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol 16:557–567
Maniscalco WM, Watkins RH, Pryhuber GS, Bhatt A, Shea C, Huyck H (2002) Angiogenic factors and alveolar vasculature: development and alterations by injury in very premature baboons. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol 282:L811–L823
Bland RD, Xu L, Ertsey R, Rabinovitch M, Albertine KH, Wynn KA et al (2007) Dysregulation of pulmonary elastin synthesis and assembly in preterm lambs with chronic lung disease. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol 292:L1370–L1384
Bland RD, Mokres LM, Ertsey R, Jacobson BE, Jiang S, Rabinovitch M et al (2007) Mechanical ventilation with 40% oxygen reduces pulmonary expression of genes that regulate lung development and impairs alveolar septation in newborn mice. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol 293:L1099–L1110
Kallapur SG, Bachurski CJ, Le Cras TD, Joshi SN, Ikegami M, Jobe AH (2004) Vascular changes after intra-amniotic endotoxin in preterm lamb lungs. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol 287:L1178–L1185
Lassus P, Turanlahti M, Heikkila P, Andersson LC, Nupponen I, Sarnesto A, Andersson S (2001) Pulmonary vascular endothelial growth factor and Flt-1 in fetuses, in acute and chronic lung disease, and in persistent pulmonary hypertension of the newborn. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 164:1981–1987
Lassus P, Ristimaki A, Ylikorkala O, Viinikka L, Andersson S (1999) Vascular endothelial growth factor in human preterm lung. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 159:1429–1433
Bhatt AJ, Pryhuber GS, Huyck H, Watkins RH, Metlay LA, Maniscalco WM (2001) Disrupted pulmonary vasculature and decreased vascular endothelial growth factor, Flt-1, and TIE-2 in human infants dying with bronchopulmonary dysplasia. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 164:1971–1980
D’Angio CT, Maniscalco WM, Ryan RM, Avissar NE, Basavegowda K, Sinkin RA (1999) Vascular endothelial growth factor in pulmonary lavage fluid from premature infants: effects of age and postnatal dexamethasone. Biol Neonate 76:266–273
Shweiki D, Itin A, Soffer D, Keshet E (1992) Vascular endothelial growth factor induced by hypoxia may mediate hypoxia-initiated angiogenesis. Nature 359:843–845
Hjalmarson O, Sandberg K (2002) Abnormal lung function in healthy preterm infants. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 165:83–87
Asikainen TM, Ahmad A, Schneider BK, White CW (2005) Effect of preterm birth on hypoxia-inducible factors and vascular endothelial growth factor in primate lungs. Pediatr Pulmonol 40:538–546
Grover TR, Asikainen TM, Kinsella JP, Abman SH, White CW (2007) Hypoxia-inducible factors HIF-1alpha and HIF-2alpha are decreased in an experimental model of severe respiratory distress syndrome in preterm lambs. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol 292:L1345–L1351
Sato TN, Tozawa Y, Deutsch U, Wolburg-Buchholz K, Fujiwara Y, Gendron-Maguire M et al (1995) Distinct roles of the receptor tyrosine kinases Tie-1 and Tie-2 in blood vessel formation. Nature 376:70–74
Suri C, Jones PF, Patan S, Bartunkova S, Maisonpierre PC, Davis S et al (1996) Requisite role of angiopoietin-1, a ligand for the TIE2 receptor, during embryonic angiogenesis. Cell 87:1171–1180
Dumont DJ, Gradwohl G, Fong GH, Puri MC, Gertsenstein M, Auerbach A, Breitman ML (1994) Dominant-negative and targeted null mutations in the endothelial receptor tyrosine kinase, tek, reveal a critical role in vasculogenesis of the embryo. Genes Dev 8:1897–1909
Suri C, McClain J, Thurston G, McDonald DM, Zhou H, Oldmixon EH et al (1998) Increased vascularization in mice overexpressing angiopoietin-1. Science 282:468–471
Thurston G, Suri C, Smith K, McClain J, Sato TN, Yancopoulos GD, McDonald DM (1999) Leakage-resistant blood vessels in mice transgenically overexpressing angiopoietin-1. Science 286:2511–2514
Bhatt AJ, Amin SB, Chess PR, Watkins RH, Maniscalco WM (2000) Expression of vascular endothelial growth factor and Flk-1 in developing and glucocorticoid-treated mouse lung. Pediatr Res 47:606–613
Thomas W, Seidenspinner S, Kramer BW, Kawczynska-Leda N, Chmielnicka-Kopaczyk M, Marx A et al (2009) Airway concentrations of angiopoietin-1 and endostatin in ventilated extremely premature infants are decreased after funisitis and unbalanced with bronchopulmonary dysplasia/death. Pediatr Res 65:468–473
Bhandari V, Choo-Wing R, Lee CG, Zhu Z, Nedrelow JH, Chupp GL et al (2006) Hyperoxia causes angiopoietin 2-mediated acute lung injury and necrotic cell death. Nat Med 12:1286–1293
MacRitchie AN, Albertine KH, Sun J, Lei PS, Jensen SC, Freestone AA et al (2001) Reduced endothelial nitric oxide synthase in lungs of chronically ventilated preterm lambs. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol 281:L1011–L1020
Afshar S, Gibson LL, Yuhanna IS, Sherman TS, Kerecman JD, Grubb PH et al (2003) Pulmonary NO synthase expression is attenuated in a fetal baboon model of chronic lung disease. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol 284:L749–L758
Iosef C, Alastalo TP, Hou Y, Chen C, Adams ES, Lyu SC et al (2012) Inhibiting NF-kappaB in the developing lung disrupts angiogenesis and alveolarization. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol 302:L1023–L1036
Kalinichenko VV, Zhou Y, Shin B, Stolz DB, Watkins SC, Whitsett JA, Costa RH (2002) Wild-type levels of the mouse Forkhead Box f1 gene are essential for lung repair. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol 282:L1253–L1265
Ren X, Ustiyan V, Pradhan A, Cai Y, Havrilak JA, Bolte CS et al (2014) FOXF1 transcription factor is required for formation of embryonic vasculature by regulating VEGF signaling in endothelial cells. Circ Res 115:709–720
Stankiewicz P, Sen P, Bhatt SS, Storer M, Xia Z, Bejjani BA et al (2009) Genomic and genic deletions of the FOX gene cluster on 16q24.1 and inactivating mutations of FOXF1 cause alveolar capillary dysplasia and other malformations. Am J Hum Genet 84:780–791
Carmeliet P, Tessier-Lavigne M (2005) Common mechanisms of nerve and blood vessel wiring. Nature 436:193–200
Prodhan P, Kinane TB (2002) Developmental paradigms in terminal lung development. Bioessays 24:1052–1059
Wilkinson GA, Schittny JC, Reinhardt DP, Klein R (2008) Role for ephrinB2 in postnatal lung alveolar development and elastic matrix integrity. Dev Dyn 237:2220–2234
Vadivel A, Alphonse RS, Collins JJ, van Haaften T, O’Reilly M, Eaton F, Thebaud B (2013) The axonal guidance cue semaphorin 3C contributes to alveolar growth and repair. PLoS One 8, e67225
Becker PM, Tran TS, Delannoy MJ, He C, Shannon JM, McGrath-Morrow S (2011) Semaphorin 3A contributes to distal pulmonary epithelial cell differentiation and lung morphogenesis. PLoS One 6, e27449
Joza S, Wang J, Fox E, Hillman V, Ackerley C, Post M (2012) Loss of semaphorin-neuropilin-1 signaling causes dysmorphic vascularization reminiscent of alveolar capillary dysplasia. Am J Pathol 181:2003–2017
Joza S, Wang J, Tseu I, Ackerley C, Post M (2013) Fetal, but not postnatal, deletion of semaphorin-neuropilin-1 signaling affects murine alveolar development. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol 49:627–636
Schwarz MA, Zhang F, Gebb S, Starnes V, Warburton D (2000) Endothelial monocyte activating polypeptide II inhibits lung neovascularization and airway epithelial morphogenesis. Mech Dev 95:123–132
Janer J, Andersson S, Haglund C, Lassus P (2007) Pulmonary endostatin perinatally and in lung injury of the newborn infant. Pediatrics 119:e241–e246
Richter AG, McKeown S, Rathinam S, Harper L, Rajesh P, McAuley DF et al (2009) Soluble endostatin is a novel inhibitor of epithelial repair in idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Thorax 64:156–161
Chetty A, Bennett M, Dang L, Nakamura D, Cao GJ, Mujahid S et al (2015) Pigment epithelium-derived factor mediates impaired lung vascular development in neonatal hyperoxia. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol 52:295–303
Nakanishi H, Sugiura T, Streisand JB, Lonning SM, Roberts JD Jr (2007) TGF-beta-neutralizing antibodies improve pulmonary alveologenesis and vasculogenesis in the injured newborn lung. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol 293:L151–L161
ten Dijke P, Goumans MJ, Pardali E (2008) Endoglin in angiogenesis and vascular diseases. Angiogenesis 11:79–89
De Paepe ME, Patel C, Tsai A, Gundavarapu S, Mao Q (2008) Endoglin (CD105) up-regulation in pulmonary microvasculature of ventilated preterm infants. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 178:180–187
Kunig A, Balasubramaniam V, Markham NE, Seedorf G, Gien J, Abman SH (2006) Recombinant human VEGF treatment transiently increases lung edema but enhances lung structure after neonatal hyperoxia. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol 289:L529–L535
Kunig AM, Balasubramaniam V, Markham NE, Morgan D, Montgomery G, Grover TR, Abman SH (2005) Recombinant human VEGF treatment enhances alveolarization after hyperoxic lung injury in neonatal rats. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol 289:L529–L535
Asikainen TM, Chang LY, Coalson JJ, Schneider BK, Waleh NS, Ikegami M et al (2006) Improved lung growth and function through hypoxia-inducible factor in primate chronic lung disease of prematurity. FASEB J 20:1698–1700
Ballard RA, Truog WE, Cnaan A, Martin RJ, Ballard PL, Merrill JD et al (2006) Inhaled nitric oxide in preterm infants undergoing mechanical ventilation. N Engl J Med 355:343–353
Kinsella JP, Cutter GR, Walsh WF, Gerstmann DR, Bose CL, Hart C et al (2006) Early inhaled nitric oxide therapy in premature newborns with respiratory failure. N Engl J Med 355:354–364
Schreiber MD, Gin-Mestan K, Marks JD, Huo D, Lee G, Srisuparp P (2003) Inhaled nitric oxide in premature infants with the respiratory distress syndrome. N Engl J Med 349:2099–2107
Kinsella JP, Cutter GR, Steinhorn RH, Nelin LD, Walsh WF, Finer NN, Abman SH (2014) Noninvasive inhaled nitric oxide does not prevent bronchopulmonary dysplasia in premature newborns. J Pediatr 165:1104–1108, e1101
Mercier JC, Hummler H, Durrmeyer X, Sanchez-Luna M, Carnielli V, Field D et al (2010) Inhaled nitric oxide for prevention of bronchopulmonary dysplasia in premature babies (EUNO): a randomised controlled trial. Lancet 376:346–354
Luong C, Rey-Perra J, Vadivel A, Gilmour G, Sauve Y, Koonen D et al (2011) Antenatal sildenafil treatment attenuates pulmonary hypertension in experimental congenital diaphragmatic hernia. Circulation 123:2120–2131
Vadivel A, Abozaid S, van Haaften T, Sawicka M, Eaton F, Chen M, Thebaud B (2010) Adrenomedullin promotes lung angiogenesis, alveolar development, and repair. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol 43:152–160
Vadivel A, Alphonse RS, Ionescu L, Machado DS, O’Reilly M, Eaton F et al (2014) Exogenous hydrogen sulfide (H2S) protects alveolar growth in experimental O2-induced neonatal lung injury. PLoS One 9, e90965
Vadivel A, Aschner JL, Rey-Parra GJ, Magarik J, Zeng H, Summar M et al (2010) L-citrulline attenuates arrested alveolar growth and pulmonary hypertension in oxygen-induced lung injury in newborn rats. Pediatr Res 68:519–525
Ladha F, Bonnet S, Eaton F, Hashimoto K, Korbutt G, Thebaud B (2005) Sildenafil improves alveolar growth and pulmonary hypertension in hyperoxia-induced lung injury. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 172:750–756
Vadivel A, van Haaften T, Alphonse RS, Rey-Parra GJ, Ionescu L, Haromy (2012) Critical role of the axonal guidance cue EphrinB2 in lung growth, angiogenesis, and repair. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 185:564–574
Acknowledgments
B.T. is supported by the Canadian Institutes for Health Research (CIHR), the Ontario Thoracic Society, the Canadian Stem Cell Network, the Children’s Hospital of Eastern Ontario Research Institute and the Ottawa Hospital Research Institute. M.Y. is supported in part by the Riley Children’s Foundation.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2015 Springer International Publishing Switzerland
About this chapter
Cite this chapter
Thébaud, B., Yoder, M.C. (2015). Lung Vasculogenesis and Angiogenesis. In: Bertoncello, I. (eds) Stem Cells in the Lung. Stem Cell Biology and Regenerative Medicine. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-21082-7_3
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-21082-7_3
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-319-21081-0
Online ISBN: 978-3-319-21082-7
eBook Packages: Biomedical and Life SciencesBiomedical and Life Sciences (R0)