Abstract
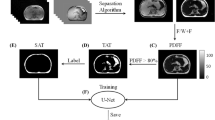
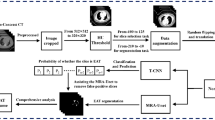
Epicardial adipose tissue (EAT) has been recognized as a risk factor and independent predictor for cardiovascular diseases (CVDs), due to its intimate relationship with the myocardium and coronary arteries. Dixon MRI is widely used to depict adipose tissue by deriving fat and water signals. The purpose of this study was to automatically segment and quantify EAT from Dixon MRI data using a fully automated deep learning pipeline based on fat maps (FM-Net). Data used in this study was from a sub-study (HEALTH) of the Swedish CArdioPulmonarybiolmage Study (SCAPIS), with 6504 Dixon MRI 2D images from 90 participants (45 each for type 2 diabetes and controls). FM-Net was comprised of a double Res-UNet CNN architecture, designed to compensate for the severe class imbalance and complex geometry of EAT. The first network accurately detected the region of interest (ROI) containing fat, and the second network performed targeted regional segmentation of the ROI. Performance of fat segmentation was improved by using fat maps as input of FM-Net, to enhance fat features by combining out-of-phase, water, and fat phase images. Performance was evaluated using dice similarity coefficient (DSC) and 95% Hausdorff distance (HD95). Overall, FM-Net obtained a promising DSC of 86.3%, and a low HD95 of 3.11 mm, outperforming existing state-of-the-art methods. The proposed method enables automatic and accurate quantification of EAT from Dixon MRI data, which could enhance the understanding of the role of EAT in CVDs.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Iacobellis, G., Corradi, D., Sharma, A.M.: Epicardial adipose tissue: anatomic, biomolecular and clinical relationships with the heart. Nat. Rev. Cardiol. 2, 536–543 (2005)
Sacks, H.S., Fain, J.N.: Human epicardial adipose tissue: a review. Am. Heart J. 153, 907–917 (2007)
Patel, K.H.K., Hwang, T., Se Liebers, C., Ng, F.S.: Epicardial adipose tissue as a mediator of cardiac arrhythmias. Am. J. Physiol.-Heart Circulatory Physiol. 322, H129–H144 (2022)
Auer, J.: Fat: an emerging player in the field of atrial fibrillation. Eur. Heart J. 38, 62–65 (2017)
Iacobellis, G.: Epicardial adipose tissue in contemporary cardiology. Nat. Rev. Cardiol. 19, 593–606 (2022)
Karampetsou, N., Alexopoulos, L., Minia, A., Pliaka, V., et al.: Epicardial adipose tissue as an independent cardiometabolic risk factor for coronary artery disease. Cureus (2022)
Konwerski, M., Gąsecka, A., Opolski, G., Grabowski, M., Mazurek, T.: Role of epicardial adipose tissue in cardiovascular diseases: a review. Biology 11, 355 (2022)
Hatem, S.N., Sanders, P.: Epicardial adipose tissue and atrial fibrillation. Cardiovasc. Res. 102, 205–213 (2014)
Bertaso, A.G., Bertol, D., Duncan, B.B., et al.: Epicardial fat: definition, measurements and systematic review of main outcomes. Arquivos Brasileiros de Cardiologia (2013)
Xiong, Z., Fedorov, V.V., Fu, X., et al.: Fully automatic left atrium segmentation from late gadolinium enhanced magnetic resonance imaging using a dual fully convolutional neural network. IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging 38, 515–524 (2019)
Xiong, Z., Xia, Q., Hu, Z., Huang, N.,et al.: A global benchmark of algorithms for segmenting late gadolinium-enhanced cardiac magnetic resonance imaging. 26 (2021)
Commandeur, F., Goeller, M., Betancur, J., et al.: Deep learning for quantification of epicardial and thoracic adipose tissue from non-contrast CT. IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging 37, 1835–1846 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1109/TMI.2018.2804799
Commandeur, F., Goeller, M., Razipour, A., et al.: Fully automated CT quantification of epicardial adipose tissue by deep learning: a multicenter study. Radiol. Artif. Intell. 1, e190045 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1148/ryai.2019190045
Santini, G., Latta, D.D., Vatti, A., et al.: Deep learning for pericardial fat extraction and evaluation on a population study. Radiol. Imaging (2020)
Li, X., Sun, Y., Xu, L., et al.: Automatic quantification of epicardial adipose tissue volume. Med. Phys. 48, 4279–4290 (2021)
Zhang, Q., Zhou, J., Zhang, B., et al.: Automatic epicardial fat segmentation and quantification of CT scans using dual U-Nets with a morphological processing layer. IEEE Access 8, 128032–128041 (2020)
He, X., Guo, B.J., Lei, Y., et al.: Automatic segmentation and quantification of epicardial adipose tissue from coronary computed tomography angiography. Phys. Med. Biol. 65, 095012 (2020)
Daudé, P., Ancel, P., Confort Gouny, S., et al.: Deep-learning segmentation of epicardial adipose tissue using four-chamber cardiac magnetic resonance imaging. Diagnostics 12, 126 (2022)
Bard, A., Raisi-Estabragh, Z., Ardissino, M., et al.: Automated quality-controlled cardiovascular magnetic resonance pericardial fat quantification using a convolutional neural network in the UK biobank. Front. Cardiovasc. Med. 8, 677574 (2021)
Homsi, R., Meier-Schroers, M., Gieseke, J., et al.: 3D-Dixon MRI based volumetry of peri- and epicardial fat. Int. J. Cardiovasc. Imaging 32, 291–299 (2016)
Homsi, R., Sprinkart, A.M., Gieseke, J., et al.: 3D-Dixon cardiac magnetic resonance detects an increased epicardial fat volume in hypertensive men with myocardial infarction. Eur. J. Radiol. 85, 936–942 (2016)
Langner, T., Hedström, A., Mörwald, K., et al.: Fully convolutional networks for automated segmentation of abdominal adipose tissue depots in multicenter water–fat MRI. Magn. Reson. Med. 81, 2736–2745 (2019)
Edin, C., Ekstedt, M., Scheffel, T., et al.: Ectopic fat is associated with cardiac remodeling—a comprehensive assessment of regional fat depots in type 2 diabetes using multi-parametric MRI. Front. Cardiovasc. Med. 9, 813427 (2022)
Milletari, F., Navab, N., Ahmadi, S.-A.: V-Net: fully convolutional neural networks for volumetric medical image segmentation. In: 2016 Fourth International Conference on 3D Vision (3DV), Stanford, CA, USA, pp. 565–571. IEEE (2016)
Henningsson, M., Brundin, M., Scheffel, T., et al.: Quantification of epicardial fat using 3D cine Dixon MRI. BMC Med. Imaging 20, 80 (2020)
Cardoso, M.J., Li, W., Brown, R., et al.: MONAI: an open-source framework for deep learning in healthcare. http://arxiv.org/abs/2211.02701 (2022)
Yang, Z., Farsiu, S.: Directional connectivity-based segmentation of medical images (2023)
Cai, H., Li, S., Qi, L., et al.: Orthogonal annotation benefits barely-supervised medical image segmentation. http://arxiv.org/abs/2303.13090 (2023)
Alom, Z., Taha, T.M., Asari, V.K.: Recurrent residual convolutional neural network based on U-Net (R2U-Net) for medical image segmentation. 12 (2018)
Zhou, Z., Siddiquee, M.M.R., Tajbakhsh, N., Liang, J.: UNet++: a nested U-Net architecture for medical image segmentation. http://arxiv.org/abs/1807.10165 (2018)
Xia, Q., Yao, Y., Hu, Z., Hao, A.: Automatic 3D atrial segmentation from GE-MRIs using volumetric fully convolutional networks. In: Pop, M., Sermesant, M., Zhao, J., Li, S., McLeod, K., Young, A., Rhode, K., Mansi, T. (eds.) STACOM 2018. LNCS, vol. 11395, pp. 211–220. Springer, Cham (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-12029-0_23
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2024 The Author(s), under exclusive license to Springer Nature Switzerland AG
About this paper
Cite this paper
Feng, F. et al. (2024). FM-Net: A Fully Automatic Deep Learning Pipeline for Epicardial Adipose Tissue Segmentation. In: Camara, O., et al. Statistical Atlases and Computational Models of the Heart. Regular and CMRxRecon Challenge Papers. STACOM 2023. Lecture Notes in Computer Science, vol 14507. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-52448-6_9
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-52448-6_9
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-031-52447-9
Online ISBN: 978-3-031-52448-6
eBook Packages: Computer ScienceComputer Science (R0)