Abstract
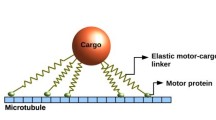
Many different types of cellular cargos are transported bidirectionally along microtubules by teams of molecular motors. The motion of this cargo-motors system has been experimentally characterized in vivo as processive with rather persistent directionality. Different theoretical approaches have been suggested in order to explore the origin of this kind of motion. An effective theoretical approach, introduced by Müller et al. [9], describes the cargo dynamics as a tug-of-war between different kinds of motors. An alternative approach has been suggested recently by Kunwar et al. [7], who considered the coupling between motor and cargo in more detail.Based on this framework we introduce a model considering single motor positions which we propagate in continuous time. Furthermore, we analyze the possible influence of the discrete time update schemes used in previous publications on the system’s dynamic.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
N. J. Carter et al., Nature 435(7040), 308–312 (2005)
K. Döhner et al., Trends Microbiol. 13(7), 320–327 (2005)
D.T. Gillespie, J. Comput. Phys. 22(4), 403–434 (1976)
D.T. Gillespie, J. Comput. Phys. 28(3), 395–407 (1978)
S.P. Gross et al., J. Cell Biol. 156(4), 715–724 (2002)
N. Hirokawa et al., Curr. Opin. Cell Biol. 10(1), 60–73 (1998)
A. Kunwar et al., Proc. Nat. Acad. Sci. 108(47), 18960–18965 (2011)
R. Mallik et al., Curr. Biol. 15(23), 2075–2085 (2005)
M.J.I. Müller et al., Proc. Nat. Acad. Sci. 105(12), 4609–4614 (2008)
G. Steinberg et al., J. Microsc. 214(2), 114–123 (2004)
B. Trinczek et al., J. Cell Sci. 112(Pt 14), 2355–2367 (1999)
M.A. Welte, Curr. Biol. 14(13), R525–R537 (2004)
M.A. Welte et al., Cell 92(4), 547–557 (1998)
S. Klein, C. Appert-Rolland, L. Santen, EPL 107(1), 18004 (2004)
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the Deutsche Forschungsgemeinschaft (DFG) within the collaborative research center SFB 1027 and the research training group GRK 1276.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2015 Springer International Publishing Switzerland
About this paper
Cite this paper
Klein, S., Appert-Rolland, C., Santen, L. (2015). Stochastic Modeling of Cargo Transport by Teams of Molecular Motors. In: Chraibi, M., Boltes, M., Schadschneider, A., Seyfried, A. (eds) Traffic and Granular Flow '13. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-10629-8_69
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-10629-8_69
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-319-10628-1
Online ISBN: 978-3-319-10629-8
eBook Packages: Mathematics and StatisticsMathematics and Statistics (R0)