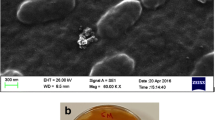
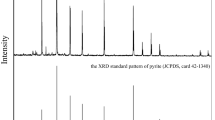
Abstract
Studies were carried out on ferrous oxidation and bacterial leaching of copper flotation concentrate to selectively leach nickel by two strains of Acidothiobacillus ferrooxidans. However, slower growth rates of these strains have led to prolonged lag periods during leaching process with low nickel recovery. Hence, attempts were made to adapt these strains to high concentrations of copper salt, nickel salt, mixture of copper and nickel salts and flotation concentrate which would facilitate the preferential leaching of Ni containing pentlandite phase from a floatation concentrate with chalcopyrite phase in predominance. When unadapted strains of Tf were replaced with adapted strains, the lag period during leaching process was drastically declined with immediate resurgence of pH fall indicating biologically produced acid. Cells adapted to metals and concentrate has shown positive effect on oxidizing ability of pyrite and nickel leaching efficiency. Unadapted Tf-44 and Tf-231 strains have shown selective leaching of nickel (55 % and 49.7 %) while the leachabilities obtained with adapted strains were 80 % and 83.5 % respectively.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Acevado, F. (2002). Present and future of biotechnology in developing countries. Electronic Journal of Biotechnology (online). IISN-0717-3458. www.ejb.org/content/vol3/issue3/full/4/4/index/html.
Adamov, E. V., Karavaiko, G. I., Koreshkov, N. G., Lankov, B. Y. U., & Krylova, L. N. (1997). Use of Acidothiobacillus ferrooxidans for bacterial oxidation of pyrrhotite concentrates. Prikladnaya Biokhimiya i Mikrobiologiya, 33(2), 189–193.
Ballester, A., Gonzalez, F., Blazanez, M. L., & Miller, J. L. (1990). The influence of various ions in the bioleaching of metal sulphides. Hydrometallurgy, 23, 221–235.
Bandhyopadhyay, A. (2003). Environmental issues in mineral processing. In V. N. Misra, G. Yadav, & K. S. Rao (Eds.), Mineral processing and engineering (pp. 202–206). India: Indian Institute of Chemical Engineers.
Bharathi, K., Lakshmi Narasu, M., Ravindra, P., & Bhagvanth Rao, M. (2004). Effect of biochemical reactions on enhancement rate of bioleaching. Chemical Engineering Science, 59(22–23), 5069–5073.
Bharathi, K., & Ravindra, P. (2006). Optimization of bacterial oxidation process parameters for selective leaching of nickel by Acidohiobacillus ferrooxidans. International Journal of Chemical Reactor Engineering, 4, A1. http://www.bepress.com/ijcre/vol4/A1.
Bharathi, K., Lakshmi Narasu, M., & Ravindra, P. (2008). Role of galvanic interaction in selective leaching of nickel from copper flotation concentrate. Advances in Natural and Applied Sciences, 2(2), 68–72.
Bharathi, K., Bhagvanth Rao, M., & Ravindra, P. (2000). New trends in mineral bioprocessing—An over view. In Proceedings of CHEMCON, Dec, Calcutta, India. BIO 81–84.
Bharathi, K., Suresh, P., Bhagvanth Rao, M., Polasa, H., & Ravindra, P. (2002). Comparative studies of nickel leachability with different Strains of Thiobacillus ferrooxidans. In Proceedings of CHEMCON, Dec, Hyderabad, India.
Bosecker, K. (2001). Microbial leaching in environmental clean up programmes. Hydrometallurgy, 59, 245–248.
Das, A., Modak, J. M., & Natarajan, K. A. (1997). Studies on multi metal tolerance of Acidothiobacillus ferrooxidans. Minerals Engineering, 10(7), 743–749.
Elzeky, M., & Attia, Y. A. (1995). Effect of bacterial adaptation on kinetics and mechanisms of bioleaching ferrous sulfides. The Chemical Engineering Journal, 56, B115–B124.
Garcia, O., Jr., & da‘Silva, L. L. (1991). Differences in growth and iron oxidation among Acidothiobacillus ferrooxidans cultures in the presence of some toxic metals. Biotechnology Letters, 13(8), 567–570.
Gehrke, T., Hallmann, R., Kinzler, K., & Sand, W. (2001). The EPS of Acidothiobacillus ferrooxidans—A model for structure–function relationships of attached bacteria and their physiology. Water Science and Technology, 43(6), 159–167.
Gehrke, T., Telegdi, J., Thierry, D., & Sand, W. (1998). Importance of extracellular polymeric substances from Acidothiobacillus ferrooxidans for bioleaching. Applied Environmental Microbiology, 64(7), 2743–2747.
Giaveno, A., & Donati, E. (2001). Bioleaching of heazelwoodite by Thiobacillus spp. Process Biochemistry, 36, 955–962.
Jeffery, G. H., Bassett, J., Mendham, J., & Denny, R. C. (1989). Titrimetric analysis. In Vogel’s textbook of quantitative analysis (5th ed., pp. 376–377). London, UK: ELBS-Longman.
Kai, T., Nishi, M., & Takahashi, T. (1995). Adaptation of Acidothiobacillus ferrooxidans to nickel ion and bacterial oxidation of nickel sulfide. Biotechnology Letters, 17(2), 229–232.
Kar, R. N., Sukla, K. M., & Misra, V. N. (2003). Perspectives of mineral biotechnology. In V. N. Misra, G. Yadav, & K. S. Rao (Eds.), Mineral processing and engineering (pp. 163–171). India: Indian Institute of Chemical Engineers Publications.
Leduce, L. G., Ferroni, G. D., & Trevors, J. T. (1997). Resistance to heavy metals in different strains of Acidothiobacillus ferrooxidans. World Journal of Microbiology and Biotechnology, 13(4), 453–455.
Li, H. L., & Ke, J. J. (2001). Influence of Cu2+ and Mg2+ on the growth and activity of Ni2+ adapted Acidothiobacillus ferrooxidans. Hydrometallurgy, 61, 151–156.
Mason, L. J., & Rice, N. M. (2002). The adaptation of Acidothiobacillus ferrooxidans for the treatment of nickel-iron sulfide concentrates. Minerals Engineering, 15, 759–808.
Mehta, K. D., Pandey, B. D., & Premchand. (1999). Bio-assisted leaching of copper, nickel and cobalt from converter slag. Materials Transactions, JIM, 40(3), 214–221.
Mehta, K. D., Pandey, B. D., & Premchand. (1997). Bioleaching of copper, nickel and cobalt from copper converter slag by Acidothiobacillus ferrooxidans. NML Technical Journal, 39, 59–70.
Natarajan, K. A., & Iwasaki, I. (1983). Environmental leaching behaviour of copper-nickel bearing Duluth Gabbro and floatation tailings. Hydrometallurgy, 10, 329–342.
Natarajan, K. A., Sudeesha, K., & Rao, G. R. (1994). Stability of copper tolerance in Acidothiobacillus ferrooxidans. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek, 66(4), 303–306.
Paknikar, K. M., & Agate, A. D. (1995). Laboratory manual. In International workshop on metal–microbe interactions and their applications. United Nations Environment Programme (pp. 24–36).
Puskas, A., Pap, G., Hollo, J., & Lakatos, T. (1980). Effects of dissolved metal ions on the physiology of Acidothiobacillus ferrooxidans. In Proceedings of international conference on use of microorganisms in hydrometallurgy (pp. 189–196). Hungary: Hungarian Academy of Sciences.
Ravindra, P., & Bharathi, K. (2009). Bacterial leaching of low-grade nickel ores. EMS Publications. ISBN 978-967-5224-37-9.
Selvi, S. C., Modak, J. M., & Natarajan, K. A. (1998). Electrobioleaching of sphalerite floatation concentrate. Minerals Engineering, 11(8), 783–788.
Torma, A. E. (1997). The role of Acidothiobacillus ferrooxidans in hydrometallurgical process. Advances in Biochemical Engineering, 6, 1–31.
Valix, M., Tang, J. Y., & Cheung, W. H. (2001). The effects of mineralogy on the biological leaching of nickel lateritic ores. Minerals Engineering, 14(12), 1629–1635.
Vogel, A. I. (1978). Textbook of quantitative inorganic analysis. London, UK: Longman Publishers. 354.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2015 Springer International Publishing Switzerland
About this chapter
Cite this chapter
Ravindra, P., Kodli, B., Veera Rao, V.P.R. (2015). Effect of Adaptation of Acidothiobacillus ferrooxidans on Ferrous Oxidation and Nickel Leaching Efficiency. In: Ravindra, P. (eds) Advances in Bioprocess Technology. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-17915-5_2
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-17915-5_2
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-319-17914-8
Online ISBN: 978-3-319-17915-5
eBook Packages: Chemistry and Materials ScienceChemistry and Material Science (R0)