Abstract
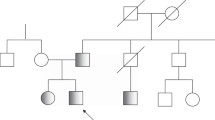
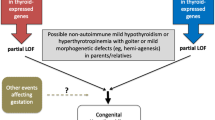
PAX8 is one of the best characterized thyroid-specific transcription factors that play a role in development and physiology of the thyroid gland. PAX8 causes, when mutated, congenital hypothyroidism in both mice and humans, although mode of inheritance is different among the two species (mice, recessive; humans, dominant). Genetically engineered PAX8-deficient mice show abnormalities in early proliferation of thyroid precursor cells, resulting in markedly severe thyroid hypoplasia. In humans, clinical phenotypes of mutation carriers are highly variable, ranging from severe congenital hypothyroidism with thyroid hypoplasia to normal thyroid function with a morphologically normal gland. Several genetic epidemiology studies have revealed that PAX8 mutation is a relatively rare cause of human congenital hypothyroidism, observed in about 2 % of cases. Nonetheless, PAX8 mutation is the leading genetic cause of congenital hypothyroidism showing dominant inheritance. Thus, clinicians should consider PAX8 mutations when he/she encounters a patient with positive family history of congenital hypothyroidism. This review focuses on the molecular genetics of human congenital hypothyroidism due to PAX8 mutations.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Plachov D, Chowdhury K, Walther C et al (1990) Pax8, a murine paired box gene expressed in the developing excretory system and thyroid gland. Development 110:643–651
Zannini M, Francis-Lang H, Plachov D et al (1992) Pax-8, a paired domain-containing protein, binds to a sequence overlapping the recognition site of a homeodomain and activates transcription from two thyroid-specific promoters. Mol Cell Biol 12:4230–4241
Ohno M, Zannini M, Levy O et al (1999) The paired-domain transcription factor Pax8 binds to the upstream enhancer of the rat sodium/iodide symporter gene and participates in both thyroid-specific and cyclic-AMP-dependent transcription. Mol Cell Biol 19:2051–2060
Pasca di Magliano M, Di Lauro R, Zannini M (2000) Pax8 has a key role in thyroid cell differentiation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 97:13144–13149
Mansouri A, Chowdhury K, Gruss P (1998) Follicular cells of the thyroid gland require Pax8 gene function. Nat Genet 19:87–90
Gehring WJ, Ikeo K (1999) Pax 6: mastering eye morphogenesis and eye evolution. Trends Genet 15:371–377
Antonica F, Kasprzyk DF, Opitz R et al (2012) Generation of functional thyroid from embryonic stem cells. Nature 491:66–71
Di Palma T, Nitsch R, Mascia A et al (2003) The paired domain-containing factor Pax8 and the homeodomain-containing factor TTF-1 directly interact and synergistically activate transcription. J Biol Chem 278:3395–3402
Miccadei S, De Leo R, Zammarchi E et al (2002) The synergistic activity of thyroid transcription factor 1 and Pax 8 relies on the promoter/enhancer interplay. Mol Endocrinol 16:837–846
Macchia PE, Lapi P, Krude H et al (1998) PAX8 mutations associated with congenital hypothyroidism caused by thyroid dysgenesis. Nat Genet 19:83–86
Congdon T, Nguyen LQ, Nogueira CR et al (2001) A novel mutation (Q40P) in PAX8 associated with congenital hypothyroidism and thyroid hypoplasia: evidence for phenotypic variability in mother and child. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 86:3962–3967
Komatsu M, Takahashi T, Takahashi I et al (2001) Thyroid dysgenesis caused by PAX8 mutation: the hypermutability with CpG dinucleotides at codon 31. J Pediatr 139:597–599
Vilain C, Rydlewski C, Duprez L et al (2001) Autosomal dominant transmission of congenital thyroid hypoplasia due to loss-of-function mutation of PAX8. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 86:234–238
de Sanctis L, Corrias A, Romagnolo D et al (2004) Familial PAX8 small deletion (c.989_992delACCC) associated with extreme phenotype variability. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 89:5669–5674
Meeus L, Gilbert B, Rydlewski C et al (2004) Characterization of a novel loss of function mutation of PAX8 in a familial case of congenital hypothyroidism with in-place, normal-sized thyroid. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 89:4285–4291
Grasberger H, Ringkananont U, Lefrancois P et al (2005) Thyroid transcription factor 1 rescues PAX8/p300 synergism impaired by a natural PAX8 paired domain mutation with dominant negative activity. Mol Endocrinol 19:1779–1791
Al Taji E, Biebermann H, Limanova Z et al (2007) Screening for mutations in transcription factors in a Czech cohort of 170 patients with congenital and early-onset hypothyroidism: identification of a novel PAX8 mutation in dominantly inherited early-onset non-autoimmune hypothyroidism. Eur J Endocrinol 156:521–529
Di Palma T, Zampella E, Filippone MG et al (2010) Characterization of a novel loss-of-function mutation of PAX8 associated with congenital hypothyroidism. Clin Endocrinol (Oxf) 73:808–814
Jo W, Ishizu K, Fujieda K et al (2010) Congenital hypothyroidism caused by a PAX8 gene mutation manifested as sodium/iodide symporter gene defect. J Thyroid Res 2010:619013
Narumi S, Yoshida A, Muroya K et al (2011) PAX8 mutation disturbing thyroid follicular growth: a case report. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 96:E2039–E2044
Alcantara-Ortigoza MA, Gonzalez-del Angel A, Martinez-Cruz V et al (2012) Molecular analysis of the PAX8 gene in a sample of Mexican patients with primary congenital hypothyroidism: identification of the recurrent p.Arg31His mutation. Clin Endocrinol (Oxf) 76:148–150
Liu SG, Zhang SS, Zhang LQ et al (2012) Screening of PAX8 mutations in Chinese patients with congenital hypothyroidism. J Endocrinol Invest 35:889–892
Carvalho A, Hermanns P, Rodrigues AL et al (2013) A new PAX8 mutation causing congenital hypothyroidism in three generations of a family is associated with abnormalities in the urogenital tract. Thyroid 23:1074–1078
Narumi S, Araki S, Hori N et al (2012) Functional characterization of four novel PAX8 mutations causing congenital hypothyroidism: new evidence for haploinsufficiency as a disease mechanism. Eur J Endocrinol 167:625–632
Narumi S, Muroya K, Asakura Y et al (2010) Transcription factor mutations and congenital hypothyroidism: systematic genetic screening of a population-based cohort of Japanese patients. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 95:1981–1985
Hermanns P, Grasberger H, Cohen R et al (2013) Two cases of thyroid dysgenesis caused by different novel PAX8 mutations in the DNA-binding region: in vitro studies reveal different pathogenic mechanisms. Thyroid 23:791–796
Shepard TH, Andersen H, Andersen HJ (1964) Histochemical studies of the human fetal thyroid during the first half of fetal life. Anat Rec 149:363–379
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2015 Springer International Publishing Switzerland
About this chapter
Cite this chapter
Narumi, S., Hasegawa, T. (2015). Congenital Hypothyroidism due to PAX8 Mutations. In: Bona, G., De Luca, F., Monzani, A. (eds) Thyroid Diseases in Childhood. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-19213-0_7
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-19213-0_7
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-319-19212-3
Online ISBN: 978-3-319-19213-0
eBook Packages: MedicineMedicine (R0)