Abstract
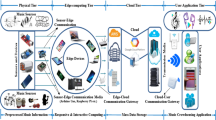
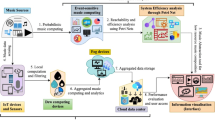
The field of music composition has seen significant advancements with the introduction of artificial intelligence (AI) techniques. However, traditional cloud-based approaches suffer from limitations such as latency and network dependency. This survey paper explores the emerging concept of edge intelligence and its application in music composition. Edge intelligence leverages local computational resources to enable real-time and on-device music generation, enhancing the creative process and expanding accessibility. By examining various aspects of music composition, including melody creation, harmonization, rhythm generation, arrangement and orchestration, and lyric writing, this paper showcases the potential benefits of incorporating edge intelligence. It also discusses the challenges and limitations associated with this paradigm, such as limited computational resources and privacy concerns. Through a review of existing AI-based music composition tools and platforms, examples of edge intelligence in action are highlighted. The survey paper concludes by emphasizing the transformative potential of edge intelligence in revolutionizing the field of music composition and identifies future research opportunities to further advance this promising domain.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Harmonymaster. https://www.harmonymaster.com. Accessed 6 Aug 2023
Lyriccraft. https://www.lyriccrafttool.com. Accessed 6 Aug 2023
Melodai. https://www.melodai.com. Accessed 6 Aug 2023
Orchestratorx. https://www.orchestratorx.com. Accessed 6 Aug 2023
Rhythmgenius. https://www.rhythmgenius.com. Accessed 6 Aug 2023
Barbuto, V., Savaglio, C., Chen, M., Fortino, G.: Disclosing edge intelligence: a systematic meta-survey. Big Data Cogn. Comput. 7(1), 44 (2023)
Bown, O.: Sociocultural and design perspectives on AI-based music production: why do we make music and what changes if AI makes it for us? In: Handbook of Artificial Intelligence for Music: Foundations, Advanced Approaches, and Developments for Creativity, pp. 1–20 (2021)
Chang, A., Kragness, H.E., Livingstone, S.R., Bosnyak, D.J., Trainor, L.J.: Body sway reflects joint emotional expression in music ensemble performance. Sci. Rep. 9(1), 205 (2019)
Chen, H., Xiao, Q., Yin, X.: Generating music algorithm with deep convolutional generative adversarial networks. In: 2019 IEEE 2nd International Conference on Electronics Technology (ICET), pp. 576–580. IEEE (2019)
Chu, H., et al.: An empirical study on how people perceive AI-generated music. In: Proceedings of the 31st ACM International Conference on Information and Knowledge Management, pp. 304–314 (2022)
Civit, M., Civit-Masot, J., Cuadrado, F., Escalona, M.J.: A systematic review of artificial intelligence-based music generation: scope, applications, and future trends. Expert Syst. Appl. 118190 (2022)
Coca, A.E., Corrêa, D.C., Zhao, L.: Computer-aided music composition with LSTM neural network and chaotic inspiration. In: The 2013 International Joint Conference on Neural Networks (IJCNN), pp. 1–7. IEEE (2013)
Cyriac, S., Kim, Y.W., Tavis, R.L., et al.: Application of LSTM model for western music composition. In: 2022 13th International Conference on Information and Communication Technology Convergence (ICTC), pp. 136–141. IEEE (2022)
de Barros, M.P., et al.: The poorly conducted orchestra of steroid hormones, oxidative stress and inflammation in frailty needs a maestro: regular physical exercise. Exp. Gerontol. 155, 111562 (2021)
Ramon Lopez De Mantaras and Josep Lluis Arcos: AI and music: from composition to expressive performance. AI Mag. 23(3), 43–43 (2002)
Déguernel, K., Giraud, M., Groult, R., Gulluni, S.: Personalizing AI for co-creative music composition from melody to structure. In: Sound and Music Computing (SMC 2022), pp. 314–321 (2022)
Deruty, E., Grachten, M., Lattner, S., Nistal, J., Aouameur, C.: On the development and practice of AI technology for contemporary popular music production. Trans. Int. Soc. Music Inf. Retrieval 5(1) (2022)
Dervakos, E., Filandrianos, G., Stamou, G.: Heuristics for evaluation of AI generated music. In: 2020 25th International Conference on Pattern Recognition (ICPR), pp. 9164–9171. IEEE (2021)
Fernández, J.D., Vico, F.: AI methods in algorithmic composition: a comprehensive survey. J. Artif. Intell. Res. 48, 513–582 (2013)
Gioti, A.-M.: From artificial to extended intelligence in music composition. Organ. Sound 25(1), 25–32 (2020)
Hernandez-Olivan, C., Beltran, J.R.: Music composition with deep learning: a review. In: Biswas, A., Wennekes, E., Wieczorkowska, A., Laskar, R.H. (eds.) Advances in Speech and Music Technology. Signals and Communication Technology, pp. 25–50. Springer, Cham (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-18444-4_2
Hong, J.-W., Fischer, K., Ha, Y., Zeng, Y.: Human, I wrote a song for you: an experiment testing the influence of machines’ attributes on the AI-composed music evaluation. Comput. Hum. Behav. 131, 107239 (2022)
Jeong, B., Baek, S., Park, S., Jeon, J., Jeong, Y.-S.: Stable and efficient resource management using deep neural network on cloud computing. Neurocomputing 521, 99–112 (2023)
Jin, J., Yu, K., Kua, J., Zhang, N., Pang, Z., Han, Q.-L.: Cloud-fog automation: vision, enabling technologies, and future research directions. IEEE Trans. Ind. Inform. (2023)
Johansson, E., Lindgren, J.: The Gunnlod dataset: engineering a dataset for multi-modal music generation (2023)
Johns, A.M.: Ll composition theories: implications for developing theories of l2 composition. The Pitt Building, Trumpington Street, Cambridge CB2 1 RP, p. 25 (1991)
Kumar, N.H., Ashwin, P.S., Ananthakrishnan, H.: Mellisai-an AI generated music composer using RNN-LSTMs. Int. J. Mach. Learn. Comput. 10(2), 247–252 (2020)
Leemhuis, A., Waloschek, S., Hadjakos, A.: Bacher than Bach? On musicologically informed AI-based Bach chorale harmonization. In: Cellier, P., Driessens, K. (eds.) ECML PKDD 2019. CCIS, vol. 1168, pp. 462–469. Springer, Cham (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-43887-6_39
Liang, M.: An improved music composing technique based on neural network model. Mob. Inf. Syst. 2022 (2022)
Lin, Y., Gao, Z., Du, H., Niyato, D., Kang, J., Deng, R., Shen, X.S.: A unified blockchain-semantic framework for wireless edge intelligence enabled web 3.0. IEEE Wirel. Commun. (2023)
Louie, R., Engel, J., Huang, C.-Z.A.: Expressive communication: evaluating developments in generative models and steering interfaces for music creation. In: 27th International Conference on Intelligent User Interfaces, pp. 405–417 (2022)
Ma, X., Wang, Y., Kan, M.-Y., Lee, W.S.: AI-lyricist: generating music and vocabulary constrained lyrics. In: Proceedings of the 29th ACM International Conference on Multimedia, pp. 1002–1011 (2021)
Mao, B., Liu, J., Wu, Y., Kato, N.: Security and privacy on 6g network edge: a survey. IEEE Commun. Surv. Tutor. (2023)
McCormack, J., Hutchings, P., Gifford, T., Yee-King, M., Llano, M.T., D’inverno, M.: Design considerations for real-time collaboration with creative artificial intelligence. Organised Sound 25(1), 41–52 (2020)
Miranda, E.R., Yeung, R., Pearson, A., Meichanetzidis, K., Coecke, B.: A quantum natural language processing approach to musical intelligence. In: Miranda, E.R. (ed.) Quant. Comput. Music, pp. 313–356. Springer, Cham (2022)
Moruzzi, C.: Creative AI: music composition programs as an extension of the composer’s mind. In: Müller, V.C. (ed.) PT-AI 2017. SAPERE, vol. 44, pp. 69–72. Springer, Cham (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-96448-5_8
Pons, L., et al.: Cloud white: detecting and estimating QoS degradation of latency-critical workloads in the public cloud. Future Gener. Comput. Syst. 138, 13–25 (2023)
Qiu, Z., et al.: Mind band: a crossmedia AI music composing platform. In: Proceedings of the 27th ACM International Conference on Multimedia, pp. 2231–2233 (2019)
Youyang, Q., Shui, Yu., Zhou, W., Peng, S., Wang, G., Xiao, K.: Privacy of things: emerging challenges and opportunities in wireless internet of things. IEEE Wirel. Commun. 25(6), 91–97 (2018)
Sepahvand, M., Abdali-Mohammadi, F., Taherkordi, A.: An adaptive teacher-student learning algorithm with decomposed knowledge distillation for on-edge intelligence. Eng. Appl. Artif. Intell. 117, 105560 (2023)
Serra-Peralta, M., Serrà, J., Corral, Á.: Heaps’ law and vocabulary richness in the history of classical music harmony. EPJ Data Sci. 10(1), 40 (2021)
Singh, R., Gill, S.S.: Edge AI: a survey. Internet of Things and Cyber-Physical Systems (2023)
Siphocly, N.N.J., El-Horbaty, E.-S.M., Salem, A.-B.M.: Top 10 artificial intelligence algorithms in computer music composition. Int. J. Comput. Digit. Syst. 10(01), 373–394 (2021)
Sturm, B.L., et al.: Machine learning research that matters for music creation: a case study. J. New Music Res. 48(1), 36–55 (2019)
Vellela, S.S., Venkateswara Reddy, B., Chaitanya, K.K., Venkateswara Rao, M.: An integrated approach to improve e-healthcare system using dynamic cloud computing platform. In: 2023 5th International Conference on Smart Systems and Inventive Technology (ICSSIT), pp. 776–782. IEEE (2023)
Wang, J., Chng, E., Changsheng, X., Hanqinq, L., Tian, Q.: Generation of personalized music sports video using multimodal cues. IEEE Trans. Multimedia 9(3), 576–588 (2007)
Wang, K., Gou, C., Duan, Y., Lin, Y., Zheng, X., Wang, F.-Y.: Generative adversarial networks: introduction and outlook. IEEE/CAA J. Automatica Sinica 4(4), 588–598 (2017)
Wang, S., Zheng, Y., Jia, X.: SecGNN: privacy-preserving graph neural network training and inference as a cloud service. IEEE Trans. Serv. Comput. (2023)
Xu, M., et al.: Sparks of GPTs in edge intelligence for metaverse: caching and inference for mobile AIGC services. arXiv preprint arXiv:2304.08782 (2023)
Yang, R., Feng, L., Wang, H., Yao, J., Luo, S.: Parallel recurrent convolutional neural networks-based music genre classification method for mobile devices. IEEE Access 8, 19629–19637 (2020)
Yang, T., Nazir, S.: A comprehensive overview of AI-enabled music classification and its influence in games. Soft. Comput. 26(16), 7679–7693 (2022)
Yu, Y., Srivastava, A., Canales, S.: Conditional LSTM-GAN for melody generation from lyrics. ACM Trans. Multimedia Comput. Commun. Appl. (TOMM) 17(1), 1–20 (2021)
Zhang, C., et al.: Relyme: improving lyric-to-melody generation by incorporating lyric-melody relationships. In: Proceedings of the 30th ACM International Conference on Multimedia, pp. 1047–1056 (2022)
Zhang, J., Letaief, K.B.: Mobile edge intelligence and computing for the internet of vehicles. Proc. IEEE 108(2), 246–261 (2019)
Zhang, K., Zhu, Y., Maharjan, S., Zhang, Y.: Edge intelligence and blockchain empowered 5g beyond for the industrial internet of things. IEEE Netw. 33(5), 12–19 (2019)
Zhang, Y., Huang, H., Yang, L.-X., Xiang, Y., Li, M.: Serious challenges and potential solutions for the industrial internet of things with edge intelligence. IEEE Netw. 33(5), 41–45 (2019)
Zulić, H., et al.: How AI can change/improve/influence music composition, performance and education: three case studies. INSAM J. Contemp. Music Art Technol. 1(2), 100–114 (2019)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2024 ICST Institute for Computer Sciences, Social Informatics and Telecommunications Engineering
About this paper
Cite this paper
Wang, Q., Qu, Y., Nan, S., Jiang, W., Gu, B., Gu, S. (2024). A Survey on Edge Intelligence for Music Composition: Principles, Applications, and Privacy Implications. In: Liu, J., Xu, L., Huang, X. (eds) Tools for Design, Implementation and Verification of Emerging Information Technologies. TridentCom 2023. Lecture Notes of the Institute for Computer Sciences, Social Informatics and Telecommunications Engineering, vol 523. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-51399-2_3
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-51399-2_3
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-031-51398-5
Online ISBN: 978-3-031-51399-2
eBook Packages: Computer ScienceComputer Science (R0)