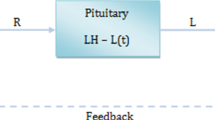
Abstract
The continuous part of a hybrid (pulse-modulated) model of testosterone (Te) feedback regulation in the human male is extended with infinite-dimensional and nonlinear blocks, to obtain the dynamics that better agree with the hormone concentration profiles observed in clinical data. A linear least-squares based optimization algorithm is developed for the purpose of detecting impulses of gonadotropin-releasing hormone (GnRH) from measured concentration of luteinizing hormone (LH). The estimated impulse parameters are instrumental in evaluating the frequency and amplitude modulation functions parameterizing the pulse-modulated feedback. The proposed approach allows for the identification of all model parameters from the hormone concentrations of Te and LH. Simulation results of the complete estimated closed-loop system exhibiting similar to the clinical data behavior are provided.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
R.H. Abraham, H. Kocak, W.R. Smith, Chaos and intermittency in an endocrine system model, in Chaos, Fractals, and Dynamics, ed. by P. Fischer, W.R. Smith, vol. 98 (Marcel Dekker, New York, 1985), pp. 33–70
S. Boyd, L. Vandenberghe, Convex Optimization (Cambridge University Press, New York, 2004)
M. Cartwright, M. Husain, A model for the control of testosterone secretion. J. Theor. Biol. 123(2), 239–250 (1986)
F. Chang, R. Luus, A noniterative method for identification using Hammerstein model. IEEE Trans. Autom. Contr. 16(5), 464–468 (1971)
A. Churilov, A. Medvedev, P. Mattsson, Analysis of a pulse-modulated model of endocrine regulation with time-delay, in IEEE 51st Annual Conference on Decision and Control (CDC), Maui (2012), pp. 362–367
A. Churilov, A. Medvedev, P. Mattsson, On finite-dimensional reducibility of time-delay systems under pulse-modulated feedback, in IEEE 52nd Annual Conference on Decision and Control (CDC), Firenze (2013), pp. 362–367
A. Churilov, A. Medvedev, A. Shepeljavyi, Mathematical model of non-basal testosterone regulation in the male by pulse modulated feedback. Automatica 45(1), 78–85 (2009)
F. Clément, J.-P. Françoise, Mathematical modeling of the GnRH-pulse and surge generator. SIAM J. Appl. Dyn. Syst. 6(2), 441–456 (2007)
D.J. Dierschke, A.N. Bhattacharya, L.E. Atkinson, E. Knobil, Circhoral oscillations of plasma LH levels in the ovariectomized rhesus monkey. Endocrinology 87, 850–853 (1970)
F. Ding, X.P. Liu, G. Liu, Identification methods for Hammerstein nonlinear systems. Digit. Signal Process. 21(2), 215–238 (2011)
D. Efimov, A. Fradkov, Oscillatority conditions for nonlinear systems with delay. J. Appl. Math. (2007). article ID 72561
G. Enciso, E.D. Sontag, On the stability of a model of testosterone dynamics. J. Math. Biol. 49, 627–634 (2004)
L.S. Farhy, Modeling of oscillations in endocrine networks with feedback, in Numerical Computer Methods, Part E, ed. by M.L. Johnson, L. Brand. Methods in Enzymology, vol. 384 (Academic, San Diego,2004), pp. 54–81
T. Glad, L. Ljung, Control Theory: Multivariable and Nonlinear Methods (Taylor and Francis, New York/London, 2000)
W.J. Heuett, H. Qian, A stochastic model of oscillatory blood testosterone levels. Bull. Math. Biol. 68(6), 1383–1399 (2006)
E. Hidayat, A. Medvedev, Identification of a pulsatile endocrine model from hormone concentration data, in IEEE International Conference on Control Applications (CCA), Dubrovnik (2012), pp. 356–363
E. Hidayat, A. Medvedev, Laguerre domain identification of continuous linear time-delay systems from impulse response data. Automatica 48(11), 2902–2907 (2012)
M.L. Johnson, L. Pipes, P.P. Veldhuis, L.S. Farhy, R. Nass, M.O. Thorner, W.S. Evans, AutoDecon: a robust numerical method for the quantification of pulsatile events, in Computer Methods, Volume A, ed. by M.L. Johnson, L. Brand. Methods in Enzymology, vol. 454 (Elsevier, Amsterdam, 2009), pp. 367–404
D.M. Keenan, J.D. Veldhuis, A biomathematical model of time-delayed feedback in the human male hypothalamic-pituitary-leydig cell axis. Am. J. Physiol. Endocrinol. Metab. 275(1), E157–E176 (1998)
D.M. Keenan, S. Chattopadhyay, J.D. Veldhuis, Composite model of time-varying appearance and disappearance of neurohormone pulse signals in blood. J. Theor. Biol. 236(3), 242–255 (2005)
D.M. Keenan, I. Clarke, J.D. Veldhuis, Non-invasive analytical estimation of endogenous gonadotropin-releasing hormone (GnRH) drive: analysis using graded competitive GnRH-receptor antagonism and a calibrating pulse of exogenous GnRH. Endocrinology 152(12), 4882–4893 (2011)
D.M. Keenan, W. Sun, J.D. Veldhuis, A stochastic biomathematical model of male reproductive hormone systems. SIAM J. Appl. Math. 61(3), 934–965 (2000)
B.P. Kovatchev, M. Breton, C. Dalla Man, C. Cobelli, In silico preclinical trials: a proof of concept in closed-loop control of type 1 diabetes. J. Diabetes Sci. Technol. 3(1), 44–55 (2009)
P. Mattsson, A. Medvedev, Estimation of input impulses by means of continuous finite memory observers, in American Control Conference, Montreal, June 2012, pp. 6769–6774
P. Mattsson, A. Medvedev, Modeling of testosterone regulation by pulse-modulated feedback: an experimental data study, in International Symposium on Computational Models for Life Sciences, ed. by C. Sun, T. Bednarz, T.D. Pham, P. Vallotton, D. Wang. AIP Conference Proceedings, Sydney, vol. 1559 (2013), pp. 333–342
A. Medvedev, A. Churilov, P. Mattsson, Periodical solutions in a pulse-modulated model of endocrine regulation with time-delay. IEEE Trans. Autom. Contr. 59(3), 728–733 (2014)
J.D. Murray, Mathematical Biology, I: An Introduction, 3rd edn. (Springer, New York, 2002)
N.L. Rasgon, L. Pumphrey, P. Prolo, S. Elman, A.B. Negrao, J. Licinio, A. Garfinkel, Emergent oscillations in mathematical model of the human menstrual cycle. CNS Spectr. 8(11), 805–814 (2003)
W.R. Smith, Hypothalamic regulation of pituitary secretion of luteinizing hormone. II. Feedback control of gonadotropin secretion. Bull. Math. Biol. 42(1), 57–78 (1980)
T. Söderström, P. Stoica, System Identification (Prentice-Hall, Upper Saddle River, 1988)
C.T. Sparrow, Chaos in a three-dimensional single loop feedback system with a piecewise linear feedback function. J. Math. Anal. Appl. 83(1), 275–291 (1981)
R. Tibshirani, Regression shrinkage and selection via the LASSO. J. R. Stat. Soc. Ser. B (Methodol.) 58(1), 267–288 (1996)
J.D. Veldhuis, Recent insights into neuroendocrine mechanisms of aging of the human male hypothalamic-pituitary-gonadal axis. J. Androl. 20(1), 1–18 (1999)
J.D. Veldhuis, J.C. King, R.J. Urban, A.D. Rogol, W.S. Evans, L.A. Kolp, M.L. Johnson, Operating characteristics of the male hypothalamo-pituitary-gonadal axis: pulsatile release of testosterone and follicle-stimulating hormone and their temporal coupling with luteinizing hormone. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 65(5), 929–41 (1987)
J.J. Walker, J.R. Terry, K. Tsaneva-Atanasova, S.P. Armstrong, C.A. McArdle, S.L. Lightman, Encoding and decoding mechanisms of pulsatile hormone secretion. J. Neuroendocr. 22, 1226–1238 (2009)
Z.T. Zhusubaliyev, A.N. Churilov, A. Medvedev, Bifurcation phenomena in an impulsive model of non-basal testosterone regulation. Chaos Interdiscip. J. Nonlinear Sci. 22(1), 013121 (2012)
M. Zitzmann, E. Nieschlag, Testosterone levels in healthy men and the relation to behavioural and physical characteristics: facts and constructs. Eur. J. Endocr. 144(3), 183–197 (2001)
Acknowledgements
This work was in part financed by the European Research Council, Advanced Grant 247035 (SysTEAM) and Grant 2012-3153 from the Swedish Research Council.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2015 Springer International Publishing Switzerland
About this chapter
Cite this chapter
Mattsson, P., Medvedev, A. (2015). Modeling of Testosterone Regulation by Pulse-Modulated Feedback. In: Sun, C., Bednarz, T., Pham, T., Vallotton, P., Wang, D. (eds) Signal and Image Analysis for Biomedical and Life Sciences. Advances in Experimental Medicine and Biology, vol 823. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-10984-8_2
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-10984-8_2
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-319-10983-1
Online ISBN: 978-3-319-10984-8
eBook Packages: Biomedical and Life SciencesBiomedical and Life Sciences (R0)