Abstract
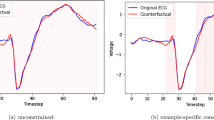
Since neural networks play an increasingly important role in critical sectors, explaining network predictions has become a key research topic. Counterfactual explanations can help to understand why classifier models decide for particular class assignments and, moreover, how the respective input samples would have to be modified such that the class prediction changes. Previous approaches mainly focus on image and tabular data. In this work we propose SPARCE, a generative adversarial network (GAN) architecture that generates SPARse Counterfactual Explanations for multivariate time series. Our approach provides a custom sparsity layer and regularizes the counterfactual loss function in terms of similarity, sparsity, and smoothness of trajectories. We evaluate our approach on real-world human motion datasets as well as a synthetic time series interpretability benchmark. Although we make significantly sparser modifications than other approaches, we achieve comparable or better performance on all metrics. Moreover, we demonstrate that our approach predominantly modifies salient time steps and features, leaving non-salient inputs untouched.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ates, E., Aksar, B., Leung, V.J., Coskun, A.K.: Counterfactual explanations for multivariate time series. In: 2021 International Conference on Applied Artificial Intelligence (ICAPAI), pp. 1–8. IEEE (2021)
Dandl, S., Molnar, C., Binder, M., Bischl, B.: Multi-objective counterfactual explanations. In: Bäck, T., Preuss, M., Deutz, A., Wang, H., Doerr, C., Emmerich, M., Trautmann, H. (eds.) PPSN 2020. LNCS, vol. 12269, pp. 448–469. Springer, Cham (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-58112-1_31
Delaney, E., Greene, D., Keane, M.T.: Instance-based counterfactual explanations for time series classification. In: Sánchez-Ruiz, A.A., Floyd, M.W. (eds.) ICCBR 2021. LNCS (LNAI), vol. 12877, pp. 32–47. Springer, Cham (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-86957-1_3
Goodfellow, I., et al.: Generative adversarial nets. In: Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems, vol. 27 (2014)
Gumbsch, C., Butz, M.V., Martius, G.: Sparsely changing latent states for prediction and planning in partially observable domains. In: Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems, vol. 34 (2021)
Hochreiter, S., Schmidhuber, J.: Long short-term memory. Neural Comput. 9(8), 1735–1780 (1997)
Ismail, A.A., Gunady, M., Corrada Bravo, H., Feizi, S.: Benchmarking deep learning interpretability in time series predictions. Adv. Neural. Inf. Process. Syst. 33, 6441–6452 (2020)
Karimi, A.H., Schölkopf, B., Valera, I.: Algorithmic recourse: from counterfactual explanations to interventions. In: Proceedings of the 2021 ACM Conference on Fairness, Accountability, and Transparency, pp. 353–362 (2021)
Keane, M.T., Smyth, B.: Good counterfactuals and where to find them: a case-based technique for generating counterfactuals for explainable AI (XAI). In: Watson, I., Weber, R. (eds.) ICCBR 2020. LNCS (LNAI), vol. 12311, pp. 163–178. Springer, Cham (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-58342-2_11
Kingma, D.P., Ba, J.: Adam: a method for stochastic optimization. In: International Conference on Learning Representations (2015)
Lang, J., Giese, M.A., Synofzik, M., Ilg, W., Otte, S.: Early recognition of ball catching success in clinical trials with RNN-based predictive classification. In: Farkaš, I., Masulli, P., Otte, S., Wermter, S. (eds.) ICANN 2021. LNCS, vol. 12894, pp. 444–456. Springer, Cham (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-86380-7_36
Van der Maaten, L., Hinton, G.: Visualizing data using t-SNE. J. Mach. Learn. Res. 9(11), 1–27 (2008)
Malekzadeh, M., Clegg, R.G., Cavallaro, A., Haddadi, H.: Mobile sensor data anonymization. In: Proceedings of the International Conference on Internet of Things Design and Implementation, pp. 49–58. IoTDI 2019, ACM, New York, NY, USA (2019)
Mothilal, R.K., Sharma, A., Tan, C.: Explaining machine learning classifiers through diverse counterfactual explanations. In: Proceedings of the 2020 Conference on Fairness, Accountability, and Transparency, pp. 607–617 (2020)
Nair, V., Hinton, G.E.: Rectified linear units improve restricted Boltzmann machines. In: ICML (2010)
Nemirovsky, D., Thiebaut, N., Xu, Y., Gupta, A.: CounterGAN: generating realistic counterfactuals with residual generative adversarial nets. arXiv preprint arXiv:2009.05199 (2020)
Van Looveren, A., Klaise, J., Vacanti, G., Cobb, O.: Conditional generative models for counterfactual explanations. arXiv preprint arXiv:2101.10123 (2021)
Wachter, S., Mittelstadt, B., Russell, C.: Counterfactual explanations without opening the black box: automated decisions and the GDPR. Harv. JL & Tech. 31, 841 (2017)
Yoon, J., Jarrett, D., Van der Schaar, M.: Time-series generative adversarial networks. In: Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems, vol. 32 (2019)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2023 The Author(s), under exclusive license to Springer Nature Switzerland AG
About this paper
Cite this paper
Lang, J., Giese, M.A., Ilg, W., Otte, S. (2023). Generating Sparse Counterfactual Explanations for Multivariate Time Series. In: Iliadis, L., Papaleonidas, A., Angelov, P., Jayne, C. (eds) Artificial Neural Networks and Machine Learning – ICANN 2023. ICANN 2023. Lecture Notes in Computer Science, vol 14259. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-44223-0_15
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-44223-0_15
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-031-44222-3
Online ISBN: 978-3-031-44223-0
eBook Packages: Computer ScienceComputer Science (R0)