Abstract
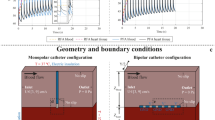
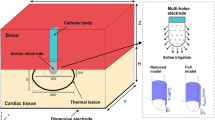
Radiofrequency ablation is a typical treatment for severe cases of cardiac arrhythmias. A catheter, inserted from the patient’s groin, delivers current at frequencies of 450–500 kHz to the arrhythmogenic area, inflicting thermal damage. The electrical current delivered to the tissue depends (among others) on the tip shape and the catheter orientation. A modified Penne’s bioheat equation with an electric source and cooling blood convection is the standard choice for RFA models. The incompressible Navier-Stokes equation describes the interaction of the blood flow and the irrigated saline. The cardiac tissue is a nonlinear orthotropic hyperelastic material and the Hertz-Signorini-Moreau contact boundary conditions model the frictionless interaction of the electrode with the cardiac tissue. In this work, we consider a spherical electrode tip shape and different orientation angles (from perpendicular up to 60\(^{\circ }\) from the vertical position). We perform a virtual ablation for a standard protocol of power 30 W for a duration of 30 s on a simulated porcine cardiac slab. We compare the contact surface of the electrode with the tissue for the different orientations and the characteristics of the generated lesions.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Augustin, C.M., et al.: A computationally efficient physiologically comprehensive 3D–0D closed-loop model of the heart and circulation. Comput. Methods Appl. Mech. Eng. 386, 114092 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cma.2021.114092
Bianchi, L., Bontempi, M., De Simone, S., Franceschet, M., Saccomandi, P.: Temperature dependence of thermal properties of Ex vivo porcine heart and lung in hyperthermia and ablative temperature ranges. Ann. Biomed. Eng. 51(6), 1181–1198 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10439-022-03122-9
Gallagher, N., Fear, E.C., Byrd, I.A., Vigmond, E.J.: Contact geometry affects lesion formation in radio-frequency cardiac catheter ablation. PLoS ONE 8, e73242 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0073242
Guerra, J.M., et al.: Effects of open-irrigated radiofrequency ablation catheter design on lesion formation and complications: in vitro comparison of 6 different devices. J. Cardiovasc. Electrophysiol. 24(10), 1157–1162 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1111/jce.12175
Jaspard, F., Nadi, M.: Dielectric properties of blood: an investigation of temperature dependence. Physiol. Meas. 23(3), 547 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1088/0967-3334/23/3/306
Masnok, K., Watanabe, N.: Catheter contact area strongly correlates with lesion area in radiofrequency cardiac ablation: an ex vivo porcine heart study. J. Interv. Card. Electrophysiol. 63, 561–572 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10840-021-01054-3
O’Neill, D.P., et al.: A three-state mathematical model of hyperthermic cell death. Ann. Biomed. Eng. 39, 570–579 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10439-010-0177-1
Petras, A., Leoni, M., Guerra, J., Jansson, J., Gerardo-Giorda, L.: Effect of tissue elasticity in cardiac radiofrequency catheter ablation models. In: 2018 Computing in Cardiology Conference (CinC), pp. 3–6 (2018). https://doi.org/10.22489/CinC.2018.035
Petras, A., Leoni, M., Guerra, J.M., Gerardo-Giorda, L.: Calibration of a three-state cell death model for cardiomyocytes and its application in radiofrequency ablation. Physiol. Meas. 44(6), 065003 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1088/1361-6579/acdcdd
Petras, A., Leoni, M., Guerra, J.M., Jansson, J., Gerardo-Giorda, L.: A computational model of open-irrigated radiofrequency catheter ablation accounting for mechanical properties of the cardiac tissue. Int. J. Numer. Methods Biomed. Eng. 35, e3232 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1002/cnm.3232
Petras, A., Weidmann, Z.M., Ferrero, M.E., Leoni, M., Guerra, J.M., Gerardo-Giorda, L.: Impact of electrode tip shape on catheter performance in cardiac radiofrequency ablation. Heart Rhythm O2 3(6), 699–705 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.hroo.2022.07.014
Pérez, J.J., D’Angelo, R., González-Suárez, A., Nakagawa, H., Berjano, E., d’Avila, A.: Low-energy (360 J) radiofrequency catheter ablation using moderate power - short duration: proof of concept based on in silico modeling. J. Interv. Card. Electrophysiol. 66, 1085–1093 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10840-022-01292-z
Rosentrater, K.A., Flores, R.A.: Physical and rheological properties of slaughterhouse swine blood and blood components. Trans. ASAE 40(3), 683–689 (1997). https://doi.org/10.13031/2013.21287
Squara, F., et al.: In vitro evaluation of ice-cold saline irrigation during catheter radiofrequency ablation. J. Cardiovasc. Electrophysiol. 25, 1125–1132 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1111/jce.12479
Usyk, T.P., Mazhari, R., McCulloch, A.D.: Effect of laminar orthotropic myofiber architecture on regional stress and strain in the canine left ventricle. J. Elast. 61, 143–164 (2000). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1010883920374
Wen, J., Wan, N., Bao, H., Li, J.: Quantitative measurement and evaluation of red blood cell aggregation in normal blood based on a modified Hanai equation. Sensors 19(5), 1095 (2019). https://doi.org/10.3390/s19051095
Wittkampf, F.H., Nakagawa, H.: RF catheter ablation: lessons on lesions. Pacing Clin. Electrophysiol. 29, 1285–1297 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1540-8159.2006.00533.x
Yastrebov, V.A.: Numerical Methods in Contact Mechanics. Wiley (2013). https://doi.org/10.1002/9781118647974
Acknowledgements
This work has been partially supported by the State of Upper Austria. This research was funded in part by the Austrian Science Fund (FWF) P35374N. For the purpose of Open Access, the author has applied a CC BY public copyright license to any Author Accepted Manuscript (AAM) version arising from this submission.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2024 The Author(s), under exclusive license to Springer Nature Switzerland AG
About this paper
Cite this paper
Leoni, M., Petras, A., Weidmann, Z.M., Guerra, J.M., Gerardo-Giorda, L. (2024). Impact of Catheter Orientation on Cardiac Radiofrequency Ablation. In: Camara, O., et al. Statistical Atlases and Computational Models of the Heart. Regular and CMRxRecon Challenge Papers. STACOM 2023. Lecture Notes in Computer Science, vol 14507. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-52448-6_15
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-52448-6_15
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-031-52447-9
Online ISBN: 978-3-031-52448-6
eBook Packages: Computer ScienceComputer Science (R0)