Abstract
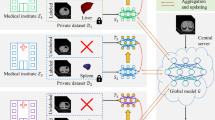
Developing a generalized segmentation model capable of simultaneously delineating multiple organs and diseases is highly desirable. Federated learning (FL) is a key technology enabling the collaborative development of a model without exchanging training data. However, the limited access to fully annotated training data poses a major challenge to training generalizable models. We propose “ConDistFL”, a framework to solve this problem by combining FL with knowledge distillation. Local models can extract the knowledge of unlabeled organs and tumors from partially annotated data from the global model with an adequately designed conditional probability representation. We validate our framework on four distinct partially annotated abdominal CT datasets from the MSD and KiTS19 challenges. The experimental results show that the proposed framework significantly outperforms FedAvg and FedOpt baselines. Moreover, the performance on an external test dataset demonstrates superior generalizability compared to models trained on each dataset separately. Our ablation study suggests that ConDistFL can perform well without frequent aggregation, reducing the communication cost of FL. Our implementation will be available at https://github.com/NVIDIA/NVFlare/tree/main/research/condist-fl.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Altini, N., et al.: Liver, kidney and spleen segmentation from CT scans and MRI with deep learning: a survey. Neurocomputing 490, 30–53 (2022)
Asad, M., Moustafa, A., Ito, T.: FedOpt: towards communication efficiency and privacy preservation in federated learning. Appl. Sci. 10(8), 2864 (2020)
Cardoso, M.J., et al.: MONAI: an open-source framework for deep learning in healthcare. arXiv preprint arXiv:2211.02701 (2022)
Cerrolaza, J.J., et al.: Computational anatomy for multi-organ analysis in medical imaging: a review. Med. Image Anal.56, 44–67 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.media.2019.04.002, https://linkinghub.elsevier.com/retrieve/pii/S1361841518306273
Fang, X., Yan, P.: Multi-organ segmentation over partially labeled datasets with multi-scale feature abstraction. IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging 39(11), 3619–3629 (2020)
Fu, Y., Lei, Y., Wang, T., Curran, W.J., Liu, T., Yang, X.: A review of deep learning based methods for medical image multi-organ segmentation. Physica Med. 85, 107–122 (2021)
Gul, S., Khan, M.S., Bibi, A., Khandakar, A., Ayari, M.A., Chowdhury, M.E.: Deep learning techniques for liver and liver tumor segmentation: a review. Comput. Biol. Med. 157, 105620 (2022)
Heller, N., et al.: The KiTs19 challenge data: 300 kidney tumor cases with clinical context, CT semantic segmentations, and surgical outcomes. https://doi.org/10.48550/ARXIV.1904.00445, https://arxiv.org/abs/1904.00445 (2019)
Hinton, G., Vinyals, O., Dean, J.: Distilling the knowledge in a neural network (2015)
Hongdong, M., et al.: Multi-scale organs image segmentation method improved by squeeze-and-attention based on partially supervised learning. Int. J. Comput. Assist. Radiol. Surg. 17(6), 1135–1142 (2022)
Huang, R., Zheng, Y., Hu, Z., Zhang, S., Li, H.: Multi-organ segmentation via co-training weight-averaged models from few-organ datasets. In: Martel, A.L., et al. (eds.) MICCAI 2020. LNCS, vol. 12264, pp. 146–155. Springer, Cham (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-59719-1_15
Isensee, F., Jaeger, P.F., Kohl, S.A.A., Petersen, J., Maier-Hein, K.H.: nnU-Net: a self-configuring method for deep learning-based biomedical image segmentation. Nat. Methods 18(2), 203–211 (2021)
Ji, Y., et al.: AMOS: a large-scale abdominal multi-organ benchmark for versatile medical image segmentation. arXiv preprint arXiv:2206.08023 (2022)
Li, T., Sahu, A.K., Zaheer, M., Sanjabi, M., Talwalkar, A., Smith, V.: Federated optimization in heterogeneous networks. Proc. Mach. learn. Syst. 2, 429–450 (2020)
Liu, P., Sun, M., Zhou, S.K.: Multi-site organ segmentation with federated partial supervision and site adaptation (2023). http://arxiv.org/abs/2302.03911
McMahan, H.B., Moore, E., Ramage, D., Hampson, S., y Arcas, B.A.: Communication-efficient learning of deep networks from decentralized data. In: AISTATS (2017)
Milletari, F., Navab, N., Ahmadi, S.A.: V-Net: fully convolutional neural networks for volumetric medical image segmentation. In: 2016 Fourth International Conference on 3d Vision (3DV), pp. 565–571. IEEE (2016)
Roth, H.R., et al.: NVIDIA FLARE: Federated learning from simulation to Real-World. (2022)
Sheller, M.J., et al.: Federated learning in medicine: facilitating multi-institutional collaborations without sharing patient data. Sci. Rep. 10(1), 1–12 (2020)
Shen, C., et al.: Joint multi organ and tumor segmentation from partial labels using federated learning. In: Albarqouni, S., et al. Distributed, Collaborative, and Federated Learning, and Affordable AI and Healthcare for Resource Diverse Global Health, pp. 58–67. Springer Nature, Switzerland (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-18523-6_6
Shi, G., Xiao, L., Chen, Y., Kevin Zhou, S.: Marginal loss and exclusion loss for partially supervised multi-organ segmentation (2020)
Simpson, A.L., et al.: A large annotated medical image dataset for the development and evaluation of segmentation algorithms. CoRR abs/1902.09063. http://arxiv.org/abs/1902.09063 (2019)
Tajbakhsh, N., Jeyaseelan, L., Li, Q., Chiang, J.N., Wu, Z., Ding, X.: Embracing imperfect datasets: a review of deep learning solutions for medical image segmentation. Med. Image Anal. 63, 101693 (2020)
Tajbakhsh, N., Roth, H., Terzopoulos, D., Liang, J.: Guest editorial annotation-efficient deep learning: the holy grail of medical imaging. IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging 40(10), 2526–2533 (2021)
Xu, J., Glicksberg, B.S., Su, C., Walker, P., Bian, J., Wang, F.: Federated learning for healthcare informatics. J. Healthc. Inf. Res. 5, 1–19 (2021)
Xu, X., Yan, P.: Federated multi-organ segmentation with partially labeled data. arXiv preprint arXiv:2206.07156 (2022)
Yang, Q., Liu, Y., Chen, T., Tong, Y.: Federated machine learning: concept and applications. ACM Trans. Intell. Syst. Technol. (TIST) 10(2), 1–19 (2019)
Yi-de, M., Qing, L., Zhi-Bai, Q.: Automated image segmentation using improved PCNN model based on cross-entropy. In: Proceedings of 2004 International Symposium on Intelligent Multimedia, Video and Speech Processing, 2004, pp. 743–746. IEEE (2004)
Zhang, J., Xie, Y., Xia, Y., Shen, C.: DoDNet: learning to segment multi-organ and tumors from multiple partially labeled datasets. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), pp. 1195–1204 (2021)
Zhao, Y., Li, M., Lai, L., Suda, N., Civin, D., Chandra, V.: Federated learning with Non-IID data. arXiv preprint arXiv:1806.00582 (2018)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2023 The Author(s), under exclusive license to Springer Nature Switzerland AG
About this paper
Cite this paper
Wang, P. et al. (2023). ConDistFL: Conditional Distillation for Federated Learning from Partially Annotated Data. In: Celebi, M.E., et al. Medical Image Computing and Computer Assisted Intervention – MICCAI 2023 Workshops . MICCAI 2023. Lecture Notes in Computer Science, vol 14393. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-47401-9_30
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-47401-9_30
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-031-47400-2
Online ISBN: 978-3-031-47401-9
eBook Packages: Computer ScienceComputer Science (R0)